Korean Circ J.
2011 Feb;41(2):109-112. 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.2.109.
Warfarin-Induced Eosinophilic Pleural Effusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. thpark65@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2225145
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2011.41.2.109
Abstract
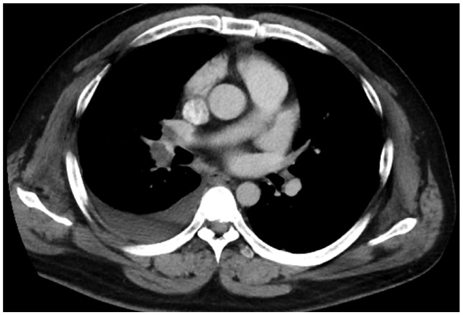
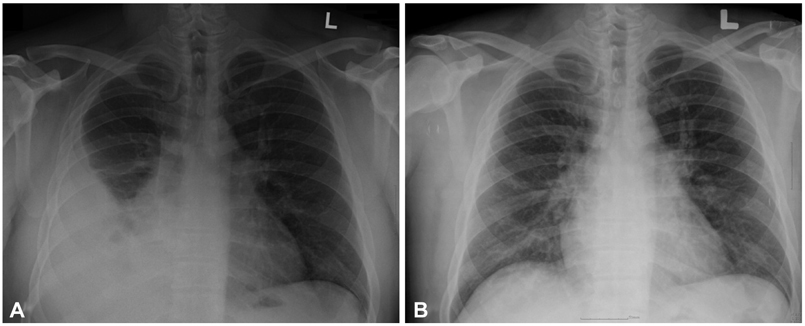
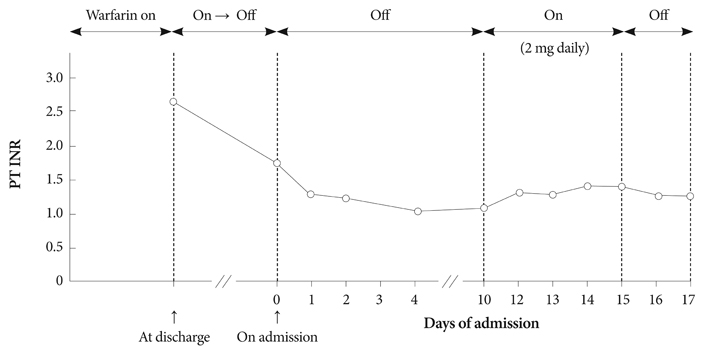
- A 29-year-old man suffering from dyspnea and eosinophilic pleural effusion after being on warfarin for pulmonary thromboembolism for a period of one month, was readmitted to our hospital. Etiology of pleural effusion other than warfarin was excluded. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of warfarin-induced pleural effusion reported in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cooper JA Jr, White DA, Matthay RA. Drug-induced pulmonary disease (part I & II). Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986. 133:488–505.2. Moufarrege G, Frank E, Carstens DD. Eosinophilic exudative pleural effusion after initiation of tizanidine treatment: a case report. Pain Med. 2003. 4:85–90.3. Anshelevich IV, Svistunova AA. Eosinophilic exudative pleurisy as a manifestation of drug allergy. Ter Arkh. 1986. 58:142–143.4. Huggins JT, Sahn SA. Drug-induced pleural disease. Clin Chest Med. 2004. 25:141–153.5. You SH, Hong SJ, Ahn CM, Lim DS. Eosinophilic endomyocarditis combined with pericardial and pleural effusion. Korean Circ J. 2009. 39:545–547.6. Krenke R, Nasilowski J, Korczynski P, et al. Incidence and aetiology of eosinophilic pleural effusion. Eur Respir J. 2009. 34:1111–1117.7. Martinez-Garcia MA, Cases-Viedma E, Cordero-Rodriguez PJ, et al. Diagnostic utility of eosinophils in the pleural fluid. Eur Respir J. 2000. 15:166–169.8. Kalomenidis I, Light RW. Eosinophilic pleural effusions. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2003. 9:254–260.9. Stein PD, Henry JW. Clinical characteristics of patients with acute pulmonary embolism stratified according to their presenting syndromes. Chest. 1997. 112:974–979.10. Simon HB, Daggett WM, DeSanctis RW. Hemothorax as a complication of anticoagulant therapy in the presence of pulmonary infarction. JAMA. 1969. 208:1830–1834.11. Kuwahara T, Hamada M, Inoue Y, Aono S, Hiwada K. Warfarin-induced eosinophilic pleurisy. Intern Med. 1995. 34:794–796.12. Mo EK, Oh YM, Jung MP, et al. A prospective study on the diagnostic value of adenosine deaminase activity in tuberculous pleural effusion. Korean J Med. 1995. 48:625–633.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Characteristics and Diagnostic Utility of Eosinophilic Pleural effusion
- Eosinophilic Endomyocarditis Combined With Pericardial and Pleural Effusion
- Intrapleural Corticosteroid Injection in Eosinophilic Pleural Effusion Associated with Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease
- CT Findings of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Case Report
- A Case of Eosinophilic Pleural Effusion Caused by Toxocariasis without Serum Eosinophilia