J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Sep;55(9):1267-1271. 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.9.1267.
Orbital Morphology for Decompression Surgery in Thyroid Eye Disease Using 2-D Orbital CT and 4 Parameters
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shbaek6534@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Nune Eye Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2217107
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2014.55.9.1267
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To present easily measurable 2D orbit computed tomography (CT) reference data that can be used in a preoperative study for orbital decompression and classification of individual orbital morphologies.
METHODS
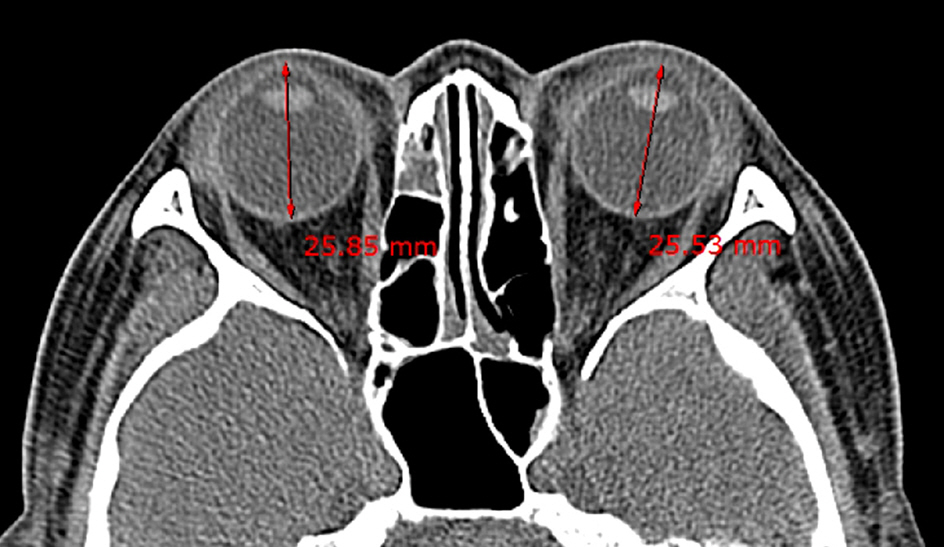
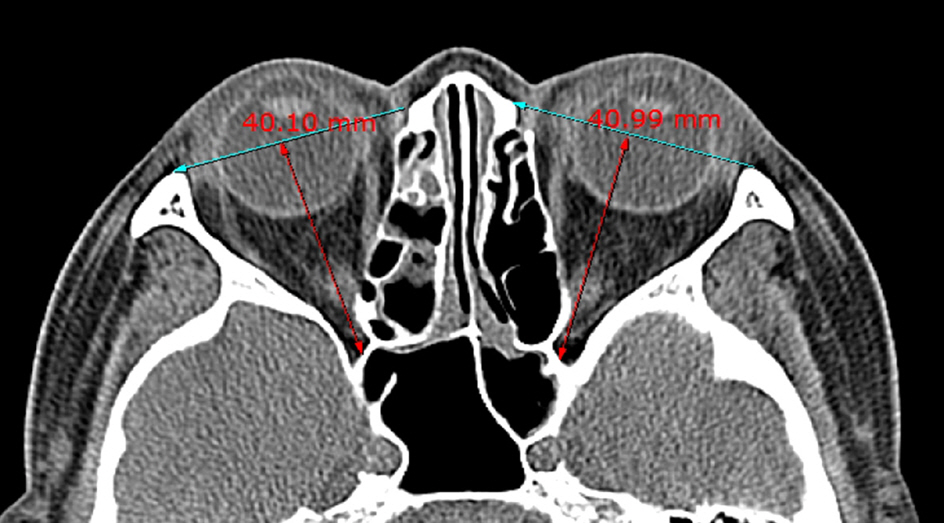
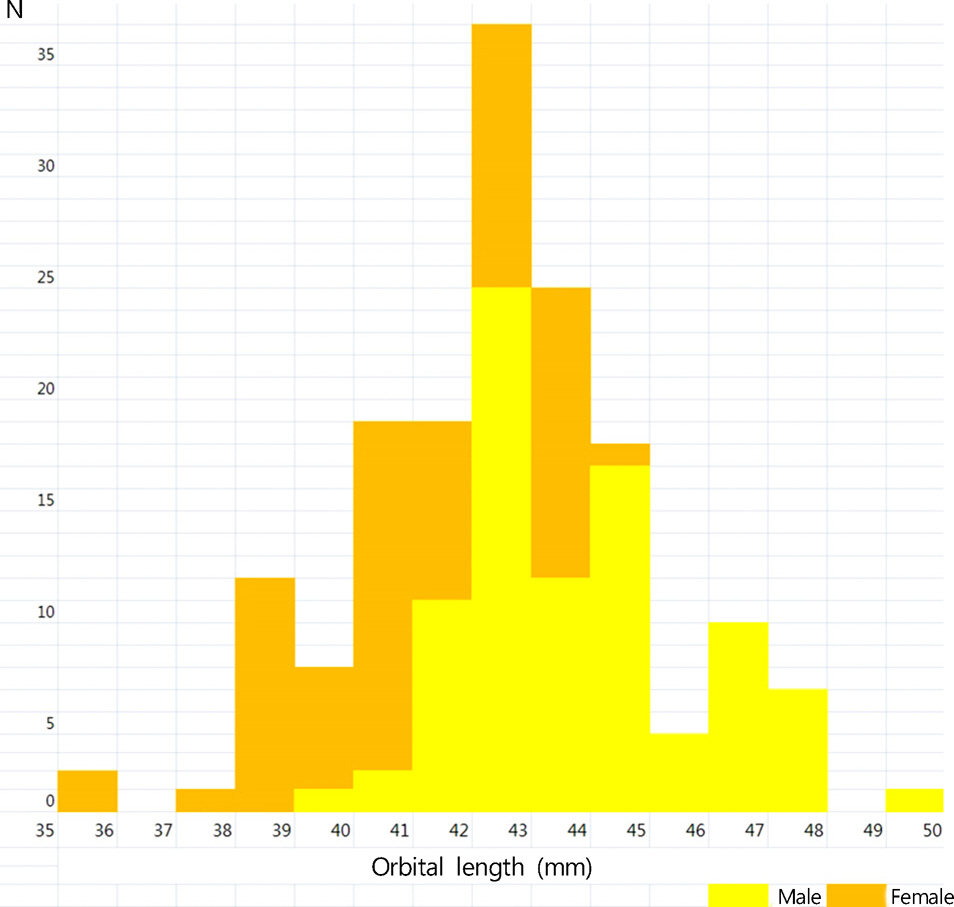
The study sample was composed of 77 patients with orbital contusion (42 Asian males + 35 Asian females = 154 orbits) who visited the emergency room of the Korea University Guro Hospital from September 2012 to June 2013. Patients with orbital wall fracture, retrobulbar hemorrhage, or eyeball rupture were excluded. Medical records including 2D orbit or facial bone CT were retrospectively reviewed and 4 orbital parameters (orbital length, OL; globe length, GL; GL/OL ratio and 2D cone angle) were measured.
RESULTS
The average OL was 42.53 +/- 2.46 mm (35.63-49.09 mm) and average GL was 24.83 +/- 1.09 mm (22.75-28.13 mm). The average GL/OL ratio using these 2 parameters was 0.59 +/- 0.04 (0.50-0.68). The posterior cone angle was on average, 45.96 +/- 5.91degrees (29.35-60.04degrees).
CONCLUSIONS
Simple measurement of 4 parameters using 2D orbit CT and classification of Asian individual orbital morphology may help in the choice of the most effective surgical technique for decompression surgery in thyroid eye disease patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bartalena L, Pinchera A, Marcocci C. Management of Graves' ophthalmopathy: reality and perspectives. Endocr Rev. 2000; 21:168–99.
Article2. Bahn RS. Graves' ophthalmopathy. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:726–38.
Article3. Borumandi F, Hammer B, Kamer L, von Arx G. How predictable is exophthalmos reduction in Graves' orbitopathy? A review of the literature. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011; 95:1625–30.
Article4. Borumandi F, Hammer B, Noser H, Kamer L. Classification of orbital morphology for decompression surgery in Graves' orbitopathy: two-dimensional versus three-dimensional orbital parameters. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013; 97:659–62.
Article5. McKeag D, Lane C, Lazarus JH, et al. Clinical features of dysthyroid optic neuropathy: a European Group on Graves' Orbitopathy (EUGOGO) survey. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007; 91:455–8.
Article6. Mourits MP, Bijl H, Altea MA, et al. Outcome of orbital decompression for disfiguring proptosis in patients with Graves' orbitopathy using various surgical procedures. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:1518–23.7. Baujat B, Krastinova D, Bach CA, et al. Orbital morphology in exophthalmos and exorbitism. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 117:542–50.
Article8. Campi I, Vannucchi GM, Minetti AM, et al. A quantitative method for assessing the degree of axial proptosis in relation to orbital tissue involvement in Graves' orbitopathy. Ophthalmology. 2013; 120:1092–8.
Article9. Dickinson AJ, Perros P. Controversies in the clinical evaluation of active thyroid-associated orbitopathy: use of a detailed protocol with comparative photographs for objective assessment. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2001; 55:283–303.
Article10. Vardizer Y, Berendschot TT, Mourits MP. Effect of exophthalmometer design on its accuracy. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 21:427–30.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Associations between Orbital Morphology and Exophthalmos Changes after Endoscopic Orbital Decompression to Treat Thyroid-related Orbitopathy
- Three Wall Orbital Decompression for Compressive Optic Neuropathy in Thyroid Ophthalmopathy
- The Effect of Previous Orbital Decompression on Outcome of Strabismus Surgery in Patients with Thyroid Ophthalmopathy
- A Case of Imploding Antrum (Silent Sinus) Syndrome after Orbital Decompression
- Evaluation of Stereotactic Navigation During Orbital Decompression in Thyroid-Associated Orbitopathy Patients