J Rheum Dis.
2013 Oct;20(5):328-331. 10.4078/jrd.2013.20.5.328.
A Case of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia Associated with Eosinophilic Pleural Effusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. jhpark10@yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2223011
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2013.20.5.328
Abstract
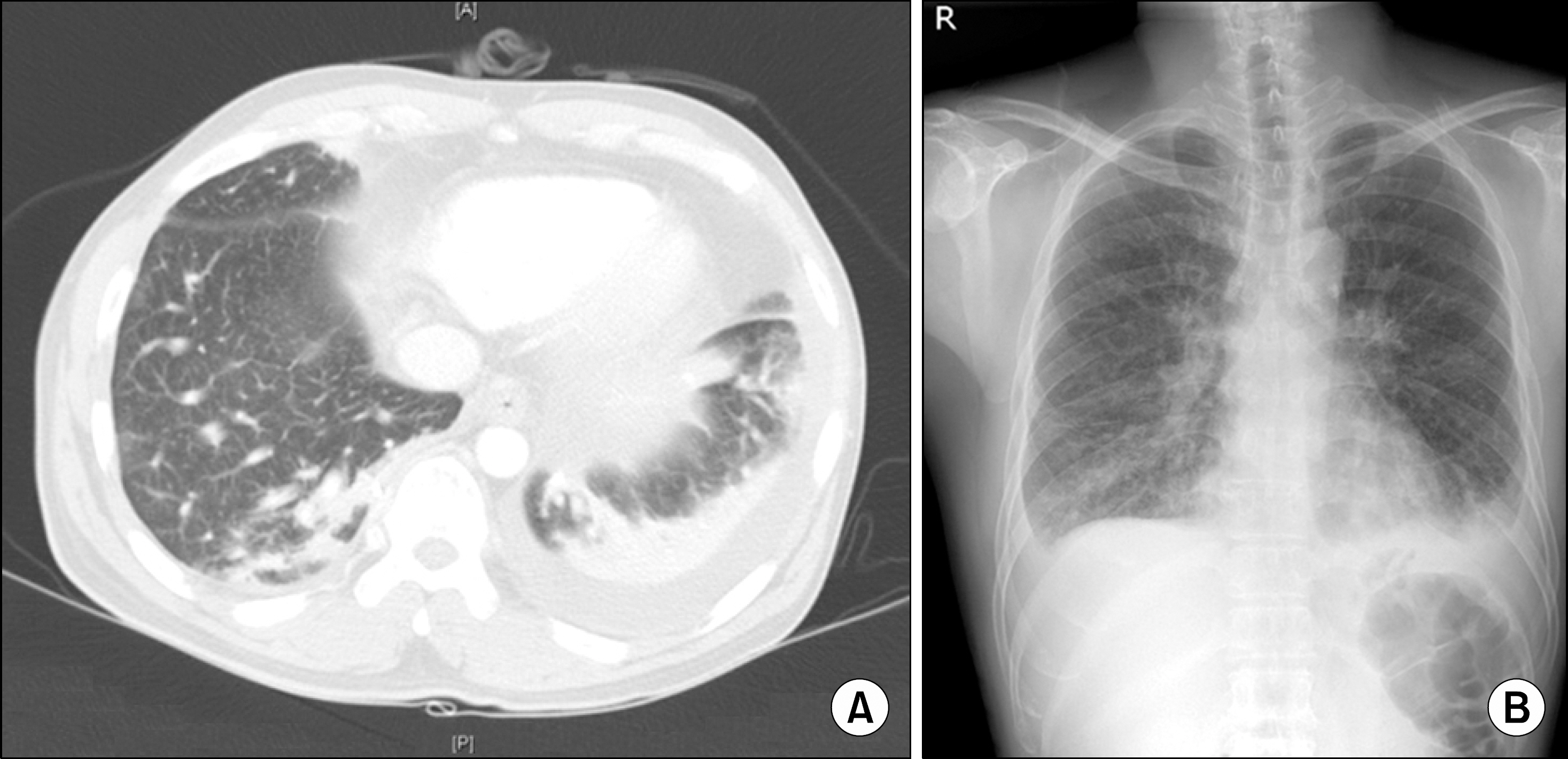
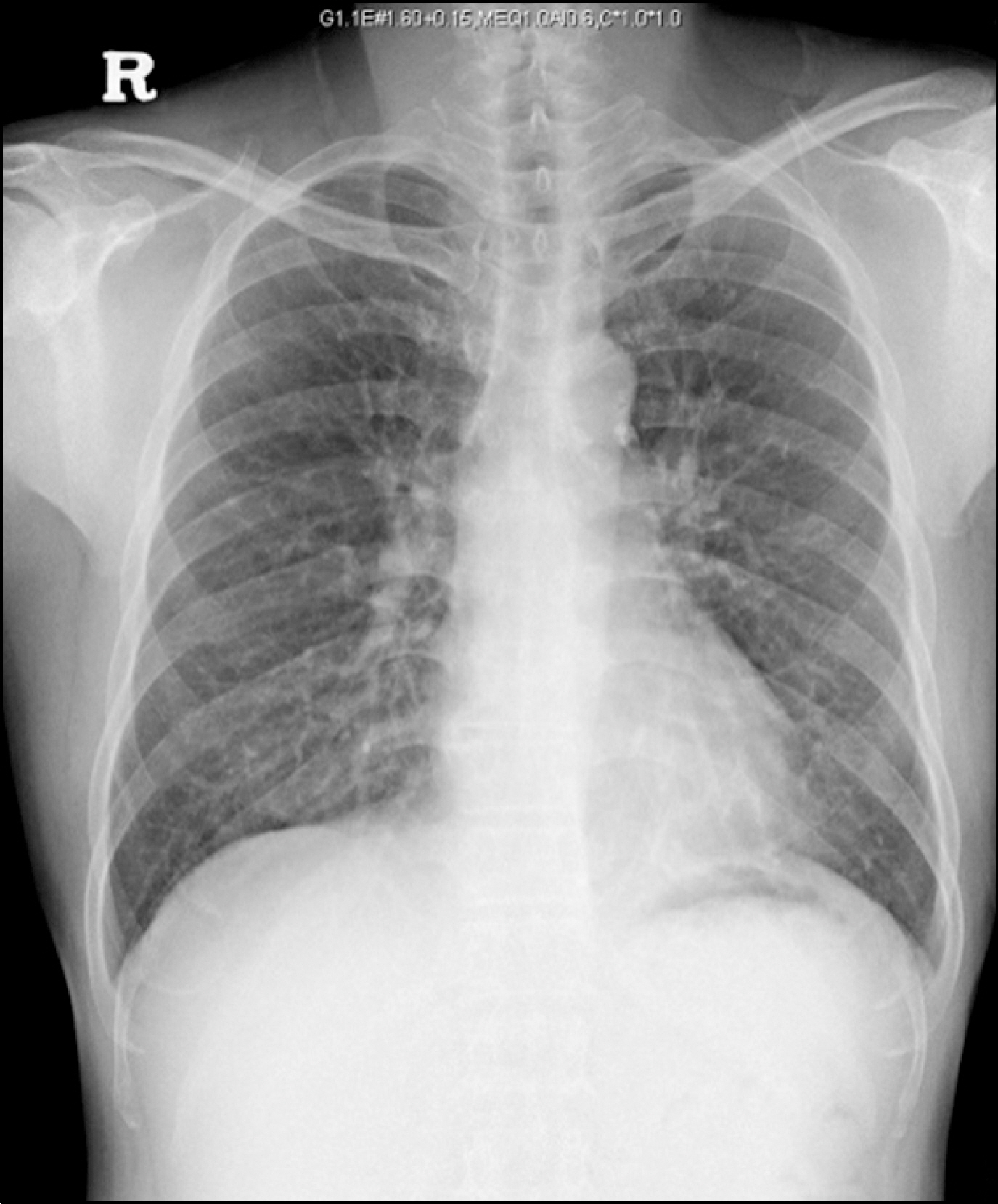
- We describe a 48-year-old man with family history of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affected by chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) with severe peripheral eosinophilia. CEP might develop as a complication of longstanding active RA. The patient with 5 months history of seropositive RA and chronic respiratory symptoms, alveolar and blood eosinophilia, peripheral pulmonary infiltrates and pleural effusion on chest imaging. The lung may be involved as an extraarticular manifestation of RA. However, CEP is not recognized as a typical lung manifestation of RA, and the two diseases rarely coexist. The effusion was an eosinophil predominant exudates and was characterized by low pH, and glucose level and high lactic dehydrogenase. The patient responded rapidly to combination of steroids and disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Tambo Y, Fujimura M, Yasui M, Kasahara K, Nakatsumi Y, Nakao S. Eosinophilic pneumonia (EP) associated with rheumatoid arthritis in which drug-induced eosinophilic pneumonia could be ruled out. Intern Med. 2008; 47:527–31.
Article2. Winchester RJ, Koffler D, Litwin SD, Kunkel HG. Observations on the eosinophilia of certain patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1971; 14:650–65.
Article3. Boudou L, Alexandre C, Thomas T, Pallot-Prade B. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (Carrington's disease) and rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2010; 77:477–80.
Article4. Jederlinic PJ, Sicilian L, Gaensler EA. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. A report of 19 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1988; 67:154–62.
Article5. Short CL, Bauer W, Reynolds WE. Rheumatoid arthritis. p. 354–6. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press;1957.6. Panush RS, Franco AE, Schur PH. Rheumatoid arthritis associated with eosinophilia. Ann Intern Med. 1971; 75:199–205.
Article7. Payne CR, Connellan SJ. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia complicating longstanding rheumatoid arthritis. Postgrad Med J. 1980; 56:519–20.
Article8. Kwak JJ, Chang JE, Lee J, Cho YJ, Sung SH. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia associated with an initiation of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2003; 22:240–3.
Article9. Kudou M, Yasuba H, Kobayashi Y, Hamada K, Kita H. Correlation between rheumatoid factor and peripheral eo-sinophil count in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Respirology. 2006; 11:830–2.
Article10. Kalomenidis I, Light RW. Pathogenesis of the eosinophilic pleural effusions. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2004; 10:289–93.
Article11. Golstein MA, Steinfeld S. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia followed by Churg-Strauss syndrome. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1996; 63:624–8.12. d'Amours P, Leblanc P, Boulet LP. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia associated with thrombocytosis and pleural effusion. CMAJ. 1990; 142:837–9.13. Ferreiro L, San José E, González-Barcala FJ, Alvarez-Dobaño JM, Golpe A, Gude F, et al. Eosinophilic pleural effusion: incidence, etiology and prognostic significance. Arch Bronconeumol. 2011; 47:504–9.
Article14. Naylor B. The pathognomonic cytologic picture of rheumatoid pleuritis. The 1989 Maurice Goldblatt Cytology award lecture. Acta Cytol. 1990; 34:465–73.15. Engel U, Aru A, Francis D. Rheumatoid pleurisy. Specificity of cytological findings. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A. 1986; 94:53–6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Characteristics and Diagnostic Utility of Eosinophilic Pleural effusion
- Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia: A Case Report
- CT Findings of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Case Report
- Cytologic Findings of Rheumatoid Pleuritis in Pleural Effusion: A Case Report
- Eosinophilic Endomyocarditis Combined With Pericardial and Pleural Effusion