Korean J Hematol.
2012 Sep;47(3):233-236. 10.5045/kjh.2012.47.3.233.
Thromboembolic events identified during diagnosis of germ cell tumors in 2 children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hanyang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. cord@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Hanyang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2251960
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2012.47.3.233
Abstract
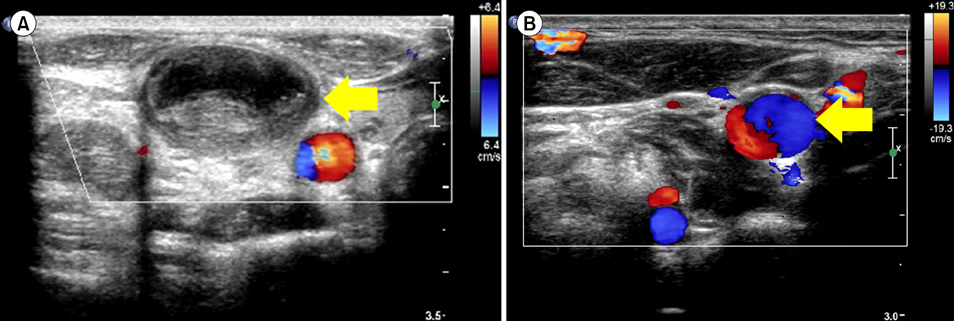
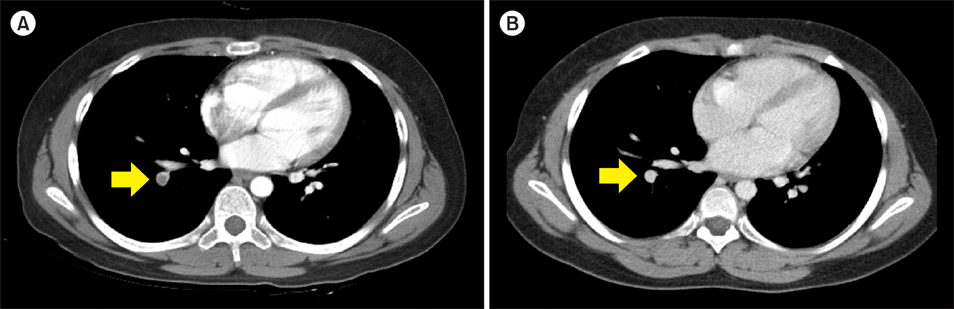
- We describe 2 cases in which radiographic evidence of thromboembolic events was obtained during germ cell tumor diagnosis. There was no evidence of coagulation factor abnormalities or contributory procedures or drugs in either patient. We used anticoagulation therapy for thrombolysis in one patient, but in the other, the thromboembolism resolved spontaneously.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Thodiyil PA, Kakkar AK. Variation in relative risk of venous thromboembolism in different cancers. Thromb Haemost. 2002. 87:1076–1077.
Article2. Piketty AC, Fléchon A, Laplanche A, et al. The risk of thromboembolic events is increased in patients with germ-cell tumours and can be predicted by serum lactate dehydrogenase and body surface area. Br J Cancer. 2005. 93:909–914.
Article3. Jafri M, Protheroe A. Cisplatin-associated thrombosis. Anticancer Drugs. 2008. 19:927–929.
Article4. Mitomi M, Kimura K, Iguchi Y, et al. A case of stroke due to tumor emboli associated with metastatic cardiac liposarcoma. Intern Med. 2011. 50:1489–1491.
Article5. Stergiopoulos K, Vasu S, Bilfinger T, Poon M. Embolic stroke in a patient with metastatic renal cell cancer. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2011. 52:256–258.6. Abdel-Razeq HN, Mansour AH, Ismael YM. Incidental pulmonary embolism in cancer patients: clinical characteristics and outcome-a comprehensive cancer center experience. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2011. 7:153–158.7. Natsuaki M, Numaguchi K, Tada H, Nakashima Y, Okabe M, Yamamoto Y. Recurrence of pulmonary embolism in young man with retroperitoneal tumor despite insertion of temporary IVC filter. Circ J. 2009. 73:1756–1758.
Article8. Dijk FN, Curtin J, Lord D, Fitzgerald DA. Pulmonary embolism in children. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2012. 13:112–122.
Article9. Oschman A, Kuhn RJ. Venous thromboembolism in the pediatric population. Orthopedics. 2010. 33:180–184.
Article10. Latorre González G, López de Silanes de Miguel C, Escribano Gascón AB. Cerebral venous thrombosis in a chemotherapy patient with dysgerminoma. An Pediatr (Barc). 2008. 69:485–486.11. Cyriac S, Sagar TG, Mahajan V. Choriocarcinoma with arterial and venous thrombosis. Neurol India. 2009. 57:505–507.
Article12. Zhou W, Ding SF. Concurrent pheochromocytoma, ventricular tachycardia, left ventricular thrombus, and systemic embolization. Intern Med. 2009. 48:1015–1019.
Article13. Owen RJ. Embolization of musculoskeletal bone tumors. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2010. 27:111–123.
Article14. Simanek R, Vormittag R, Hassler M, et al. Venous thromboembolism and survival in patients with high-grade glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2007. 9:89–95.
Article15. Moheimani F, Jackson DE. Venous thromboembolism: classification, risk factors, diagnosis, and management. ISRN Hematol. 2011. 2011:124610.
Article