Korean Circ J.
2008 Jun;38(6):313-319. 10.4070/kcj.2008.38.6.313.
The Protective Effect of Simvastatin on Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea. lds117@dongguk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Physiology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
- 3Department of Anatomy, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Daegu Catholic University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Department of Physiology, Kyungpook National University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2225778
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2008.38.6.313
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Pulmonary hypertension is characterized by abnormal proliferation of vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells, and progressive pulmonary microvascular leakage that leads to pulmonary edema. This study was designed to investigate the protective effect of simvastatin on monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension and the role of the aquaporin (AQP) water channels.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty one 8-week-old rats were randomized to the control, MCT (60 mg/kg, sc) and the MCT plus simvastatin (5 mg/kg/day, po) groups. Four weeks later, the systolic right ventricular pressure, the right ventricular hypertrophy, the medial wall thickness of the peribronchiolar artery and pulmonary arterioles and the renal function were measured to examine the effects of MCT and simvastatin in the rats. Western blotting for lung aquaporin1 (AQP1) and renal aquaporin2 (AQP2) was performed to analyze the effects of MCT and simvastatin on the AQP water channels.
RESULTS
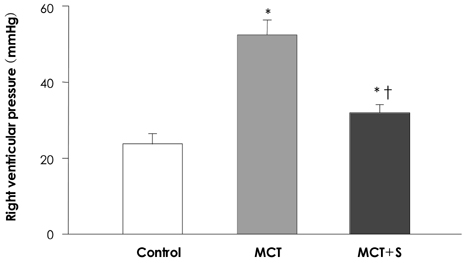
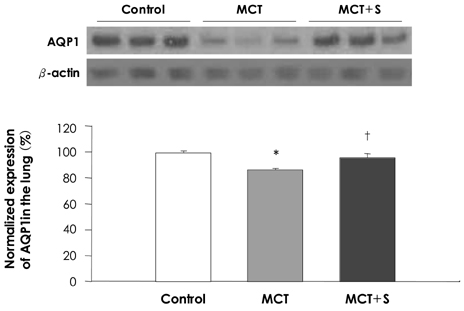
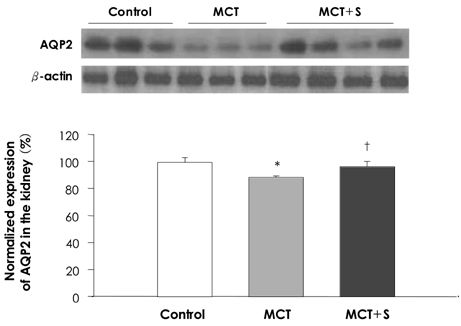
Treatment with simvastatin reduced the MCT-induced enhanced right ventricular pressure (32.3+/-2.1 vs. 52.4+/-3.9 mmHg, respectively; p<0.05), the right ventricular hypertrophy (0.32+/-0.03 vs. 0.48+/-0.07, respectively; p<0.05) and the increased medial wall thickness of the peribronchiolar artery (0.14+/-0.02 vs. 0.28+/-0.02, respectively; p<0.05) and pulmonary arterioles (0.15+/-0.04 vs. 0.29+/-0.11, respectively; p<0.05). The decreased expression of lung AQP1 and renal AQP2 protein after MCT treatment was normalized by simvastatin treatment (p<0.05). Additionally, simvastatin treatment significantly reduced the perivascular and interstitial edema in the rats' lungs without major alterations of renal function.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that simvastatin attenuates the MCT-induced pulmonary hypertension and the pulmonary edema by up-regulation of lung AQP1. Modulation of AQP may be one of the important mechanism of simvastatin.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Humbert M, Morrell NW, Archer SL, et al. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004. 43(Suppl):13S–24S.2. Martin KB, Klinger JR, Rounds SI. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: new insights and new hope. Respirology. 2006. 11:6–17.3. Lee SH, Rubin LJ. Current treatment strategies for pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Intern Med. 2005. 258:199–215.4. Kunieda T, Nakanishi N, Satoh T, Kyotani S, Okano Y, Nagaya N. Prognoses of primary pulmonary hypertension and chronic major vessel thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension determined from cumulative survival curves. Intern Med. 1999. 38:543–546.5. Puri A, McGoon MD, Kushwaha SS. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: current therapeutic strategies. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007. 4:319–329.6. Kao PN. Simvastatin treatment of pulmonary hypertension: an observational case series. Chest. 2005. 127:1446–1452.7. Hu H, Sung A, Zhao G, et al. Simvastatin enhances bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. 339:59–64.8. Girgis RE, Li D, Zhan X, et al. Attenuation of chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by simvastatin. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003. 285:H938–H945.9. Nishimura T, Vaszar LT, Faul JL, et al. Simvastatin rescues rats from fatal pulmonary hypertension by inducing apoptosis of neointimal smooth muscle cells. Circulation. 2003. 108:1640–1645.10. Taraseviciene-Stewart L, Scerbavicius R, Choe KH, et al. Simvastatin causes endothelial cell apoptosis and attenuates severe pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006. 291:L668–L676.11. King LS, Nielsen S, Agre P. Aquaporin-1 water channel protein in lung: ontogeny, steroid-induced expression, and distribution in rat. J Clin Invest. 1996. 97:2183–2191.12. King LS, Yasui M. Aquaporins and disease: lessons from mice to humans. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 13:355–360.13. Nielsen S, Terris J, Andersen D, et al. Congestive heart failure in rats is associated with increased expression and targeting of aquaporin-2 water channel in collecting duct. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. 94:5450–5455.14. Reindel JF, Ganey PE, Wagner JG, Slocombe RF, Roth RA. Development of morphologic, hemodynamic, and biochemical changes in lungs of rats given monocrotaline pyrrole. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1990. 106:179–200.15. D'Alonzo GE, Barst RJ, Ayres SM, et al. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension: results from a national prospective registry. Ann Intern Med. 1991. 115:343–349.16. Lee WD, Kim DS, Lee JH, et al. A clinical review of primary pulmonary hypertension. Korean Circ J. 2003. 33:507–512.17. Lee WS, Kim KH, Jeong DH, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of patients with severe pulmonary hypertension. Korean Circ J. 2007. 37:265–270.18. Schermuly RT, Kreisselmeier KP, Ghofrani HA, et al. Chronic sildenafil treatment inhibits monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004. 169:39–45.19. Newman JH, Fanburg BL, Archer SL, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: future directions: report of a National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute/Office of Rare Diseases workshop. Circulation. 2004. 109:2947–2952.20. Takemoto M, Liao JK. Pleiotropic effects of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001. 21:1712–1719.21. Laufs U, Fata VL, Liao JK. Inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase blocks hypoxia-mediated down-regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:31725–31729.22. Son JW, Koh KK, You SM, et al. Effects of simvastatin alone or combined with ramipril on nitric oxide bioactivity and inflammation markers in hypercholesterolemic patients. Korean Circ J. 2003. 33:1053–1059.23. Girgis RE, Mozammel S, Champion HC, et al. Regression of chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by simvastatin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007. 292:L1105–L1110.24. Hales CA, Du HK, Volokhov A, Mourfarrej R, Quinn DA. Aquaporin channels may modulate ventilator-induced lung injury. Respir Physiol. 2001. 124:159–166.25. Su X, Song Y, Jiang J, Bai C. The role of aquaporin-1 (AQP1) expression in a murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2004. 142:1–11.26. Agre P, King LS, Yasui M, et al. Aquaporin water channels-from atomic structure to clinical medicine. J Physiol. 2002. 542:3–16.27. Staahltoft D, Nielsen S, Janjua NR, et al. Losartan treatment normalizes renal sodium and water handling in rats with mild congestive heart failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002. 282:F307–F315.28. Yu CM, Wing-Hon Lai K, Li PS, Lam KY, Leung JC, Lai KN. Normalization of renal aquaporin-2 water channel expression by fosinopril, valsartan, and combination therapy in congestive heart failure: a new mechanism of action. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004. 36:445–453.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Changes of Pulmonary Pathology and Gene Expressions After Simvastatin Treatment in the Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension Rat Model
- Simvastatin, Sildenafil and Their Combination in Monocrotaline Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- Microarray Analysis in Pulmonary Hypertensive Rat Heart after Simvastatin Treatment
- Angiotensin-(1-9) ameliorates pulmonary arterial hypertension via angiotensin type II receptor
- An inhibitory effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist to gene expression in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertensive rats model