Korean J Hematol.
2008 Jun;43(2):118-121. 10.5045/kjh.2008.43.2.118.
Identification of a Hemizygous R170H Mutation in the ALAS2 Gene in a Young Male Patient with X-linked Sideroblastic Anemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sunnyhk@skku.edu
- 2Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2252205
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2008.43.2.118
Abstract
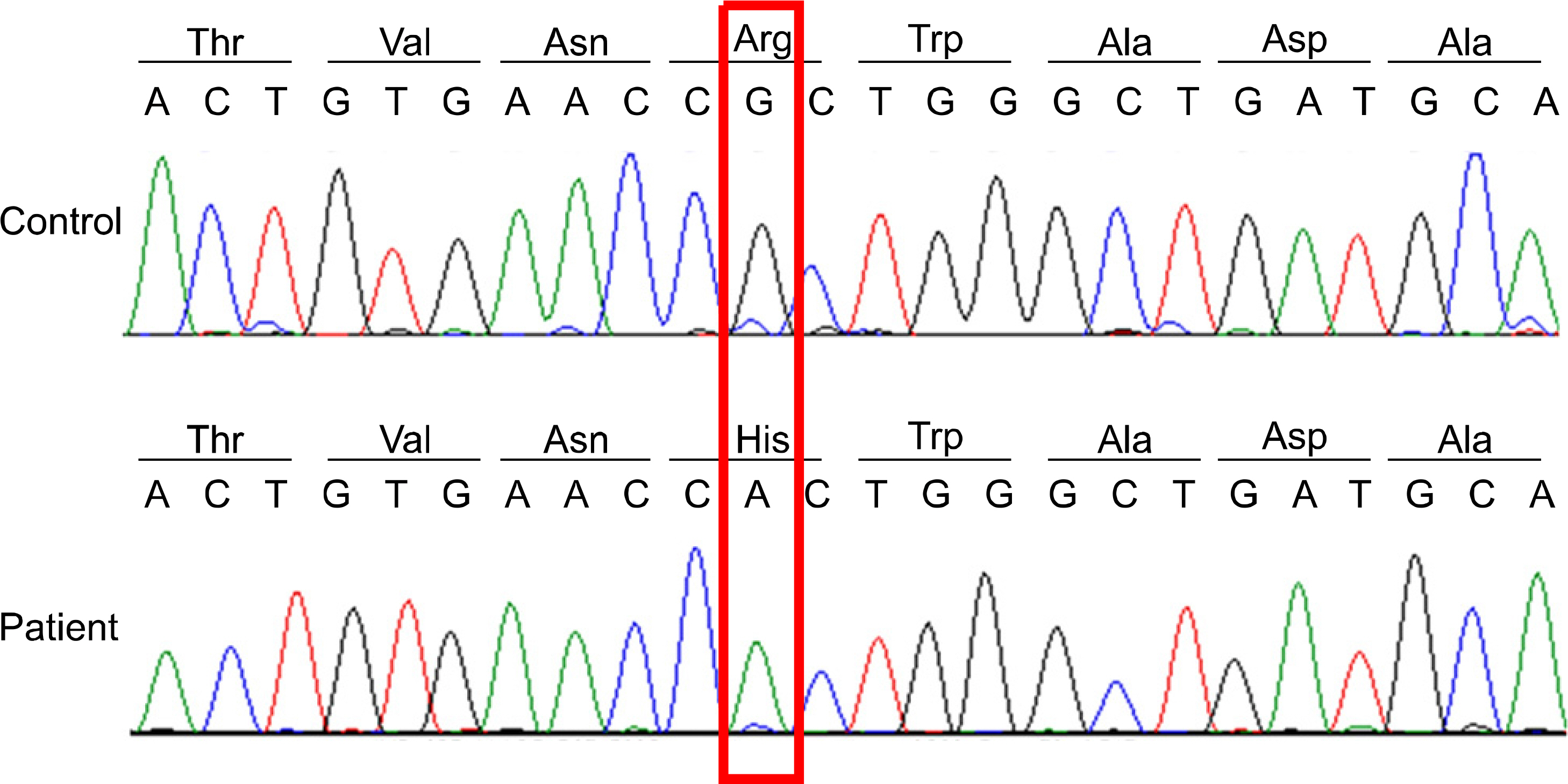
- X-linked sideroblastic anemia (XLSA) is a rare hereditary disease characterized by microcytic hypochromic anemia, ineffective erythropoiesis and the presence of numerous ringed sideroblasts in the bone marrow. The causative gene is the erythroid delta-aminolaevulinate synthase 2 gene (ALAS2) on Xp11.21. We report here a case of XLSA. The patient was a 20-year-old Korean man referred to our hospital under the impression of sideroblastic anemia (SA). Laboratory findings, including a peripheral blood smearand bone marrow study, were compatible with SA. The family history was not remarkable. Based on the early age of onset, we suspected a hereditary form of SA, particularly XLSA. Direct DNA sequencing of ALAS2 detected a hemizygous c.509G>A (R170H) mutation in exon 5 of the gene. The patient showed minimal response to pyridoxine treatment. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of genetically confirmed XLSA from a mutation in ALAS2 in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Bottomley SS. Sideroblastic anaemia. Clin Haematol. 1982. 11:389–409.
Article2). Alcindor T., Bridges KR. Sideroblastic anaemias. Br J Haematol. 2002. 116:733–43.
Article3). Cooley TB. A severe type of hereditary anemia with elliptocytosis. Interesting sequence of splenectomy. Am J Med Sci. 1945. 209:561.4). Cotter PD., Baumann M., Bishop DF. Enzymatic de-fect in "X-linked" sideroblastic anemia: molecular evidence for erythroid delta-aminolevulinate synthase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. 89:4028–32.
Article5). Fleming MD. The genetics of inherited sideroblastic anemias. Semin Hematol. 2002. 39:270–81.
Article6). Jang JH., Kang MC., Sohn CH., Park SJ. A case of hereditary sideroblastic anemia. Korean J Hematol. 1984. 19:285–9.
Article7). Kim HS., Han KJ., Hur MK, et al. Two cases of sideroblastic anemias including one case of hereditary sideroblastic anemia. Korean J Clin Path. 1986. 6:139–42.8). Jun KR., Sohn YH., Park CJ., Jang SS., Chi HS., Seo JJ. A case of hereditary sideroblastic anemia. Korean J Hematol. 2005. 40:49–53.
Article9). Cotter PD., Rucknagel DL., Bishop DF. X-linked sideroblastic anemia: identification of the mutation in the erythroid-specific delta-aminolevulinate synthase gene (ALAS2) in the original family described by Cooley. Blood. 1994. 84:3915–24.
Article10). May A., Bishop DF. The molecular biology and pyridoxine responsiveness of X-linked sideroblastic anaemia. Haematologica. 1998. 83:56–70.11). Shoolingin-Jordan PM., Al-Daihan S., Alexeev D, et al. 5-Aminolevulinic acid synthase: mechanism, mutations and medicine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. 1647:361–6.
Article12). Bottomley SS. Sideroblastic anemias. Greer JP, Foerster J, Lukens JN, Rodgers GM, Paraskevas F, Glader B, editors. Wintrobe's clinical hematology. 11th ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2004. p. 1011–33.13). Urban C., Binder B., Hauer C., Lanzer G. Congenital sideroblastic anemia successfully treated by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1992. 10:373–5.14). González MI., Caballero D., Vázquez L, et al. Allogeneic peripheral stem cell transplantation in a case of hereditary sideroblastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2000. 109:658–60.
Article15). Bottomley SS., Wise PD., Cox TC. X-linked sideroblastic anemia due to mutation of erythroid 5-aminolevulinate synthase manifested in females. Blood. 1996. 88:144a (suppl 1, abstr).16). Cazzola M., May A., Bergamaschi G., Cerani P., Rosti V., Bishop DF. Familial-skewed X-chromosome inactivation as a predisposing factor for late-onset X-linked sideroblastic anemia in carrier females. Blood. 2000. 96:4363–5.
Article17). Cotter PD., May A., Fitzsimons EJ, et al. Late-onset X-linked sideroblastic anemia. Missense mutations in the erythroid delta-aminolevulinate synthase (ALAS2) gene in two pyridoxine-responsive patients initially diagnosed with acquired refractory anemia and ringed sideroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1995. 96:2090–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Novel Hemizygous I418S Mutation in the ALAS2 Gene in a Young Korean Man with X-Linked Sideroblastic Anemia
- Pyridoxine responsive sideroblastic anemia in a boy with mitral valve prolapse
- A case of sideroblastic anemia caused by lead-containing herbal medication
- Pyridoxine Refractory Sideroblastic Anemia: Diagnosis and Misdiagnosis
- The prenatal care and delivery in a pregnant woman complicated by hereditary sideroblastic anemia