Korean J Clin Neurophysiol.
2015 Jun;17(1):28-30. 10.14253/kjcn.2015.17.1.28.
A Fatal Case of Full-Blown Neuro-Behcet Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. ricash@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2225217
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/kjcn.2015.17.1.28
Abstract
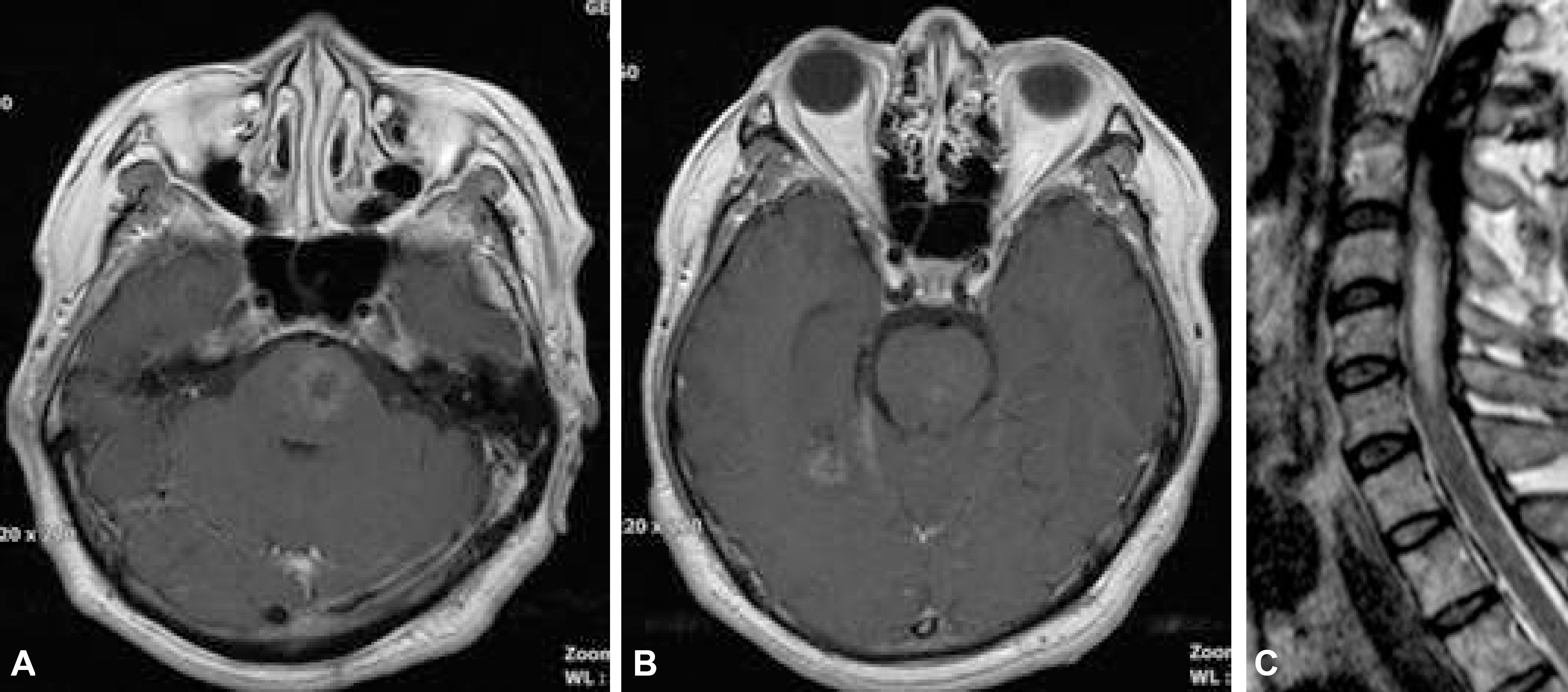
- We reported a 48-year-old man with Behcet disease, who presented with right hemiparesis. His first brain MRI showed multiple enhanced lesions. During the recovery, he had an episode of left 6th nerve palsy without new lesions in a follow-up MRI. Third episode was cervical myelitis, resulting in respiratory difficulty and quadriplegia without any reflexes. The myelitis was not responsive to immunotherapy. He died of respiratory failure complicated with pneumonia. This is a rare case of full-blown neuro-Behcet disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Kural-Seyahi E., Fresko I., Seyahi N., Ozyazgan Y., Mat C., Hamuryudan V, et al. The long-term mortality and morbidity of behcet syndrome: A 2-decade outcome survey of 387 patients followed at a dedicated center. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003. 82:60–76.2.Kocer N., Islak C., Siva A., Saip S., Akman C., Kantarci O, et al. CNS involvement in neuro-behcet syndrome: An MR study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999. 20:1015–1024.3.Lee SH., Yoon PH., Park SJ., Kim DI. MRI findings in neuro-behcet's disease. Clin Radiol. 2001. 56:485–494.4.Yesilot N., Mutlu M., Gungor O., Baykal B., Serdaroglu P., Akman-Demir G. Clinical characteristics and course of spinal cord involvement in behcet's disease. Eur J Neurol. 2007. 14:729–737.5.Fukae J., Noda K., Fujishima K., Takahashi T., Hattori N., Okuma Y. Subacute longitudinal myelitis associated with behcet's disease. Intern Med. 2010. 49:343–347.
Article6.Al-Araji A., Kidd DP. Neuro-behcet's disease: Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2009. 8:192–204.7.Trebst C., Raab P., Voss EV., Rommer P., Abu-Mugheisib M., Zettl UK, et al. Longitudinal extensive transverse myelitis--it's not all neuromyelitis optica. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011. 7:688–698.
Article8.Uygunoglu U., Pasha M., Saip S., Siva A. Recurrent longitudinal extensive transverse myelitis in a neuro-behcet syndrome treated with infliximab. J Spinal Cord Med. 2015. 38:111–114.9.Ditunno JF., Little JW., Tessler A., Burns AS. Spinal shock revisited: A four-phase model. Spinal Cord. 2004. 42:383–395.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neuro-Behcet’s Disease Manifesting as Bilateral Fornix and Left Thalamus Infarction
- Neuro-Behcet's disease presenting with isolated unilateral lateral rectus muscle palsy
- A Case of Pheochromocytoma Misdiagnosed as Activation of Behcet's Disease
- Neuro-Behcet disease presented diplopia with hemiparesis following minor head trauma
- A Clinical Analysis of 7 Patients with Neuro - Behcet's Syndrome