Korean J Hematol.
2010 Sep;45(3):197-204. 10.5045/kjh.2010.45.3.197.
Long-term outcomes of a 5-year follow up of patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura after splenectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hematology-Oncology, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. lj2lj2@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2252064
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2010.45.3.197
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The long-term outcomes of adult patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) after splenectomy are not clear.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 31 patients who underwent splenectomy after diagnosis of ITP at our institution between 1990 and 2009. Long-term follow-up was defined as a follow-up that lasted 1 year or more from splenectomy to the last follow-up.
RESULTS
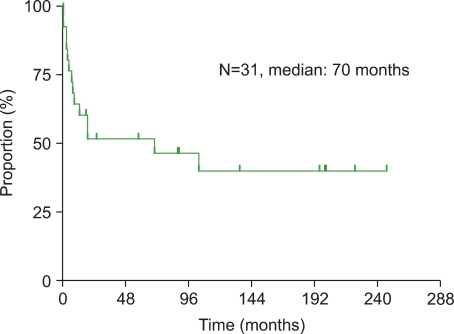
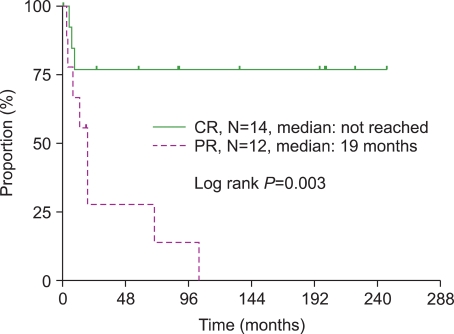
The overall response rate to splenectomy was 84%. However, the response rate at 6 and 12 months decreased to 77% and 68%, respectively. During the 6 years of median follow-up after splenectomy, 11 patients (35%) relapsed. The long-term response rate was 55%. The long-term follow-up of 26 patients after responding to splenectomy showed that the median time from splenectomy to relapse was 19 months in the partial response (PR) group; however, there was no relapse after 9 months in the complete response (CR) group. Variables, including age, were not predictive of the long-term response after splenectomy. Additional treatment in patients who did not respond or relapsed after splenectomy was mostly effective. After a median follow-up of 7 years (range: 1-25 years) from the diagnosis, there were 2 deaths, including one due to spontaneous bleeding after repair of duodenal ulcer perforation.
CONCLUSION
Although splenectomy is safe and effective, the response rate after splenectomy continuously decreases over time. The duration of response is different between the patients that achieved CR and those that achieved PR. Factors, including age, were not predictors of a response to splenectomy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McMillan R. The pathogenesis of chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Semin Hematol. 2007; 44(4 Suppl. 5):S3–S11. PMID: 18096470.
Article2. British Committee for Standards in Haematology General Haematology Task Force. Guidelines for the investigation and management of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults, children and in pregnancy. Br J Haematol. 2003; 120:574–596. PMID: 12588344.3. Kojouri K, Vesely SK, Terrell DR, George JN. Splenectomy for adult patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a systematic review to assess long-term platelet count responses, prediction of response, and surgical complications. Blood. 2004; 104:2623–2634. PMID: 15217831.
Article4. Mikhael J, Northridge K, Lindquist K, Kessler C, Deuson R, Danese M. Short-term and long-term failure of laparoscopic splenectomy in adult immune thrombocytopenic purpura patients: a systematic review. Am J Hematol. 2009; 84:743–748. PMID: 19714591.
Article5. Vesely SK, Perdue JJ, Rizvi MA, Terrell DR, George JN. Management of adult patients with persistent idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura following splenectomy: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2004; 140:112–120. PMID: 14734334.6. Psaila B, Bussel JB. Refractory immune thrombocytopenic purpura: current strategies for investigation and management. Br J Haematol. 2008; 143:16–26. PMID: 18573111.
Article7. George JN, Woolf SH, Raskob GE, et al. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a practice guideline developed by explicit methods for the American Society of Hematology. Blood. 1996; 88:3–40. PMID: 8704187.8. Ruggeri M, Fortuna S, Rodeghiero F. Heterogeneity of terminology and clinical definitions in adult idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a critical appraisal from a systematic review of the literature. Haematologica. 2008; 93:98–103. PMID: 18166791.
Article9. Balagué C, Vela S, Targarona EM, et al. Predictive factors for successful laparoscopic splenectomy in immune thrombocytopenic purpura: study of clinical and laboratory data. Surg Endosc. 2006; 20:1208–1213. PMID: 16865623.10. Godeau B, Provan D, Bussel J. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura in adults. Curr Opin Hematol. 2007; 14:535–556. PMID: 17934364.
Article11. Bourgeois E, Caulier MT, Delarozee C, Brouillard M, Bauters F, Fenaux P. Long-term follow-up of chronic autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura refractory to splenectomy: a prospective analysis. Br J Haematol. 2003; 120:1079–1088. PMID: 12648082.
Article12. Fabris F, Tassan T, Ramon R, et al. Age as the major predictive factor of long-term response to splenectomy in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 2001; 112:637–640. PMID: 11260065.
Article13. Katkhouda N, Hurwitz MB, Rivera RT, et al. Laparoscopic splenectomy: outcome and efficacy in 103 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1998; 228:568–578. PMID: 9790346.14. Kumar S, Diehn FE, Gertz MA, Tefferi A. Splenectomy for immune thrombocytopenic purpura: long-term results and treatment of postsplenectomy relapses. Ann Hematol. 2002; 81:312–319. PMID: 12107560.
Article15. Mazzucconi MG, Arista MC, Peraino M, et al. Long-term follow-up of autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura (ATP) patients submitted to splenectomy. Eur J Haematol. 1999; 62:219–222. PMID: 10227454.
Article16. Pace DE, Chiasson PM, Schlachta CM, Mamazza J, Poulin EC. Laparoscopic splenectomy for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). Surg Endosc. 2003; 17:95–98. PMID: 12360373.
Article17. Vianelli N, Galli M, de Vivo A, et al. Efficacy and safety of splenectomy in immune thrombocytopenic purpura: long-term results of 402 cases. Haematologica. 2005; 90:72–77. PMID: 15642672.18. Wang T, Xu M, Ji L, Han ZC, Yang R. Splenectomy for adult chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: experience from a single center in China. Eur J Haematol. 2005; 75:424–429. PMID: 16191093.
Article19. Schwartz J, Leber MD, Gillis S, Giunta A, Eldor A, Bussel JB. Long term follow-up after splenectomy performed for immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). Am J Hematol. 2003; 72:94–98. PMID: 12555211.
Article20. George JN. Management of patients with refractory immune thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2006; 4:1664–1672. PMID: 16879206.
Article21. George JN, Raskob GE, Vesely SK, et al. Initial management of immune thrombocytopenic purpura in adults: a randomized controlled trial comparing intermittent anti-D with routine care. Am J Hematol. 2003; 74:161–169. PMID: 14587042.
Article22. Johansson E, Engervall P, Landgren O, et al. Response to splenectomy is durable after a certain point in time in adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur J Haematol. 2006; 77:61–66. PMID: 16573739.
Article23. Portielje JE, Westendorp RG, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Brand A. Morbidity and mortality in adults with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2001; 97:2549–2554. PMID: 11313240.
Article24. Cortelazzo S, Finazzi G, Buelli M, Molteni A, Viero P, Barbui T. High risk of severe bleeding in aged patients with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1991; 77:31–33. PMID: 1984800.
Article25. Provan D, Newland A. Fifty years of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP): management of refractory itp in adults. Br J Haematol. 2002; 118:933–944. PMID: 12199770.
Article26. McMillan R, Durette C. Long-term outcomes in adults with chronic ITP after splenectomy failure. Blood. 2004; 104:956–960. PMID: 15100149.
Article27. Zoghlami-Rintelen C, Weltermann A, Bittermann C, et al. Efficacy and safety of splenectomy in adult chronic immune thrombocytopenia. Ann Hematol. 2003; 82:290–294. PMID: 12739064.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laparoscopic Splenectomy for Patients with Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Splenectomy in Patients with Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpur and Neutropenia Associatedwith Ulcerative Colitis
- Laparoscopic splenectomy for immune thrombocytopenic purpura:long-term result of 40 laparoscopic splenectomies
- Long-term results of laparoscopic splenectomy in pediatric chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura