Korean Diabetes J.
2009 Aug;33(4):299-305. 10.4093/kdj.2009.33.4.299.
Association of Spot Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio and 24 Hour-Collected Urine Albumin Excretion Rate in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. imsts@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2222407
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.4.299
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
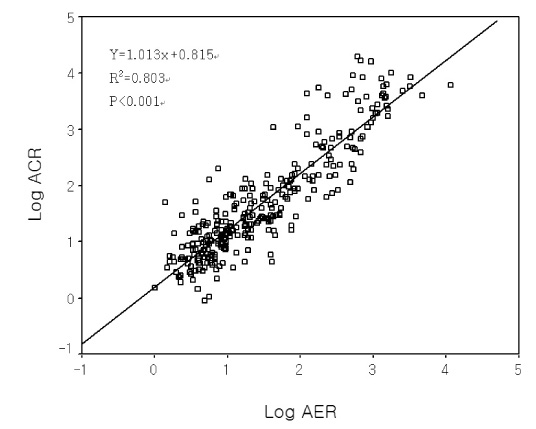
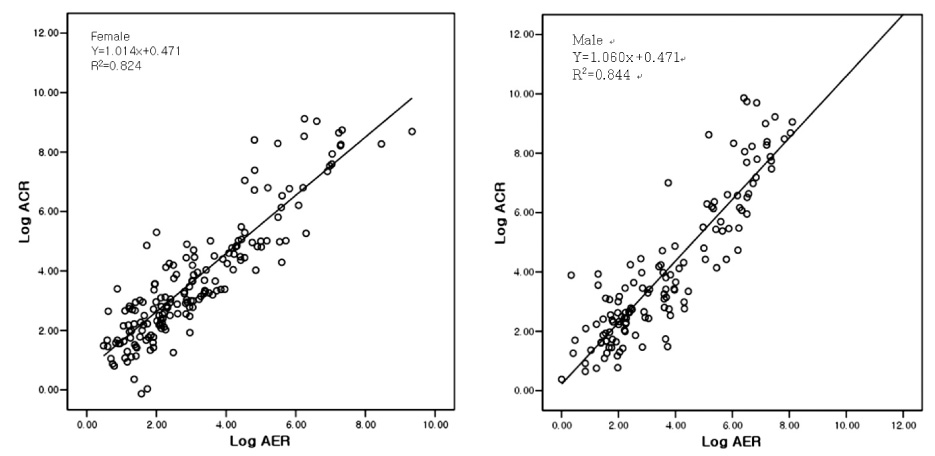
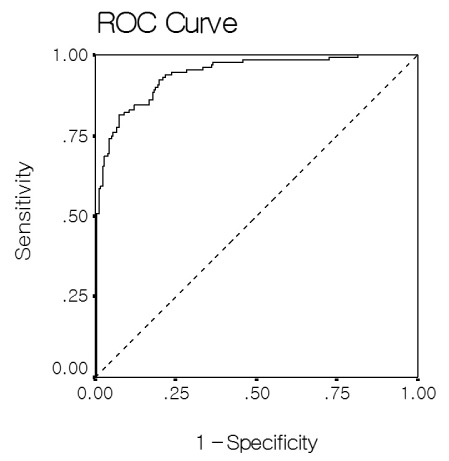
Measuring urine albumin in diabetic patients is an important screening test to identify those individuals at high risk for cardiovascular disease and the progression of kidney disease. Recently, spot urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) has replaced 24 hour-collected urine albumin excretion rate (AER) as a screening test for microalbuminuria given its comparative simplicity. The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the degree of correlation between AER and ACR in the normal, microalbuminuric and macroalbuminuric ranges, and to identify the lower limits of ACR for both genders. METHODS: A total of 310 type 2 diabetics admitted to one center were enrolled in the present study. Following the collection of a spot urine sample, urine was collected for 24 hours and albumin content was measured in both specimens. RESULTS: Mean patient age was 60.2 years. A total of 25.4% had microalbuminuria and 15.8% had macroalbuminuria. The data revealed a strongly positive correlation between AER and ACR across all ranges of albuminuria (R = 0.8). The cut-off value of ACR for 30 mg/day of AER by the regression equation was 24 microgram/mg for men, 42 microgram/mg for women and 31.2 microgram/mg for all patients. The diagnostic performance expressed as the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.938 (95% CI, 0.911-0.965) for ACR. ACR revealed a sensitivity of 84% and specificity of 84%, when a cut-off value of 31.2 microgram/mg was employed. CONCLUSION: ACR was highly correlated with AER, particularly in the range of microalbuminuria. The gender combined cut-off value of ACR in type 2 diabetic patients was determined to be 31.2 microg/mg However, additional studies of large outpatient populations, as opposed to the inpatient population used in the present study, are required to confirm the utility of this value.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weir MR. Albuminuria predicting outcome in diabetes: incidence of microalbuminuria in Asia-Pacific Rim. Kidney Int Suppl. 2004. 92:S38–S39.2. Jensen JS, Feldt RB, Borch JK, Clausen P, Appleyard M, Jensen G. Microabluminuria and its relation to cardiovascular disease and risk factors. A population-based study of 1254 hypertensive individuals. J Hum Hypertens. 1997. 11:727–732.3. Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1987. 31:673–689.4. Malachi JM, Cesar A, Carolyn SF, Fred WW. Microalbuminuria in clinical practice. Arch Intern Med. 1991. 151:1761–1765.5. Boulatov VA, Stenehjem A, Os I. Association between albumin:creatinie ratio and 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure in essential hypertension. Am J hypertens. 2001. 14:338–344.6. Eknoyan G, Hostetter T, Bakris GL, Hebert L, Levey AS, Parving HH, Steffes MW, Toto R. Proteinuria and other markers of chronic kidney disease: a position statement of the national kidney foundation (NKF) and the national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases (NIDDK). Am J Kidney Dis. 2003. 42:617–622.7. Levey AS, Coresh J, Balk E, Kausz AT, Levin A, Steffes MW, Hogg RJ, Perrone RD, Lau J, Eknoyan G. National Kidney Foundation practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Ann Intern Med. 2003. 139:137–147.8. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2009. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:suppl 1. S13–S61.9. Damsgaard EM, Froland A, Jorgensen OD, Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria as predictor of increased mortality in elderly people. BMJ. 1990. 300:297–300.10. Cowell CT, Rogers S, Silink M. First morning urinary albumin concentration is a good predictor of 24-hour urinary albumin excretion in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 1986. 29:97–99.11. Derhaschnig U, Kittler H, Woisetschlager C, Bur A, Herkner H, Hirschl MM. microalbumin measurement alone or calculation of the albumin/creatinine ratio for the screening of hypertension patients? Nephrol dial Transplant. 2002. 17:81–85.12. Houlihan CA, Tsalamandris C, Akdeniz A, Jerums G. albumin to creatinine ratio : a screening test with limiations. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002. 39:1183–1189.13. National Kidney Foundation. clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease : evlaution, classification and stratification. J Kidney Dis. 20. 39(2):suppl 1. S1–S75.14. Chaiken RL, Khawaja R, Bard M. Utility of untimed urinary albumin measurements in assessing albuminuria in black NIDDM subjects. Diabetes Care. 1997. 20:709–713.15. Marshall SM. Screening for microalbuminuria: which measurement? Diabet Med. 1991. 8:706–711.16. Gansevoort RT, Verhave JC, Hillege HL, Burgerhof JG, Bakker SJ, de Zeeuw D, de Jong PE. for the PREVEND Study Group: The validity of screening based on spot morning urine samples to detect subjects with microalbuminuria in the general population. Kidney Int Suppl. 2005. 94:S28–S35.17. Klaus K, Knut BJ, Bo FR, Gorm J, Peter C, Henrik S, Merete A, Jan SJ. Very low levels of microalbuminuria are associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease and death independently of renal function, hypertension, and diabetes. Circulation. 2004. 110:32–35.18. Warram JH, Gearin G, Laffel L, Krolewski AS. Effect of duration of type 1 diabetes on the prevalence of stages of diabetic nephropathy defined by urinary albumin/creatinine ratio. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996. 7:930–937.19. Lee JE, Park JH, Park DJ, Seong EY, Joo KW, Kim YS, Ahn CR, Han JS, Kim SG, Lee JS. Albumin Creatinine Ratio as Screening Test for Microalbuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Korean J Nephrol. 2004. 23:405–411.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spot Urine Albumin to Creatinine Ratio and Serum Cystatin C are Effective for Detection of Diabetic Nephropathy in Childhood Diabetic Patients
- Estimation of Microalbuminuria by Urinary Albumin to Creatinine Concentration Ratio
- The Efficacy of Urinary Albumin-to-Osmolality Ratio in Predicting 24-hour Urine Albumin Excretion in Type 2 DM Patients
- Clinical Utility of Random Spot Urine Protein to Creatinine Ratio Modified by Estimated Daily Creatinine Excretion
- Evaluation of Random Urine Sodium and Potassium Compensated by Creatinine as Possible Alternative Markers for 24 Hours Urinary Sodium and Potassium Excretion