Ann Dermatol.
2017 Feb;29(1):39-47. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.39.
Intense Pulsed Light Alone and in Combination with Erbium Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet Laser on Small-to-Medium Sized Congenital Melanocytic Nevi: Single Center Experience Based on Retrospective Chart Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, Incheon, Korea. hazelkimhoho@gmail.com
- KMID: 2368026
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.39
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Treatment of congenital melanocytic nevi (CMN) with intense pulsed light (IPL) has recently produced promising results.
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the clinical and histological outcomes of small-to-medium sized CMN treated with IPL alone and in combination with erbium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Er: YAG) laser.
METHODS
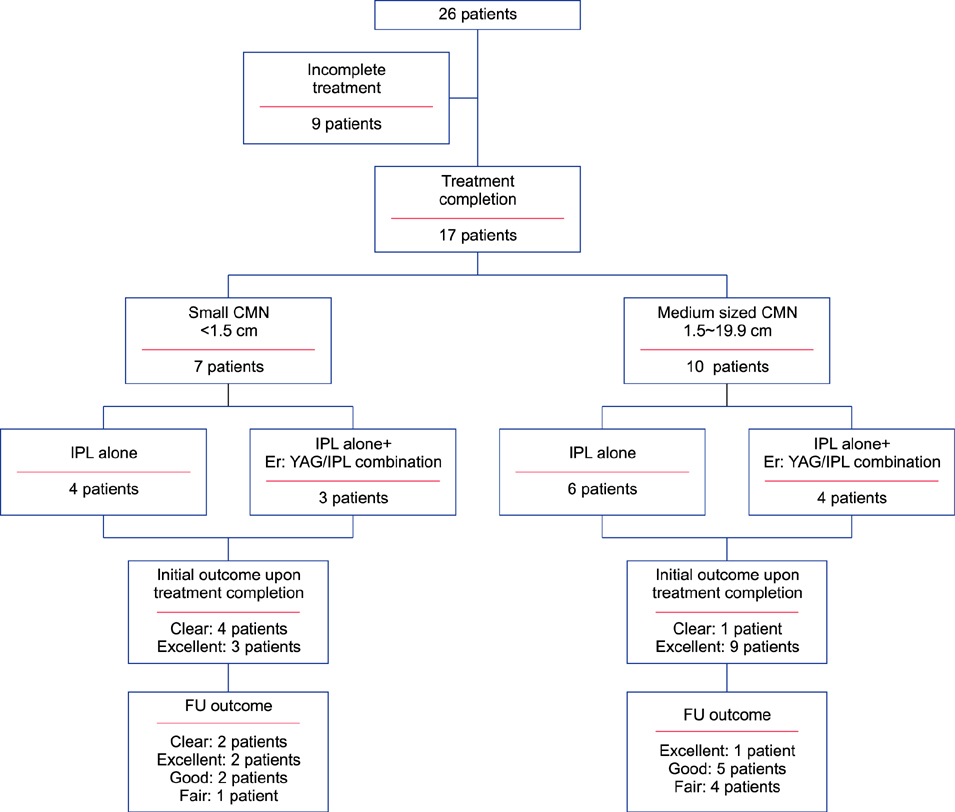
We performed a retrospective chart review of 26 small-to-medium sized CMN treated as described above. The reduction in visible pigmentation, signs of recurrence and any adverse skin changes were evaluated by two independent clinicians.
RESULTS
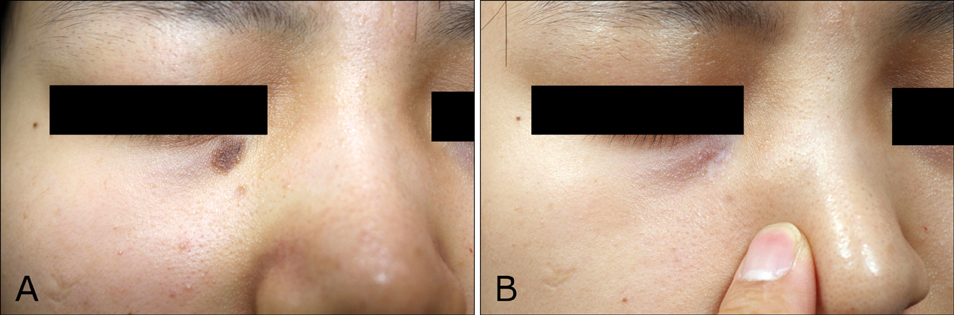
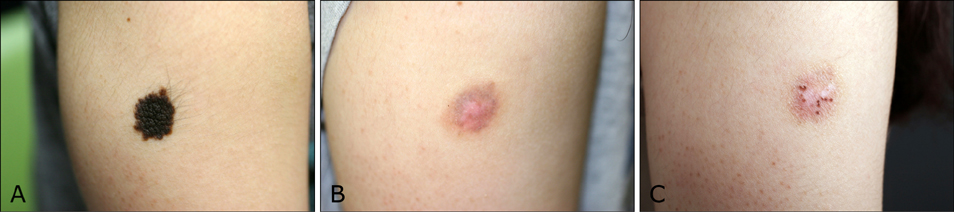
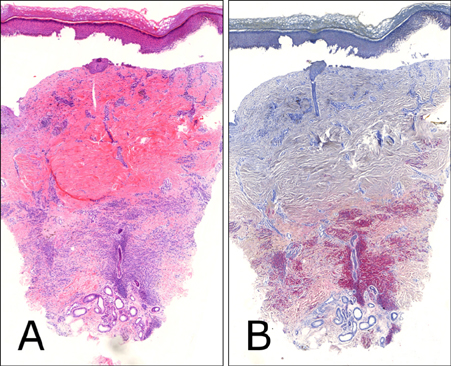
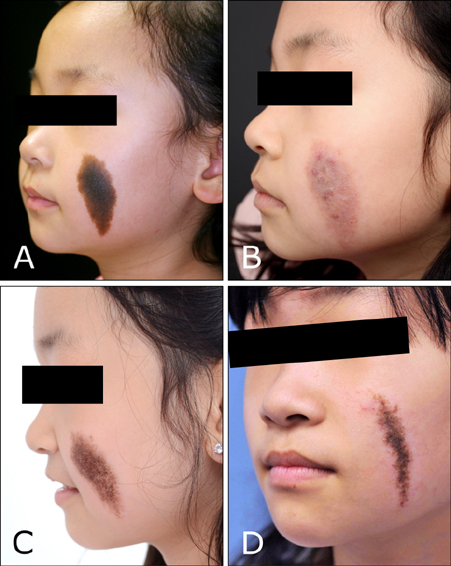
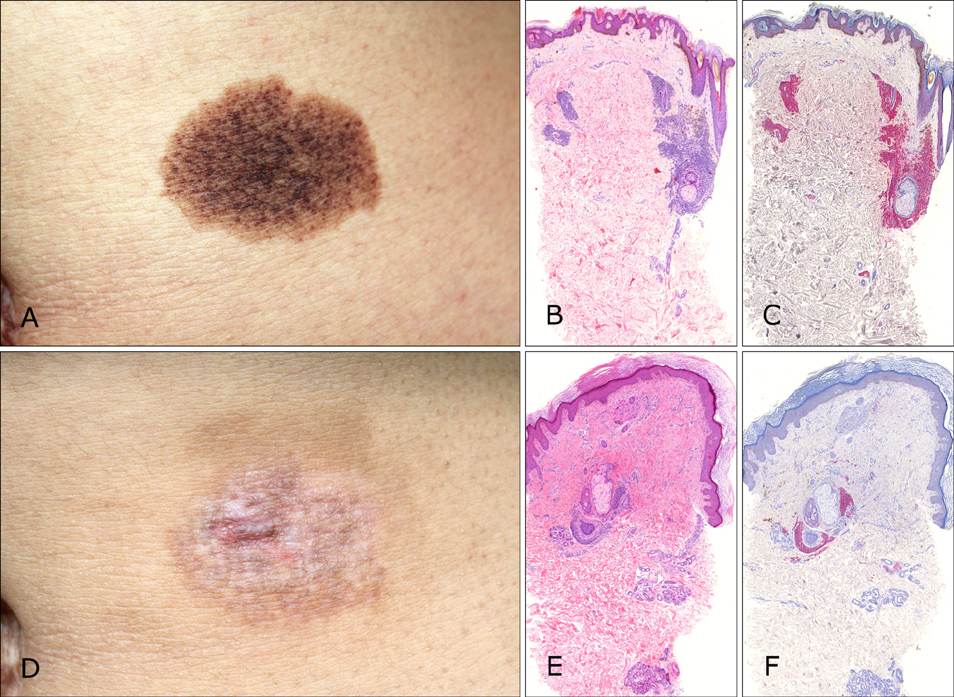
Seventeen patients completed treatment and were followed-up. Nine were not able to complete treatment due to work, change in residence, and treatment related stress. Ten patients received IPL alone (mean: 10.5 sessions) and 7 underwent treatment with IPL (mean: 7.7 sessions) and Er: YAG/IPL combination therapy (mean: 4.7 sessions). The initial treatment outcome was cleared in 5 patients and excellent in 12. Fourteen patients (82.4%) showed CMN recurrence one year after treatment completion. The histological results from a patient with an excellent clinical outcome showed remnant nevus cells nests in the deep dermis.
CONCLUSION
IPL treatment alone and in combination with Er: YAG laser are not definitive treatments for CMN and should not be considered as first-line treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Krengel S. Nevogenesis--new thoughts regarding a classical problem. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005; 27:456–465.
Article2. Kopf AW, Bart RS, Hennessey P. Congenital nevocytic nevi and malignant melanomas. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1979; 1:123–130.
Article3. Alikhan A, Ibrahimi OA, Eisen DB. Congenital melanocytic nevi: where are we now? Part I. Clinical presentation, epidemiology, pathogenesis, histology, malignant transformation, and neurocutaneous melanosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012; 67:495.e1–495.e17.4. Ibrahimi OA, Alikhan A, Eisen DB. Congenital melanocytic nevi: where are we now? Part II. Treatment options and approach to treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012; 67:515.e1–515.e13.5. Marghoob AA, Agero AL, Benvenuto-Andrade C, Dusza SW. Large congenital melanocytic nevi, risk of cutaneous melanoma, and prophylactic surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006; 54:868–870.
Article6. Kinsler VA, Chong WK, Aylett SE, Atherton DJ. Complications of congenital melanocytic naevi in children: analysis of 16 years' experience and clinical practice. Br J Dermatol. 2008; 159:907–914.
Article7. Dawson HA, Atherton DJ, Mayou B. A prospective study of congenital melanocytic naevi: progress report and evaluation after 6 years. Br J Dermatol. 1996; 134:617–623.
Article8. Berg P, Lindelöf B. Congenital melanocytic naevi and cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2003; 13:441–445.
Article9. Tannous ZS, Mihm MC Jr, Sober AJ, Duncan LM. Congenital melanocytic nevi: clinical and histopathologic features, risk of melanoma, and clinical management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005; 52:197–203.
Article10. Zaal LH, Mooi WJ, Klip H, van der Horst CM. Risk of malignant transformation of congenital melanocytic nevi: a retrospective nationwide study from The Netherlands. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 116:1902–1909.
Article11. Al-Hadithy N, Al-Nakib K, Quaba A. Outcomes of 52 patients with congenital melanocytic naevi treated with UltraPulse Carbon Dioxide and Frequency Doubled Q-Switched Nd-Yag laser. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012; 65:1019–1028.
Article12. Lee JM, Kim IH, Rhyu IJ, Ryu HJ. Combined intense pulsed light and Er:YAG laser treatment of congenital melanocytic nevus. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2015; 17:162–164.
Article13. Moreno-Arias GA, Ferrando J. Noncoherent-intense-pulsed light for the treatment of relapsing hairy intradermal melanocytic nevus after shave excision. Lasers Surg Med. 2001; 29:142–144.
Article14. Minakawa S, Takeda H, Korekawa A, Kaneko T, Urushidate S, Sawamura D. Q-switched ruby laser therapy and longterm follow-up evaluation of small to medium-sized congenital melanocytic naevi. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012; 37:438–440.
Article15. Lee SE, Choi JY, Hong KT, Lee KR. Treatment of acquired and small congenital melanocytic nevi with combined Er: YAG laser and long-pulsed alexandrite laser in Asian skin. Dermatol Surg. 2015; 41:473–480.
Article16. Arora H, Falto-Aizpurua L, Chacon A, Griffith RD, Nouri K. Lasers for nevi: a review. Lasers Med Sci. 2015; 30:1991–2001.
Article17. Moreno Arias GA, Ferrando J. Intense pulsed light for melanocytic lesions. Dermatol Surg. 2001; 27:397–400.
Article18. Martín JM, Monteagudo C, Bella R, Reig I, Jordá E. Complete regression of a melanocytic nevus under intense pulsed light therapy for axillary hair removal in a cosmetic center. Dermatology. 2012; 224:193–197.
Article19. Raulin C, Hellwig S, Schönermark MP. Treatment of a nonresponding port-wine stain with a new pulsed light source (PhotoDerm VL). Lasers Surg Med. 1997; 21:203–208.
Article20. Weiss RA, Weiss MA, Marwaha S, Harrington AC. Hair removal with a non-coherent filtered flashlamp intense pulsed light source. Lasers Surg Med. 1999; 24:128–132.
Article21. Kawada A, Shiraishi H, Asai M, Kameyama H, Sangen Y, Aragane Y, et al. Clinical improvement of solar lentigines and ephelides with an intense pulsed light source. Dermatol Surg. 2002; 28:504–508.
Article22. Goldberg DJ. Current trends in intense pulsed light. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012; 5:45–53.23. Kilmer SL, Lee MS, Grevelink JM, Flotte TJ, Anderson RR. The Q-switched Nd:YAG laser effectively treats tattoos. A controlled, dose-response study. Arch Dermatol. 1993; 129:971–978.
Article24. Bjerring P, Christiansen K. Intense pulsed light source for treatment of small melanocytic nevi and solar lentigines. J Cutan Laser Ther. 2000; 2:177–181.
Article25. Anderson RR, Parrish JA. Selective photothermolysis: precise microsurgery by selective absorption of pulsed radiation. Science. 1983; 220:524–527.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Prospective Split-Face Comparative Study of Periorbital Wrinkle Treatments: Fractional Erbium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Laser, Intense Pulsed Light, and Topical 0.1% Tretinoin Cream
- Intense Pulsed Light and Q-Switched 1,064-nm Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Laser Treatment for the Scarring Lesion of Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
- Treatment of Facial Wrinkels with Char-Free Carbon Dioxide Laser and Erbium: YAG Laser
- Erbium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Laser to Treat Familial Acanthosis Nigricans
- A Case of Malignant Melanoma Possibly Arising in a Medium-sized Congenital Melanocytic Nevus