J Rheum Dis.
2014 Feb;21(1):35-39. 10.4078/jrd.2014.21.1.35.
Treatment with Rituximab in a Patient with Refractory Felty Syndrome and Low Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. elee@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Borame Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2222987
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2014.21.1.35
Abstract
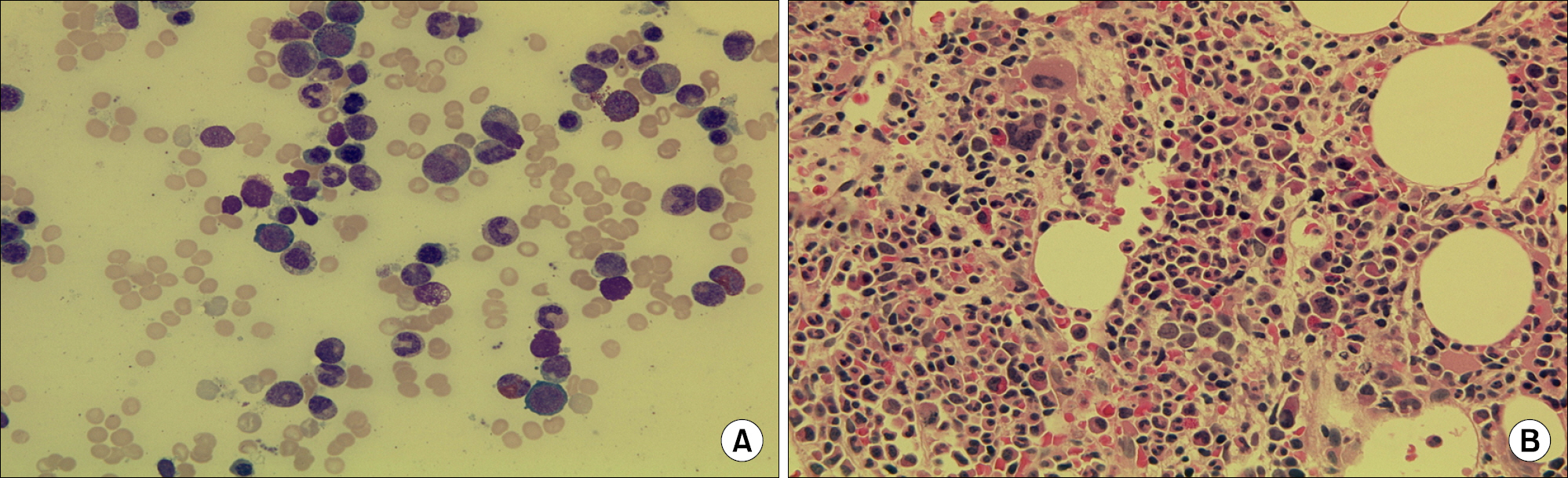
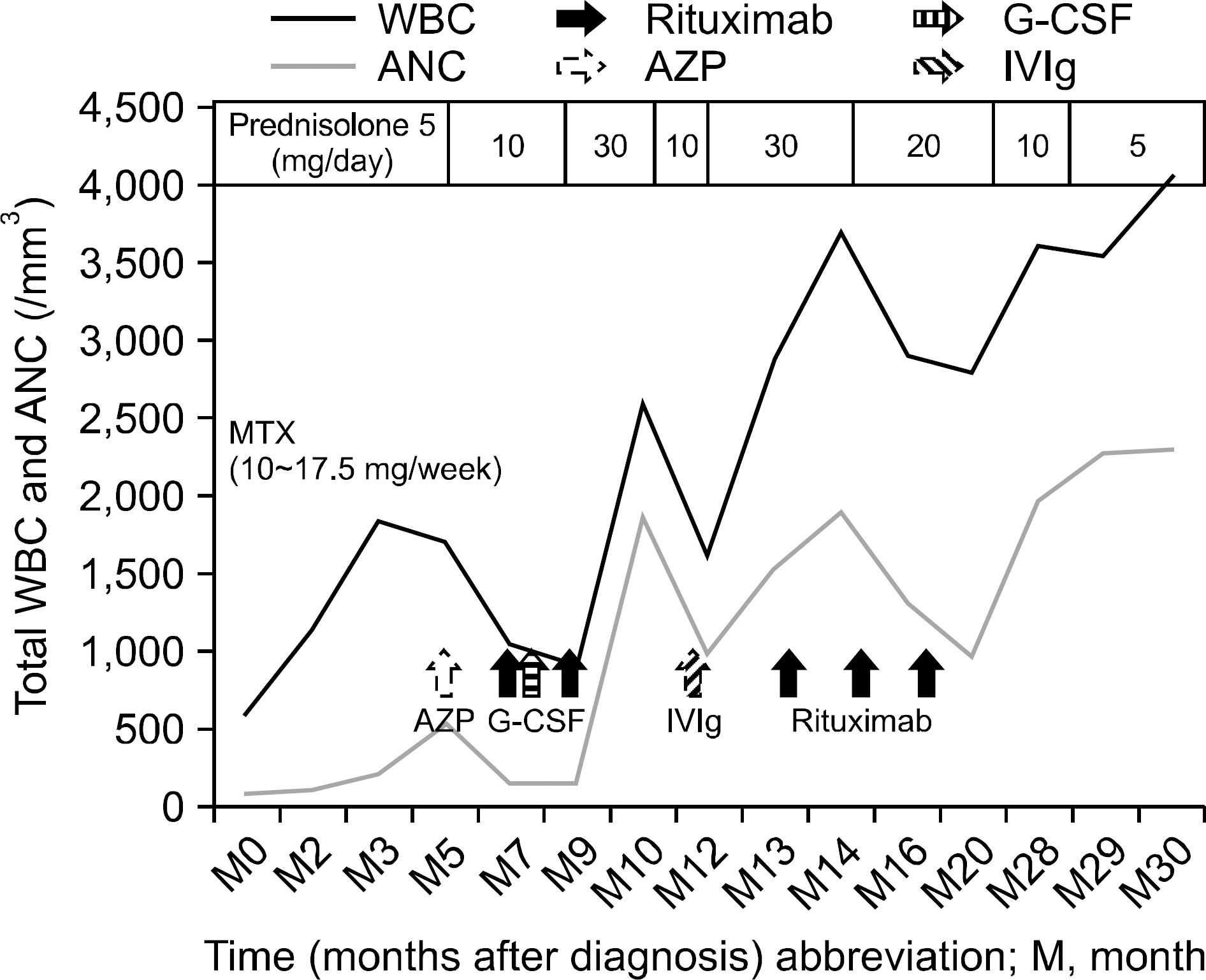
- Felty syndrome (FS) is a rare manifestation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) characterized by neutropenia and splenomegaly. Treatment for FS is not well established because there has been no randomized controlled study. A few recent reports found rituximab effective in patients with refractory FS. According to those reports, most patients with RA and FS had active arthritis. Here we report a case of a patient with glucocorticoid dependent and disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) refractory FS and quiescent RA who was successfully treated with rituximab.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Campion G, Maddison PJ, Goulding N, James I, Ahern MJ, Watt I, et al. The Felty syndrome: a case-matched study of clinical manifestations and outcome, serologic features, and immunogenetic associations. Medicine (Baltimore). 1990; 69:69–80.
Article2. Balint GP, Balint PV. Felty's syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2004; 18:631–45.
Article3. Burks EJ, Loughran TP Jr. Pathogenesis of neutropenia in large granular lymphocyte leukemia and Felty syndrome. Blood Rev. 2006; 20:245–66.
Article4. Hellmich B, Csernok E, Schatz H, Gross WL, Schnabel A. Autoantibodies against granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in Felty's syndrome and neutropenic systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46:2384–91.
Article5. Ditzel HJ, Masaki Y, Nielsen H, Farnaes L, Burton DR. Cloning and expression of a novel human antibody-antigen pair associated with Felty's syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97:9234–9.
Article6. Capsoni F, Sarzi-Puttini P, Zanella A. Primary and secondary autoimmune neutropenia. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005; 7:208–14.7. Wassenberg S, Herborn G, Rau R. Methotrexate treatment in Felty's syndrome. Br J Rheumatol. 1998; 37:908–11.
Article8. Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, Dougados M, Furie RA, Genovese MC, et al. REFLEX Trial Group. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to antitumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:2793–806.
Article9. Lal P, Su Z, Holweg CT, Silverman GJ, Schwartzman S, Kelman A, et al. Inflammation and autoantibody markers identify rheumatoid arthritis patients with enhanced clinical benefit following rituximab treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63:3681–91.
Article10. Pei SN, Ma MC, Wang MC, Kuo CY, Rau KM, Su CY, et al. Analysis of hepatitis B surface antibody titers in B cell lymphoma patients after rituximab therapy. Ann Hematol. 2012; 91:1007–12.
Article11. Kim W, Kim SH, Huh SY, Kong SY, Choi YJ, Cheong HJ, et al. Reduced antibody formation after influenza vaccination in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder treated with rituximab. Eur J Neurol. 2013; 20:975–80.
Article12. Couderc M, Mathieu S, Pereira B, Glace B, Soubrier M. Predictive factors of rituximab response in rheumatoid arthritis: results from a French university hospital. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013; 65:648–52.
Article13. Narváez J, Domingo-Domenech E, Gómez-Vaquero C, López-Vives L, Estrada P, Aparicio M, et al. Biological agents in the management of Felty's syndrome: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 41:658–68.
Article14. Salama A, Schneider U, Dörner T. Beneficial response to rituximab in a patient with haemolysis and refractory Felty syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008; 67:894–5.
Article15. Sordet C, Gottenberg JE, Hellmich B, Kieffer P, Mariette X, Sibilia J. Lack of efficacy of rituximab in Felty's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005; 64:332–3.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Bowen's Disease During Adalimumab Treatment for Felty's Syndrome
- A Case of Rituximab Use in Rheumatoid Arthritis Following Anti-TNF-Associated Tuberculosis
- A Case of Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia in a Patient with Felty's Syndome
- Inflammation is responsible for systemic bone loss in patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab
- The Effect of Bucillamine in the Initial Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Treatment of Patients with Refractory Rheumatoid Arthritis