Korean J Hematol.
2010 Dec;45(4):264-268. 10.5045/kjh.2010.45.4.264.
Elevated levels of activated and inactivated thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor in patients with sepsis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Bionano Technology, Kyungwon University, Seongnam, Korea. seongaan@kyungwon.ac.kr
- KMID: 2252039
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2010.45.4.264
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
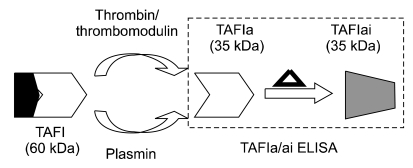
In sepsis, large scale inflammatory responses can cause extensive collateral damage to the vasculature, because both coagulation and fibrinolysis are activated unevenly. Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) plays a role in modulating fibrinolysis. Since TAFI can be activated by both thrombin and plasmin, it is thought to be affected in sepsis. Hence, activated and inactivated TAFI (TAFIa/ai) may be used to monitor changes in sepsis.
METHODS
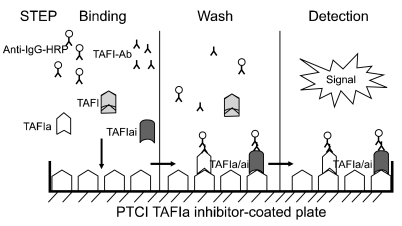
TAFIa/ai-specific in-house ELISA can detect only the TAFIa/ai form, because the ELISA capture agent is potato tuber carboxypeptidase inhibitor (PTCI), which has selective affinity towards only the TAFIa and TAFIai isoforms. TAFIa/ai levels in plasma from 25 patients with sepsis and 19 healthy volunteers were quantitated with the in-house ELISA.
RESULTS
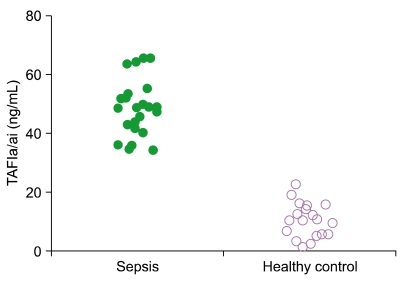
We observed increased TAFIa/ai levels in samples from patients with sepsis (48.7+/-9.3 ng/mL) than in samples from healthy individuals (10.5+/-5.9 ng/mL). In contrast, no difference in total TAFI concentration was obtained between sepsis patients and healthy controls. The results suggest that TAFI zymogen was activated and that TAFIa/ai accumulated in sepsis.
CONCLUSION
The detection of TAFIa/ai in plasma could provide a useful and simple diagnostic tool for sepsis. Uneven activation of both coagulation and fibrinolysis in sepsis could be caused by the activation of TAFI zymogen and elevation of TAFIa/ai. TAFIa/ai could be a novel marker to monitor sepsis and other blood-related disturbances.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Anas AA, Wiersinga WJ, de Vos AF, van der Poll T. Recent insights into the pathogenesis of bacterial sepsis. Neth J Med. 2010; 68:147–152. PMID: 20421654.2. Pierrakos C, Vincent JL. Sepsis biomarkers: a review. Crit Care. 2010; 14:R15. PMID: 20144219.
Article3. Levi M. The coagulant response in sepsis and inflammation. Hamostaseologie. 2010; 30:10–12. 14–16. PMID: 20162247.
Article4. Blackwell TS, Christman JW. Sepsis and cytokines: current status. Br J Anaesth. 1996; 77:110–117. PMID: 8703620.
Article5. Faust SN, Heyderman RS, Levin M. Coagulation in severe sepsis: a central role for thrombomodulin and activated protein C. Crit Care Med. 2001; 29(7 Suppl):S62–S67. PMID: 11445736.
Article6. Sawamura A, Hayakawa M, Gando S, et al. Disseminated intravascular coagulation with a fibrinolytic phenotype at an early phase of trauma predicts mortality. Thromb Res. 2009; 124:608–613. PMID: 19660788.
Article7. Esmon CT, Fukudome K, Mather T, et al. Inflammation, sepsis, and coagulation. Haematologica. 1999; 84:254–259. PMID: 10189392.8. Mackman N. The many faces of tissue factor. J Thromb Haemost. 2009; 7(Suppl 1):136–139. PMID: 19630786.
Article9. Redlitz A, Tan AK, Eaton DL, Plow EF. Plasma carboxypeptidases as regulators of the plasminogen system. J Clin Invest. 1995; 96:2534–2538. PMID: 7593646.
Article10. Bajzar L, Manuel R, Nesheim ME. Purification and characterization of TAFI, a thrombin-activable fibrinolysis inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1995; 270:14477–14484. PMID: 7782309.
Article11. Bajzar L, Morser J, Nesheim M. TAFI, or plasma procarboxypeptidase B, couples the coagulation and fibrinolytic cascades through the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:16603–16608. PMID: 8663147.
Article12. Wang W, Boffa MB, Bajzar L, Walker JB, Nesheim ME. A study of the mechanism of inhibition of fibrinolysis by activated thrombin-activable fibrinolysis inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:27176–27181. PMID: 9765237.
Article13. Hendriks D, Wang W, Scharpé S, Lommaert MP, van Sande M. Purification and characterization of a new arginine carboxypeptidase in human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990; 1034:86–92. PMID: 2328266.
Article14. Marx PF, Dawson PE, Bouma BN, Meijers JC. Plasmin-mediated activation and inactivation of thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. Biochemistry. 2002; 41:6688–6696. PMID: 12022872.
Article15. Hulme JP, An SSA. Detecting activated thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFIa) and inactivated TAFIa (TAFIai) in normal and hemophilia a plasmas. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 2009; 30:77–82.16. van Tilburg NH, Rosendaal FR, Bertina RM. Thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor and the risk for deep vein thrombosis. Blood. 2000; 95:2855–2859. PMID: 10779431.
Article17. Meijers JC, Oudijk EJ, Mosnier LO, et al. Reduced activity of TAFI (thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor) in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2000; 108:518–523. PMID: 10759708.
Article18. Silveira A, Schatteman K, Goossens F, et al. Plasma procarboxypeptidase U in men with symptomatic coronary artery disease. Thromb Haemost. 2000; 84:364–368. PMID: 11019956.
Article19. Watanabe R, Wada H, Watanabe Y, et al. Activity and antigen levels of thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor in plasma of patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Res. 2001; 104:1–6. PMID: 11583733.
Article20. Koster T, Blann AD, Briët E, Vandenbroucke JP, Rosendaal FR. Role of clotting factor VIII in effect of von Willebrand factor on occurrence of deep-vein thrombosis. Lancet. 1995; 345:152–155. PMID: 7823669.
Article21. Meijers JC, Tekelenburg WL, Bouma BN, Bertina RM, Rosendaal FR. High levels of coagulation factor XI as a risk factor for venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:696–701. PMID: 10706899.
Article22. Binette TM, Taylor FB Jr, Peer G, Bajzar L. Thrombin-thrombomodulin connects coagulation and fibrinolysis: more than an in vitro phenomenon. Blood. 2007; 110:3168–3175. PMID: 17644733.
Article23. Antovic J, Schulman S, Eelde A, Blombäck M. Total thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) antigen and pro-TAFI in patients with haemophilia A. Haemophilia. 2001; 7:557–560. PMID: 11851753.
Article24. Antovic JP, Schulman S, An SS, Greenfield RS, Blombäck M. Does an enzyme other than thrombin contribute to unexpected changes in the levels of the different forms of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor in patients with hemophilia A, hemophilia B and von Willebrand disease? Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2004; 64:745–751. PMID: 15719893.
Article25. Leung LL, Nishimura T, Myles T. Regulation of tissue inflammation by thrombin-activatable carboxypeptidase B (or TAFI). Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008; 632:61–69. PMID: 19025114.
Article26. Hoekstra J, Guimarães AH, Leebeek FW, et al. Impaired fibrinolysis as a risk factor for Budd-Chiari syndrome. Blood. 2010; 115:388–395. PMID: 19965669.
Article27. Ermantas N, Guldiken S, Demir M, Tugrul A. Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) antigen and activity assay in patients with primary hypothyroidism. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2010; 16:568–573. PMID: 19959491.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Assessment of thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) activation in acquired hemostatic dysfunction: a diagnostic challenge
- Plasma Fibrinolysis Inhibitor Levels in Acute Stroke Patients with Thrombolysis Failure
- The imbalance between coagulation and fibrinolysis is related to the severity of the illness and the prognosis in sepsis
- Thrombin Induced Apoptosis through Calcium-Mediated Activation of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 in Intestinal Myofibroblasts
- Effects of Long-term Thrombin Inhibition (Dabigatran Etexilate) on Spontaneous Thrombolytic Activity during the Progression of Atherosclerosis in ApoE−/−–LDLR−/− Double-Knockout Mice