J Rheum Dis.
2013 Feb;20(1):64-67. 10.4078/jrd.2013.20.1.64.
A Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Myelitis and Recurrent Neuromyelitis Optica
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Maryknoll Hospital, Busan, Korea. ete@lycos.co.kr
- KMID: 2223053
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2013.20.1.64
Abstract
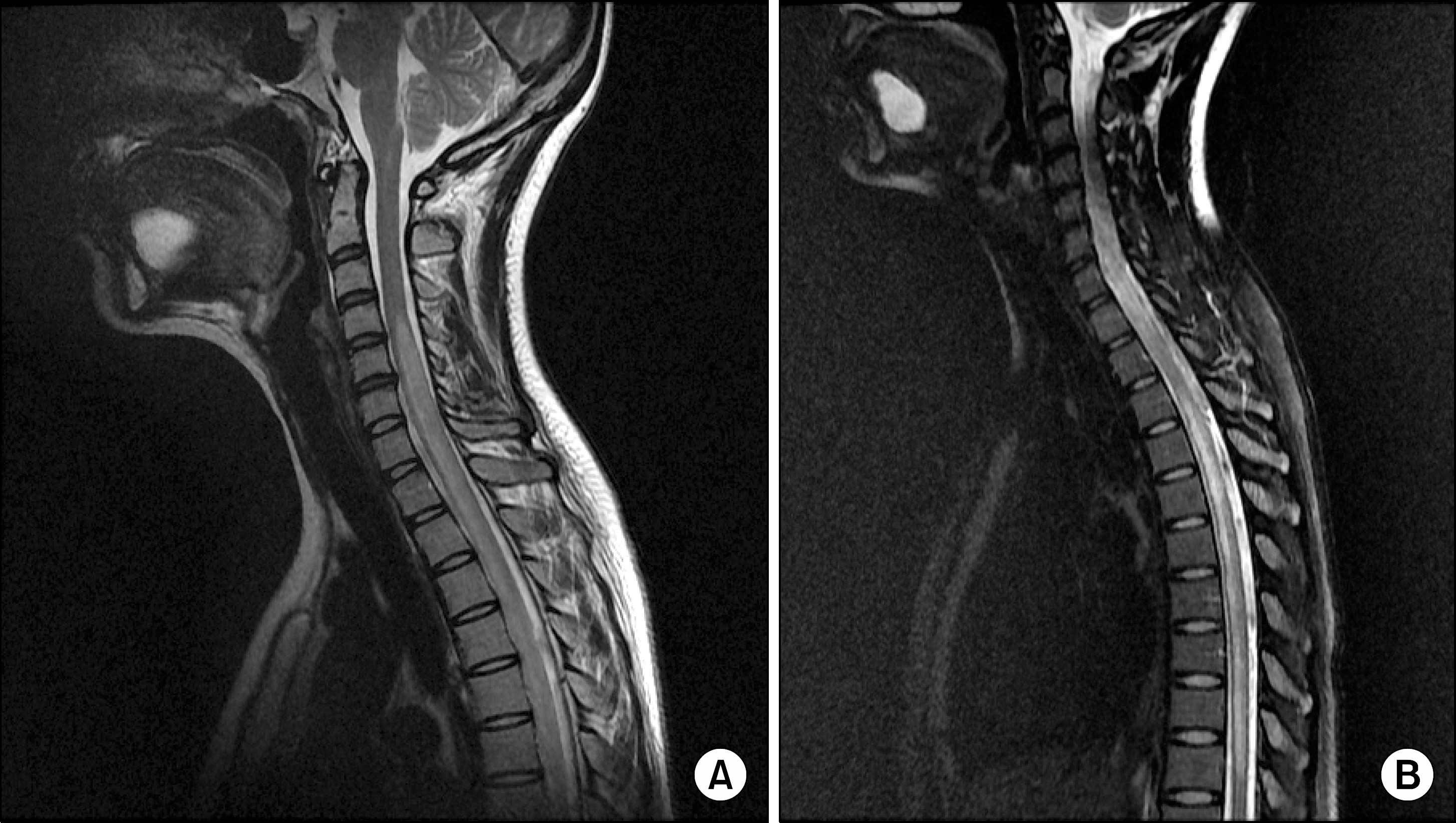
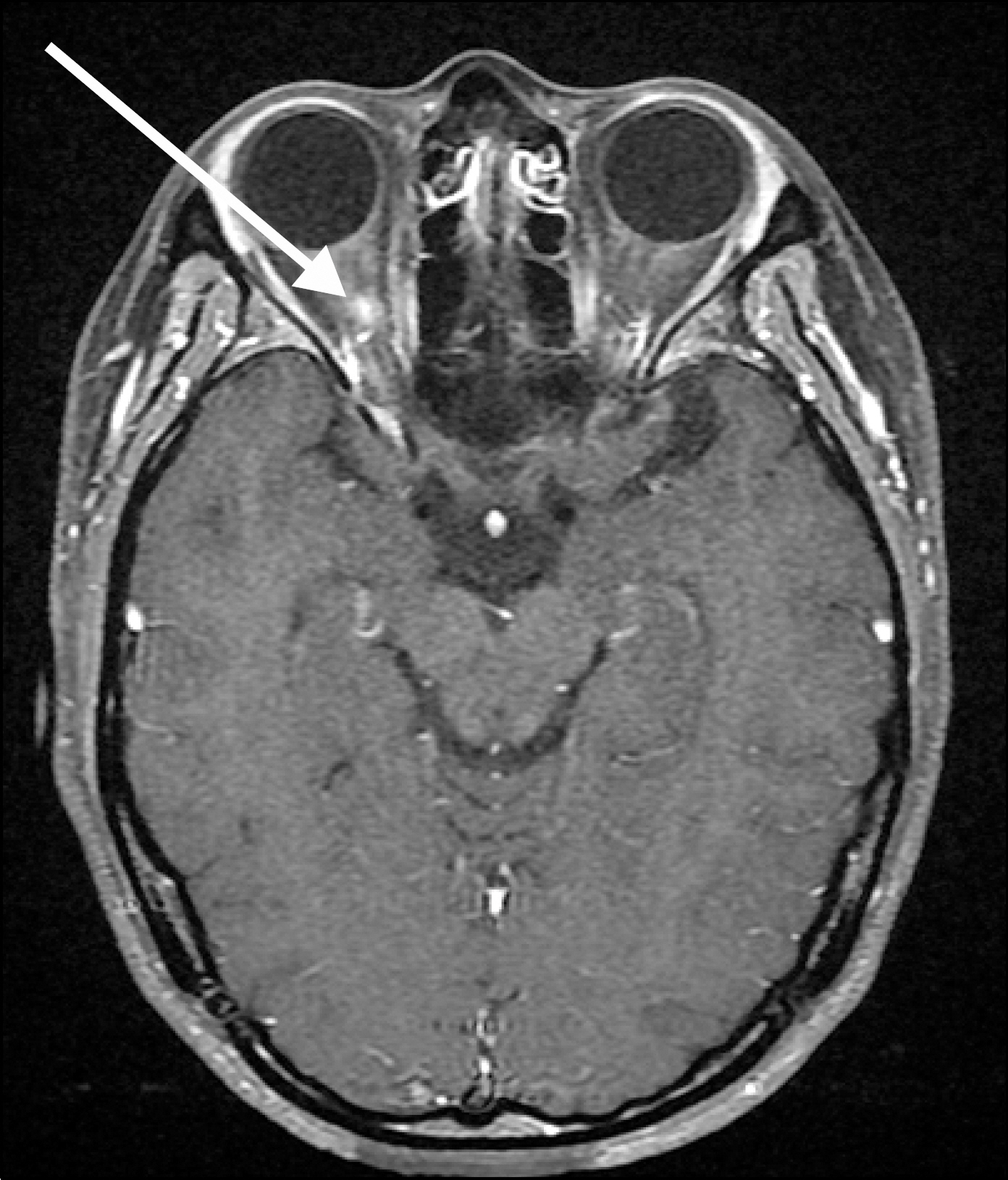
- Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) is an idiopathic, severe inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system targeting optic nerves and the spinal cord. It is characterized by acute bilateral visual loss (optic neuritis), acute transverse myelitis, and tends to spare brain early in the disease course. NMO can occur as an isolated condition or secondary to infection, toxin exposure, and autoimmune disease including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), sarcoidosis, and Behcet's disease. We experienced a case of SLE with myelitis and recurrent optic neuritis in a 28-year-old woman who presented with recurrent visual disturbance and sudden onset of paraplegia, and report here on this case along with a review of the relevant literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Wingerchuk DM, Hogancamp WF, O'Brien PC, Weinshenker BG. The clinical course of neuromyelitis optica (Devic's syndrome). Neurology. 1999; 53:1107–14.
Article2. Mandler RN. Neuromyelitis optica - Devic's syndrome, update. Autoimmun Rev. 2006; 5:537–43.
Article3. Ahn TB, Yoon BW. A case of systemic lupus erythematosus with recurrent myelitis and optic neuritis. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2000; 18:657–60.4. Oh PC, Kim GH, Jin CH, Baek HJ. A case of systemic lupus erythematous associated with neuromyelitis optica (Devic's Syndrome). J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2007; 14:263–7.
Article5. Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Weinshenker BG. Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology. 2006; 66:1485–9.
Article6. Lennon VA, Wingerchuk DM, Kryzer TJ, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Fujihara K, et al. A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: distinction from multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2004; 364:2106–12.
Article7. Takahashi T, Fujihara K, Nakashima I, Misu T, Miyaza-wa I, Nakamura M, et al. Anti-aquaporin-4 antibody is involved in the pathogenesis of NMO: a study on antibody titre. Brain. 2007; 130:1235–43.
Article8. Jarius S, Aboul-Enein F, Waters P, Kuenz B, Hauser A, Berger T, et al. Antibody to aquaporin-4 inthe longterm course of neuromyelitis optica. Brain. 2008; 131:3072–80.9. Mok CC, Lau CS, Chan EY, Wong RW. Acute transverse myelopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical presentation, treatment, and outcome. J Rheumatol. 1998; 25:467–73.10. Sellner J, Boggild M, Clanet M, Hintzen RQ, Illes Z, Montalban X, et al. EFNS guidelines on diagnosis and management of neuromyelitis optica. Eur J Neurol. 2010; 17:1019–32.
Article11. Weinshenker BG, O'Brien PC, Petterson TM, Nosewor-thy JH, Lucchinetti CF, Dodick DW, et al. A randomized trial of plasma exchange in acute central nervous system inflammatory demyelinating disease. Ann Neurol. 1999; 46:878–86.
Article12. Lucchinetti CF, Mandler RN, McGavern D, Bruck W, Gleich G, Ransohoff RM, et al. A role for humoral mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Devic's neuromyelitis optica. Brain. 2002; 125:1450–61.13. Cree BA, Lamb S, Morgan K, Chen A, Waubant E, Genain C. An open label study of the effects of rituximab in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology. 2005; 64:1270–2.
Article14. Jacob A, Weinshenker BG, Violich I, McLinskey N, Krupp L, Fox RJ, et al. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica with rituximab: retrospective analysis of 25 patients. Arch Neurol. 2008; 65:1443–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Recurrent Myelitis and Optic Neuritis
- Bilateral Optic Neuritis as the First Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Associated With Neuromyelitis Optica
- The Systemic Rheumatologic Disease and Neuromyelitis Optica
- A Case of Transverse Myelitis as a First Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A Case of Coexisting Neuromyelitis Optica in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus