J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Mar;54(3):462-468. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.3.462.
Optic Cup Slope as a Numeric Representative of Glaucomatous Cupping
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. jhchang@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2216767
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.3.462
Abstract
- PURPOSE
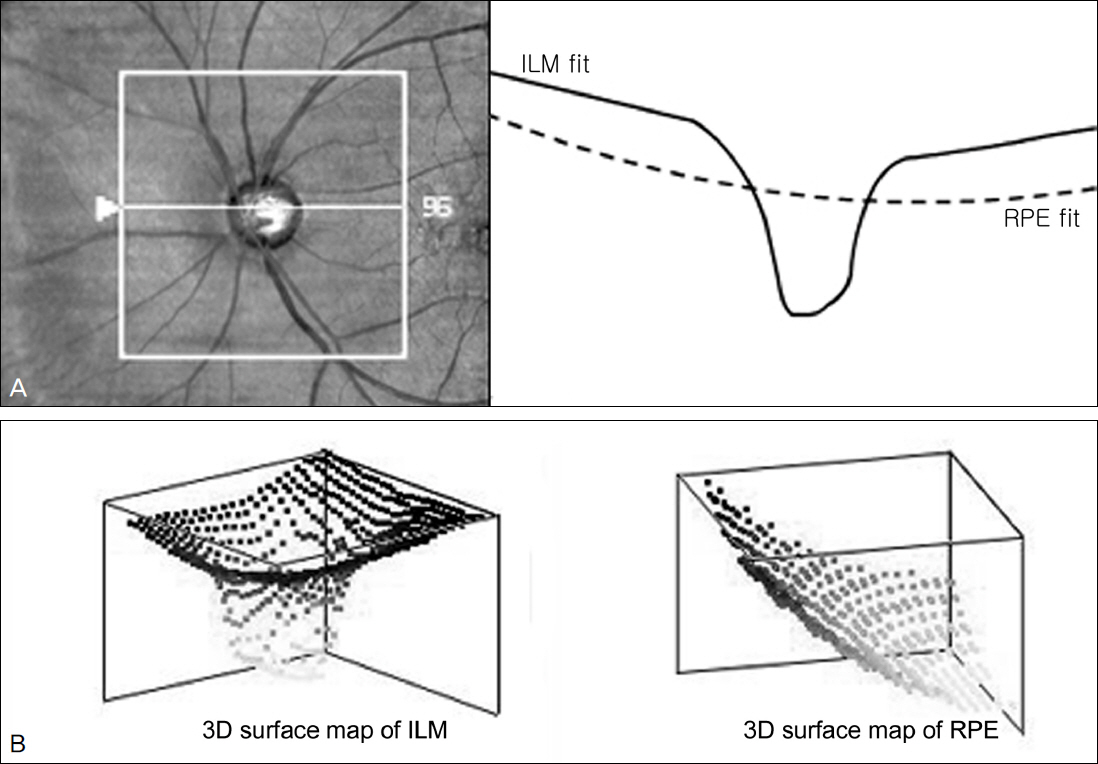
To objectively define the degree of cupping, the authors extracted 3-dimensional slope surface maps from Cirrus HDTM-OCT data and assessed their differentiating characteristics between normal subjects and glaucomatous patients.
METHODS
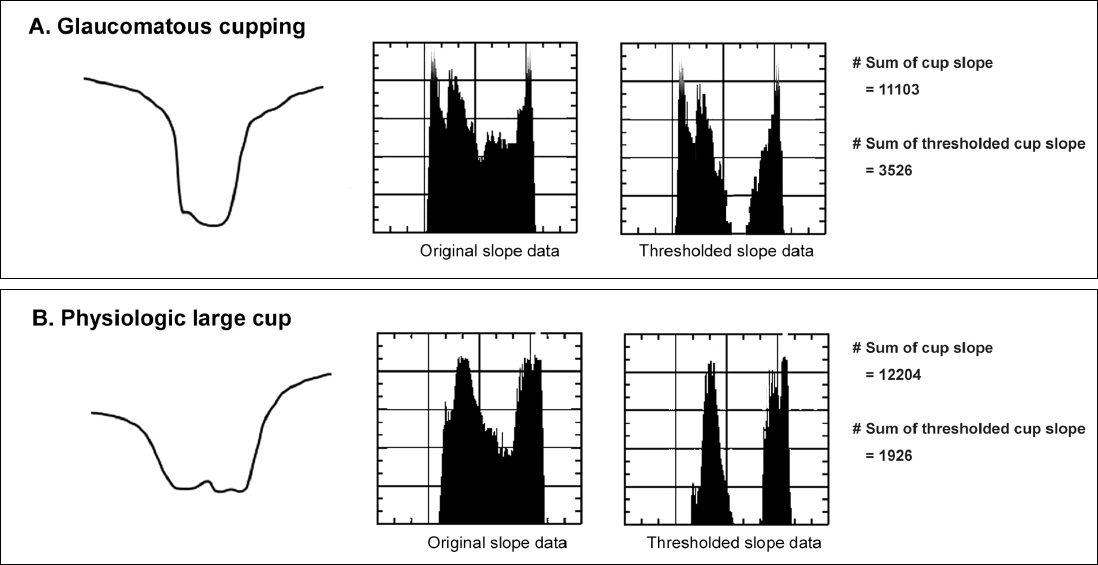
One eye from each of 40 normal subjects and 1 eye from each of 39 patients with glaucoma were examined using automated visual field perimetry and Cirrus HDTM-OCT. The Optic Disc Cube 200 x 200 protocol was performed. The individual OCT data were reconstructed as the 3-dimensional surface maps of the optic disc cup and the slope of each contour was calculated using custom-developed software. Several disc cup slope parameters were derived. The parameters measuring the internal features of the optic disc cup were calculated and compared between groups.
RESULTS
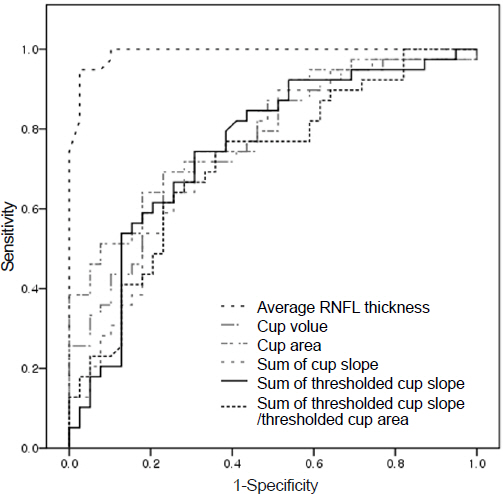
Sum of cup slope, sum of thresholded cup slope, and sum of thresholded cup slope / thresholded cup area parameters were differentiating factors between the normal and glaucoma groups (p < 0.05). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) value of the slope parameters ranged from 0.718 to 0.753. The sum of thresholded cup slope / thresholded cup area parameter was well correlated with visual field mean deviation (r = -0.250, p = 0.028).
CONCLUSIONS
The optic disc cup slope parameter obtained with OCT may be a useful parameter for representing glaucomatous cupping.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. RR Allingham, KF Damji, S Freedman. Shields' textbook of glaucoma. 5th ed.Lippincott Willliams & Wilkins;2005. chap. 5.2. Hayreh SS. Pathogenesis of cupping of the optic disc. Br J Ophthalmol. 1974; 58:863–76.
Article3. Quigley HA, Addicks EM, Green WR, Maumenee AE. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. II. The site of injury and susceptibility to damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99:635–49.
Article4. Quigley HA, Green WR. The histology of human glaucoma cupping and optic nerve damage: clinicopathologic correlation in 21 eyes. Ophthalmology. 1979; 86:1803–30.
Article5. Miglior S, Casula M, Guareschi M, et al. Clinical ability of Heidelberg retinal tomograph examination to detect glaucomatous visual field changes. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:1621–7.6. Schuman JS, Wollstein G, Farra T, et al. Comparison of optic nerve head measurements obtained by optical coherence tomography and confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 135:504–12.
Article7. Dong J, Chihara E. Slope analysis of the optic disc in eyes with ocular hypertension and early normal tension glaucoma by confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001; 85:56–62.
Article8. Cullinane AB, Waldock A, Diamond JP, Sparrow JM. Optic disc cup slope and visual field indices in normal, ocular hypertensive and early glaucomatous eyes. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:555–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reversibility of Optic Disc Cupping after Trabeculectomy in Adult Glaucoma Patients Measured by Heidelberg Retina Tomograph
- Reversal of Optic Disc Cupping in Adults with Advanced Glaucoma
- Short-term change of optic nerve head topography after trabeculectomy in adult glaucoma patients as measured by Heidelberg retina tomograph
- A Case of Optic Nerve Atrophy with Severe Disc Cupping after Methanol Poisoning
- Clinical Application of Quantitative Evaluation of Disc Pattern for Early Diagnosis of Simple Glaucoma