Ann Lab Med.
2015 Mar;35(2):238-241. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.238.
Evaluation of Random Urine Sodium and Potassium Compensated by Creatinine as Possible Alternative Markers for 24 Hours Urinary Sodium and Potassium Excretion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jeongho@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2363185
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.238
Abstract
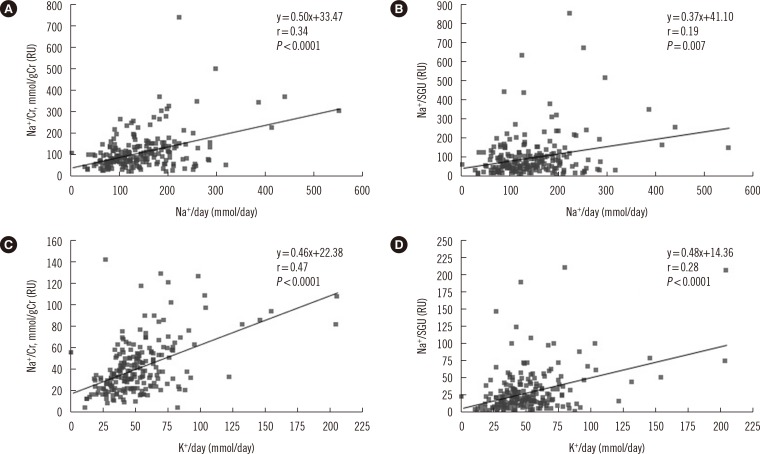
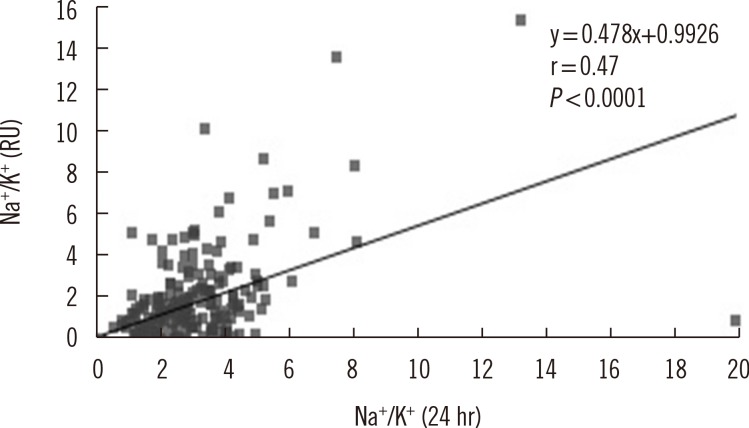
- Sodium and potassium intake was assessed on the basis of its respective excretion levels in 24 hr urine samples. However, owing to the inconvenience of collection, we evaluated random spot urine for alternative sodium and potassium excretion markers. We included 250 patients who submitted 24 hr- and spot urine for clinical tests. However, 22 patients who showed 24 hr urine creatinine excretion levels <500 mg/day were excluded, because these samples possibly resulted from incomplete urine collection. Moreover, 24 patients were excluded because of their use of diuretics during the urine collection period. We observed significant correlations between 24 hr urine sodium excretion and both the sodium/creatinine (r=0.34, P<0.0001) and the sodium/specific gravity unit (SGU) ratios (r=0.19, P=0.007) in random urine samples. Similarly, 24 hr urine potassium excretion and both the spot urine potassium/creatinine (r=0.47, P<0.0001) and potassium/SGU ratios (r=0.28, P<0.0001) were significantly correlated. Although the estimated sodium/creatinine and potassium/creatinine ratios showed a significant correlation with 24 hr urine sodium and potassium excretion, respectively, further studies are required to develop a spot urine test for individualized monitoring of sodium and potassium excretion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ezzati M, Lopez AD, Rodgers A, Vander Hoorn S, Murray CJ. Comparative Risk Assessment Collaborating Group. Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet. 2002; 360:1347–1360. PMID: 12423980.
Article2. Adrogué HJ, Madias NE. Sodium and potassium in the pathogenesis of hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:1966–1978. PMID: 17494929.
Article3. Adrogué HJ, Madias NE. Sodium surfeit and potassium deficit: keys to the pathogenesis of hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2014; 8:203–213. PMID: 24200471.
Article4. Kawano Y, Tsuchihashi T, Matsuura H, Ando K, Fujita T, Ueshima H, et al. Report of the working group for dietary salt reduction of the Japanese society of hypertension: (2) Assessment of salt intake in the management of hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2007; 30:887–893. PMID: 18049019.
Article5. Newman DJ, Pugia MJ, Lott JA, Wallace JF, Hiar AM. Urinary protein and albumin excretion corrected by creatinine and specific gravity. Clin Chim Acta. 2000; 294:139–155. PMID: 10727680.
Article6. Kihara M, Fujikawa J, Ohtaka M, Mano M, Nara Y, Horie R, et al. Interrelationships between blood pressure, sodium, potassium, serum cholesterol, and protein intake in Japanese. Hypertension. 1984; 6:736–742. PMID: 6500679.
Article7. Dahl LK, Leitl G, Heine M. Influence of dietary potassium and sodium/potassium molar ratios on the development of salt hypertension. J Exp Med. 1972; 136:318–330. PMID: 5043414.
Article8. Oliver WJ, Cohen EL, Neel JV. Blood pressure, sodium intake, and sodium related hormones in the Yanomamo Indians, a "no-salt" culture. Circulation. 1975; 52:146–151. PMID: 1132118.
Article9. Mann SJ. Estimation of 24-hour sodium excretion from spot urine samples. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2010; 12:174–180. PMID: 20433530.
Article10. Kwok TC, Chan TY, Woo J. Relationship of urinary sodium/potassium excretion and calcium intake to blood pressure and prevalence of hypertension among older Chinese vegetarians. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2003; 57:299–304. PMID: 12571663.
Article11. Woo J, Ho SC, Donnan S, Swaminathan R. Nutritional correlates of blood pressure in elderly Chinese. J Hum Hypertens. 1988; 1:287–291. PMID: 3221376.12. Woo J, Lau E, Chan A, Cockram C, Swaminathan R. Blood pressure and urinary cations in a Chinese population. J Hum Hypertens. 1992; 6:299–304. PMID: 1433165.13. Bruce NG, Cook DG, Shaper AG, Ratcliffe JG. Casual urine concentrations of sodium, potassium, and creatine in population studies of blood pressure. J Hum Hypertens. 1990; 4:597–602. PMID: 2096199.14. Tanaka T, Okamura T, Miura K, Kadowaki T, Ueshima H, Nakagawa H, et al. A simple method to estimate populational 24-h urinary sodium and potassium excretion using a casual urine specimen. J Hum Hypertens. 2002; 16:97–103. PMID: 11850766.
Article15. Jensen JS, Clausen P, Borch-Johnsen K, Jensen G, Feldt-Rasmussen B. Detecting microalbuminuria by urinary albumin/creatinine concentration ratio. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997; 12(S2):S6–S9.16. Kawasaki T, Ueno M, Uezono K, Kawano Y, Abe I, Kawazoe N, et al. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and circadian rhythm of urine variables in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Jpn Circ J. 1984; 48:168–172. PMID: 6700113.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Comparative Study on the Daily Excretion of Urinary Sodium, Potassium and Volume Between Urban and Rural Korean
- The Comparison of Renal Handling of Sodium and Potassium According to Salt Intake between Control and Hypertensive Group
- Diurnal Variation of Urinary Excretion of Protein Metabolites and Electrolytes
- A Study on the Sodium and Potassium Intakes and Urinary Excretion of Adults in Busan
- The Change of Concentration of Chemicals in the Refrigerated Urine