Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2012 Aug;16(3):93-97. 10.14701/kjhbps.2012.16.3.93.
Extrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative hepatic resection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea. gsceho@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2243213
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/kjhbps.2012.16.3.93
Abstract
- BACKGROUNDS/AIMS
This study was designed to compare the recurrence patterns after curative hepatectomy, to compare the prognosis according to the initial site of metastasis, and to investigate the independent predictive factors associated with extrahepatic recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients after curative hepatectomy.
METHODS
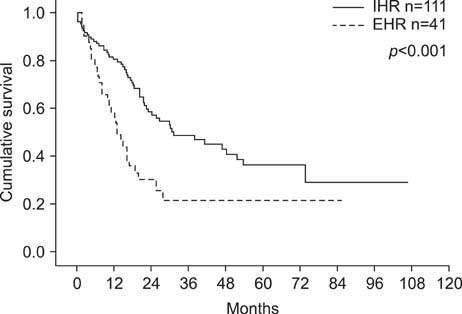
From January 2000 to July 2009, 307 patients underwent curative hepatectomies for HCC at our institution; 152 patients showed recurrences. Patients were divided into 2 groups according to their initial recurrence site: the intrahepatic recurrence (IHR) group and extrahepatic recurrence (EHR) group. The IHR group was comprised of 111 patients and the EHR group was comprised of 41 patients. The study investigated the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative factors related to the recurrence pattern retrospectively and compared the prognoses of the patients.
RESULTS
A five-year survival rate after an initial recurrence was lower in the EHR group (21.5%) than the IHR group (36.3%) (p<0.001). The preoperative alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level was an independent risk factor for extrahepatic recurrence (p=0.014).
CONCLUSIONS
Patients with a preoperative AFP level greater than 200 ng/ml have a higher incidence of extrahepatic metastases after a curative resection of HCC. Increased level of preoperative AFP is an indication for a short-term follow up hepatectomy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Abdominal Wall Metastasis from Hepatocellular Carcinoma 8 Years after Left Hemihepatectomy
Eunju Kim, Bo-Hyun Jung
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2020;75(6):362-365. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.75.6.362.A comparison of the risk factors of intrahepatic recurrence, early recurrencen, and multiple recurrences after resection for single nodular hepatocellular carcinoma
Hyun Joon An, Woo Young Shin, Keon-Young Lee, Seung-Ik Ahn
Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2015;19(3):89-97. doi: 10.14701/kjhbps.2015.19.3.89.
Reference
-
1. Taura K, Ikai I, Hatano E, et al. Implication of frequent local ablation therapy for intrahepatic recurrence in prolonged survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing hepatic resection: an analysis of 610 patients over 16 years old. Ann Surg. 2006. 244:265–273.2. Sakata J, Shirai Y, Wakai T, et al. Preoperative predictors of vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008. 34:900–905.3. Belghiti J, Regimbeau JM, Durand F, et al. Resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a European experience on 328 cases. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002. 49:41–46.4. Hanazaki K, Kajikawa S, Shimozawa N, et al. Survival and recurrence after hepatic resection of 386 consecutive patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg. 2000. 191:381–388.5. Yang Y, Nagano H, Ota H, et al. Patterns and clinicopathologic features of extrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Surgery. 2007. 141:196–202.6. Taketomi A, Toshima T, Kitagawa D, et al. Predictors of extrahepatic recurrence after curative hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010. 17:2740–2746.7. Roh MJ, Kim HJ, Yoon SS, et al. Longterm prognostic factors after hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009. 76:225–230.8. Tanaka K, Shimada H, Matsuo K, et al. Clinical features of hepatocellular carcinoma developing extrahepatic recurrences after curative resection. World J Surg. 2008. 32:1738–1747.9. Choi D, Lim HK, Rhim H, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: long-term results and prognostic factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. 14:2319–2329.10. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. SHARP Investigators Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:378–390.11. Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S, et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:4293–4300.12. Farinati F, Marino D, De Giorgio M, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic role of alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma: both or neither? Am J Gastroenterol. 2006. 101:524–532.13. Tangkijvanich P, Mahachai V, Suwangool P, et al. Gender difference in clinicopathologic features and survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. 10:1547–1550.14. Yang ZF, Ngai P, Ho DW, et al. Identification of local and circulating cancer stem cells in human liver cancer. Hepatology. 2008. 47:919–928.15. Fan ST, Yang ZF, Ho DW, et al. Prediction of posthepatectomy recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma by circulating cancer stem cells: a prospective study. Ann Surg. 2011. 254:569–576.16. Shimada M, Takenaka K, Gion T, et al. Prognosis of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a 10-year surgical experience in Japan. Gastroenterology. 1996. 111:720–726.17. Lo CM, Lai EC, Fan ST, et al. Resection for extrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg. 1994. 81:1019–1021.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Long Term Survival in Patient with Early Intrahepatic Recurrence and Extrahepatic Metastasis after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Patterns of Recurrence after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Radiological Type
- The Risk Factors for Extrahepatic Recurrence after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- A Case of Complete Remission in Patient with Extrahepatic Metastasis after Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Radiotherapy, Lung Resection and Systemic Chemotherapy
- Repeat Resection for Intrahepatic and Omental Recurrence of Ruptured Hepatocelluar Carcinoma after the Initial Surgery