Korean J Neurotrauma.
2014 Oct;10(2):155-158. 10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.155.
Lumbar Nerve Root Compression due to Leakage of Bone Cement after Vertebroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. kdsyjyw@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2256260
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.155
Abstract
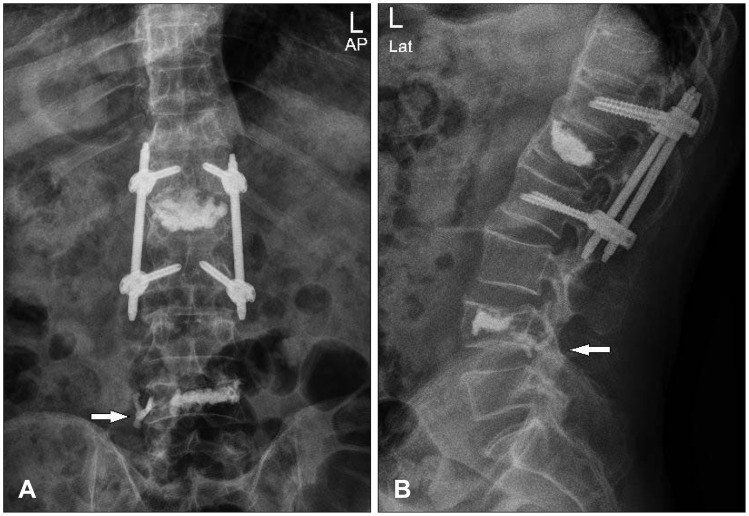
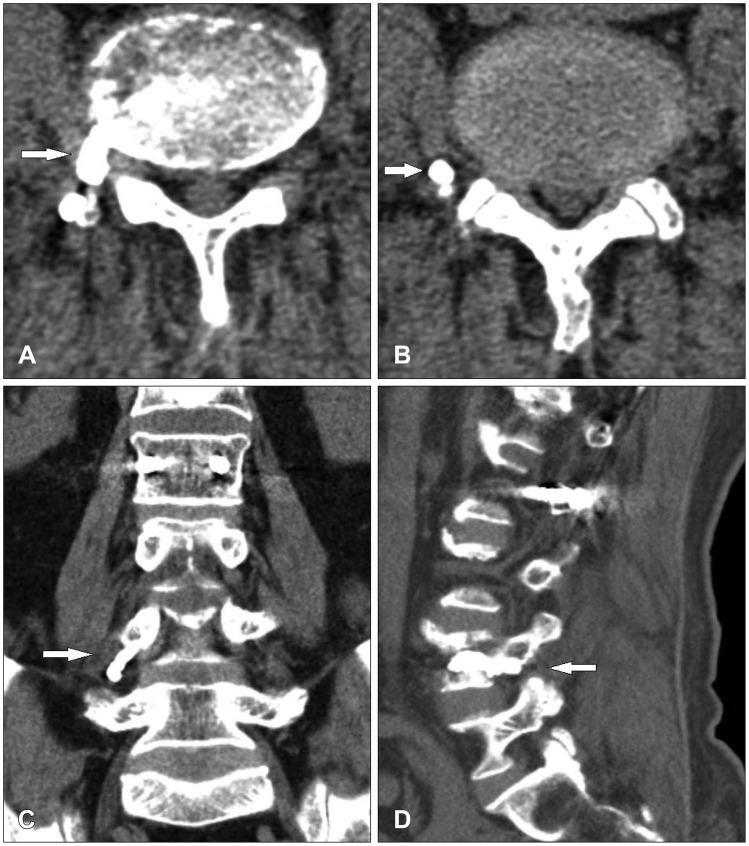
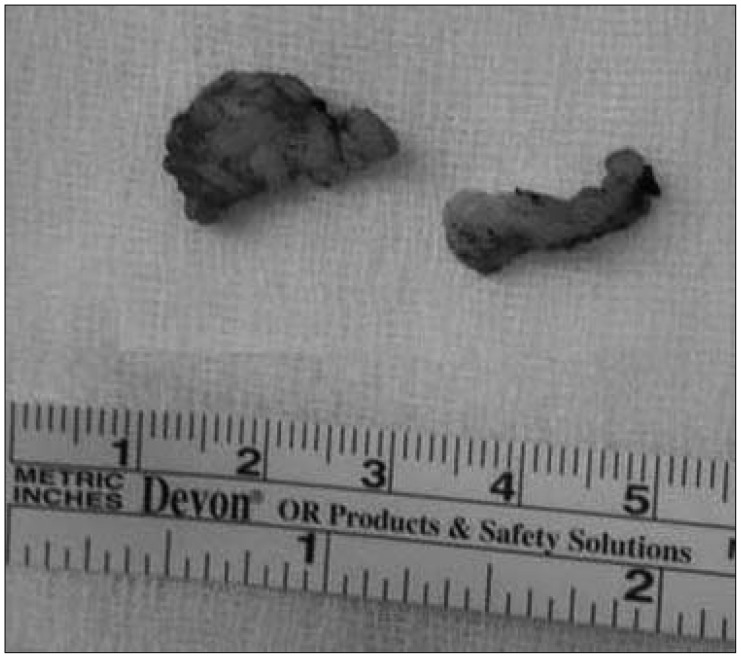
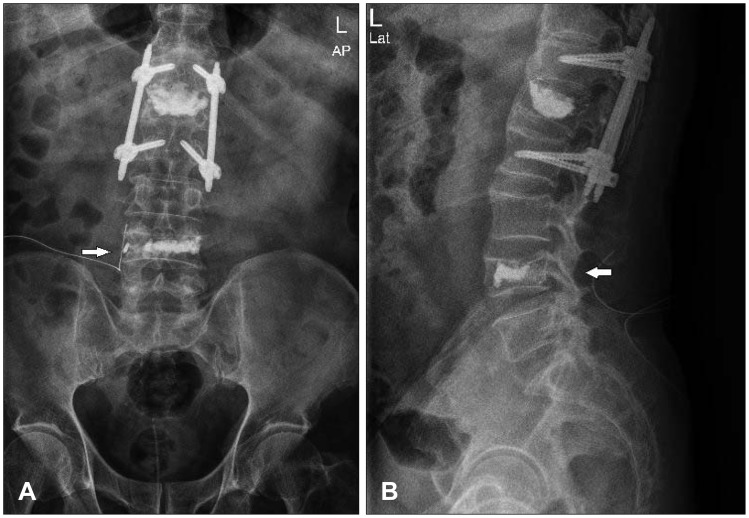
- We experienced a 73-year-old male with lumbar nerve root compression due to leakage of bone cement after vertebroplasty. He was underwent vertebroplasty for acute osteoporotic L4 compression fracture at our hospital. After vertebroplasty, his back pain was improved but right leg pain was newly developed. Lumbar computed tomography scanning showed that bone cements were leaked along the L4 nerve root. The leaked cements around L4 nerve root were removed carefully via paraspinal muscle-splitting approach. After operation, severe right leg radiating pain was improved. We recommend proper entry point, high viscosity of polymethylmethacrylate and constant monitoring can reduce complication.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chen JK, Lee HM, Shih JT, Hung ST. Combined extraforaminal and intradiscal cement leakage following percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:E358–E362. PMID: 17515810.
Article2. Cho CH, Park JT, Yun JK, Moon SK. Comparative analysis between male and female osteoporotic compression fractures in elderly patients. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2013; 9:131–134.
Article3. Cotten A, Dewatre F, Cortet B, Assaker R, Leblond D, Duquesnoy B, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical follow-up. Radiology. 1996; 200:525–530. PMID: 8685351.
Article4. Diamond TH, Champion B, Clark WA. Management of acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a nonrandomized trial comparing percutaneous vertebroplasty with conservative therapy. Am J Med. 2003; 114:257–265. PMID: 12681451.
Article5. Hadjipavlou AG, Tzermiadianos MN, Katonis PG, Szpalski M. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures and osteolytic tumours. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:1595–1604. PMID: 16326869.
Article6. Harrington KD. Major neurological complications following percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83-A:1070–1073. PMID: 11451978.7. Lee BJ, Lee SR, Yoo TY. Paraplegia as a complication of percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:E419–E422. PMID: 12394938.8. Lin EP, Ekholm S, Hiwatashi A, Westesson PL. Vertebroplasty: cement leakage into the disc increases the risk of new fracture of adjacent vertebral body. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:175–180. PMID: 14970015.9. Nieuwenhuijse MJ, Van Erkel AR, Dijkstra PD. Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: identification of risk factors. Spine J. 2011; 11:839–848. PMID: 21889417.
Article10. Park SY, Kim YC. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. In : Kim DH, Vaccaro AR, Dickman CA, Cho D, Lee S, Kim I, editors. Surgical anatomy and techniques to the spine. ed 2. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Inc.;2013. p. 697.11. Park SY, Modi HN, Suh SW, Hong JY, Noh W, Yang JH. Epidural cement leakage through pedicle violation after balloon kyphoplasty causing paraparesis in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures - a report of two cases. J Orthop Surg Res. 2010; 5:54. PMID: 20691094.
Article12. Tsai TT, Chen WJ, Lai PL, Chen LH, Niu CC, Fu TS, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate cement dislodgment following percutaneous vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:E457–E460. PMID: 14624094.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lumbar Root Injury by the Leakage of Bone Cement after the Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A case report
- Neurologic Complication after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty with Polymethylmethacrylate: A Case Report
- Prediction of Bone Cement Leakage in Patients Receiving Vertebroplasty by MRI Finding
- Fatal Hemothorax Following Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A Case Report
- Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture