Ann Dermatol.
2009 May;21(2):120-124. 10.5021/ad.2009.21.2.120.
A Combination of Dual-mode 2,940 nm Er:YAG Laser Ablation with Surgical Excision for Treating Medium-sized Congenital Melanocytic Nevus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, Maryknoll Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Serion Dermatology Clinic, Seoul, Korea. skinewkk@hotmail. com
- KMID: 2219378
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2009.21.2.120
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: There are various treatment options for congenital melanocytic nevus (CMN), including surgical excision, dermabrasions, curettage, laser treatment, chemical peels and cryosurgery. The proper choice of treatment depends on the size, location, thickness and clinical appearance of the nevi, the risk for developing melanoma, the psychological effect and the cosmetic component.
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the outcome of a combination of surgical excision with Er: YAG laser ablation for treating CMNs.
METHODS
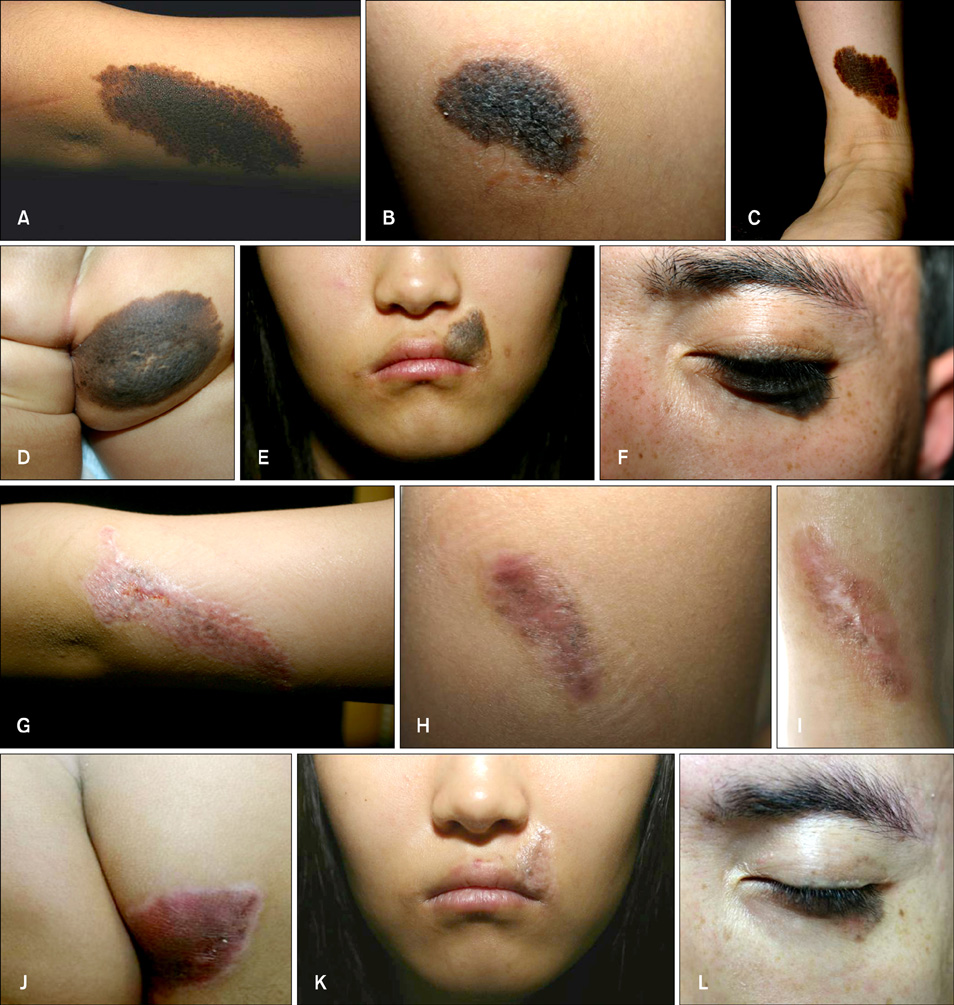
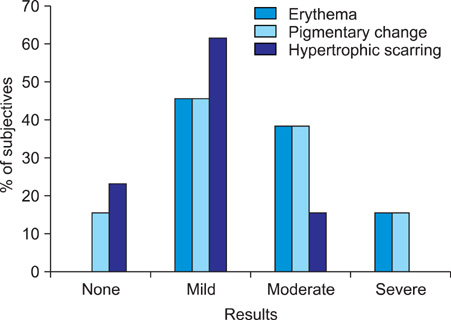
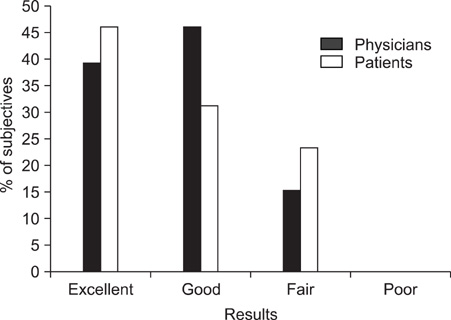
A total of 13 patients were included in this study. The nevus was excised as much as possible and only dermal suturing was performed, without epidermal suturing, for the primary closure. We then ablated the whole lesion, including the suture lines, by using a dual-mode 2,940 nm Er:YAG laser with three to five passes. All the lesions were followed up for 6 months and they were evaluated with respect to the healing status, infection, erythema, scarring, textural change and pigmentary change. Subject satisfaction was scored at the 16th week by the patients.
RESULTS
Eleven (83%) of the 13 patients were clinically rated as having a good to excellent result by the physicians' Global Assessment Scale (GAS) scores for the lesions' reduction of size, the degree of scarring and the pigmentary change with only a one stage procedure. 10 (77%) of the total 13 patients reported a good to excellent result at four months after treatment.
CONCLUSION
A combination of surgical excision with Er:YAG laser ablation as a one stage procedure is a safe, effective modality and it should be considered as one of the options for treating medium-sized CMNs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Conical-Shaped, Staged Laser Ablation Technique in the Removal of a Medium Sized Intradermal Nevus
Sang Hyung Lee, Seung Seog Han, Mi-Woo Lee, Sung Eun Chang
Ann Dermatol. 2018;30(1):122-124. doi: 10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.122.
Reference
-
1. Tromberg J, Bauer B, Benvenuto-Andrade C, Marghoob AA. Congenital melanocytic nevi needing treatment. Dermatol Ther. 2005. 18:136–150.
Article2. Whang KK, Kim MJ, Song WK, Cho S. Comparative treatment of giant congenital melanocytic nevi with curettage or Er:YAG laser ablation alone versus with cultured epithelial autografts. Dermatol Surg. 2005. 31:1660–1667.
Article3. Kopf AW, Bart RS, Hennessey P. Congenital nevocytic nevi and malignant melanomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1979. 1:123–130.
Article4. Hoffman D, Ratner D. Diagnosis and management of a changing congenital melanocytic nevus. Skinmed. 2006. 5:242–245.
Article5. Marghoob AA, Borrego JP, Halpern AC. Congenital melanocytic nevi: treatment modalities and management options. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2003. 22:21–32.
Article6. Arneja JS, Gosain AK. Giant congenital melanocytic nevi. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007. 120:26e–40e.
Article7. Konz B. Therapy of congenital melanocytic nevi. Excision, dermabrasion, laser. Hautarzt. 2007. 58:659–660. 662–666. 668–670.8. Kanzler MH. Management of large congenital melanocytic nevi: art versus science. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 54:874–876.
Article9. Watt AJ, Kotsis SV, Chung KC. Risk of melanoma arising in large congenital melanocytic nevi: a systematic review. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. 113:1968–1974.
Article10. Sahin S, Levin L, Kopf AW, Rao BK, Triola M, Koenig K, et al. Risk of melanoma in medium-sized congenital melanocytic nevi: a follow-up study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998. 39:428–433.
Article11. Shipkov CD, Anastassov YK, Yonkov A. The place of laser treatment in the management of congenital melanocytic nevi. Ann Plast Surg. 2006. 56:222–224.
Article12. Lawrence CM. Treatment options for giant congenital naevi. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000. 25:7–11.
Article13. Bauer BS, Few JW, Chavez CD, Galiano RD. The role of tissue expansion in the management of large congenital pigmented nevi of the forehead in the pediatric patient. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001. 107:668–675.
Article14. Burd A. Laser treatment of congenital melanocytic nevi. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. 113:2232–2233.
Article15. Helsing P, Mork G, Sveen B. Ruby laser treatment of congenital melanocytic naevi--a pessimistic view. Acta Derm Venereol. 2006. 86:235–237.
Article16. Kono T, Ercocen AR, Nozaki M. Treatment of congenital melanocytic nevi using the combined (normal-mode plus Q-switched) ruby laser in Asians: clinical response in relation to histological type. Ann Plast Surg. 2005. 54:494–501.
Article17. Kim S, Kang WH. Treatment of congenital nevi with the Q-switched Alexandrite laser. Eur J Dermatol. 2005. 15:92–96.18. Noordzij MJ, van den Broecke DG, Alting MC, Kon M. Ruby laser treatment of congenital melanocytic nevi: a review of the literature and report of our own experience. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. 114:660–667.
Article19. Grevelink JM, van Leeuwen RL, Anderson RR, Byers HR. Clinical and histological responses of congenital melanocytic nevi after single treatment with Q-switched lasers. Arch Dermatol. 1997. 133:349–353.
Article20. Rajpar SF, Abdullah A, Lanigan SW. Er:YAG laser resurfacing for inoperable medium-sized facial congenital melanocytic naevi in children. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007. 32:159–161.
Article21. Ostertag JU, Quaedvlieg PJ, Kerckhoffs FE, Vermeulen AH, Bertleff MJ, Venema AW, et al. Congenital naevi treated with erbium:YAG laser (Derma K) resurfacing in neonates: clinical results and review of the literature. Br J Dermatol. 2006. 154:889–895.
Article22. Horner BM, El-Muttardi NS, Mayou BJ. Treatment of congenital melanocytic naevi with CO2 laser. Ann Plast Surg. 2005. 55:276–280.
Article23. Reynolds N, Kenealy J, Mercer N. Carbon dioxide laser dermabrasion for giant congenital melanocytic nevi. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. 111:2209–2214.
Article24. Dave R, Mahaffey PJ. Combined early treatment of congenital melanocytic naevus with carbon dioxide and NdYag lasers. Br J Plast Surg. 2004. 57:720–724.
Article25. Park SH, Koo SH, Choi EO. Combined laser therapy for difficult dermal pigmentation: resurfacing and selective photothermolysis. Ann Plast Surg. 2001. 47:31–36.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- To What Depth Is a Congenital Melanocytic Nevus Affected by 84 Pigment Laser Treatments?
- Efficacy and Safety of 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser Treatment for Removing Melanocytic Nevi
- A Case of Malignant Melanoma Possibly Arising in a Medium-sized Congenital Melanocytic Nevus
- Intense Pulsed Light Alone and in Combination with Erbium Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet Laser on Small-to-Medium Sized Congenital Melanocytic Nevi: Single Center Experience Based on Retrospective Chart Review
- Hypopigmentation Occurred After Er: YAG Laser Resurfacing