J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Feb;54(2):346-350. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.2.346.
A Case of Rosai-Dorfman Disease Affecting the Palpebral Conjunctiva
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. eye@cha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2216673
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.2.346
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report a single case of Rosai-Dorfman disease of the palpebral conjunctiva with a review of the relevant literature.
CASE SUMMARY
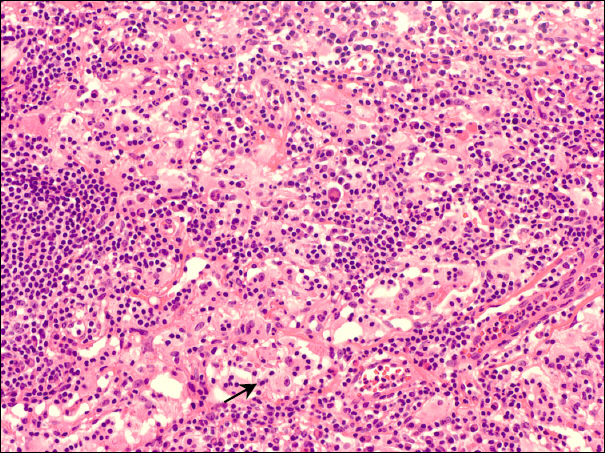
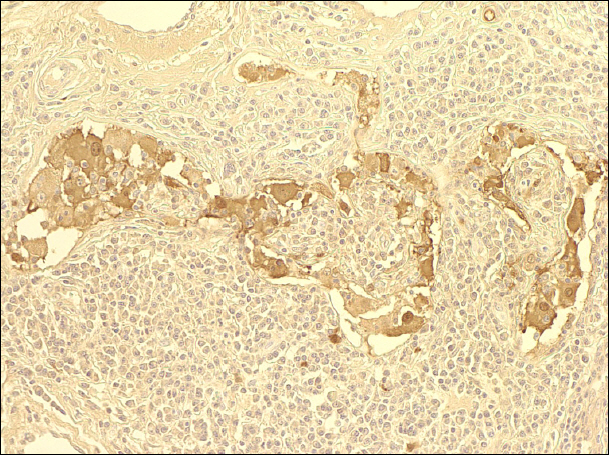
A 39-years-old woman presented with a palpebral conjunctival mass 3 weeks in duration on both eyes. The patient had a history of excisional biopsy of lymphadenitis and wanted to remove the mass for cosmetic reasons. An excisional biopsy was performed to obtain a diagnosis for proper management. The histopathologic examination of the lesion showed an intensive proliferation of monotonous and histiocytoid cells beneath the epidermis. Immunohistochemical staining for the S-100 protein was positive and anti-CD1A antibody was negative. Five months after mass excision, there was no evidence of recurrence.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Rosai J, Dorfman RF. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. A newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch Pathol. 1969; 87:63–70.2. Kaltman JM, Best SP, McClure SA. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy Rosai-Dorfman disease: a unique case presentation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011; 112:124–6.
Article3. Lai KL, Abdullah V, Ng KS, et el. Rosai-dorfman disease: Presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Head Neck. 2011; Nov. 15. PMID: 10.1002/hed.21930. [Epub ahead of print].
Article4. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman Disease). Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990; 7:1–86.5. Abdollahi A, Ardalan FA, Ayati M. Extranodal Rosai-Dorfman disease of the kidney. Ann Saudi Med. 2009; 29:55–7.
Article6. Kim KH, Shim JH, Seo SW. Neurilemoma of the bulbar conjunctiva: Report of one case. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:923–6.
Article7. Grossniklaus HE, Green WR, Luckenbach M, Chan CC. Conjunctival lesions in adults. A clinical and histopathologic review. Cornea. 1987; 6:78–116.
Article8. Chang WS, Park JB, Kim KH, Kim SY. Two cases of conjunctival mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphomas treated by cryotherapy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1165–72.
Article9. Lee YS, Lee MI, Park TS, Lee SY. The prognosis of ocular-adnexal lymphoproliferative lesions. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:1260–7.10. Kroumpouzos G, Demierre MF. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: histopathological presentation as inflammatory pseudotumor. A literature review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002; 82:292–6.11. Hazarika P, Nayak DR, Balakrishnan R, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease of the subglottis. J Laryngol Otol. 2000; 114:970–3.
Article12. Carbone A, Passannante A, Gloghini A, et al. Review of sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease) of head and neck. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999; 108(11 Pt 1):1095–104.
Article13. Bernácer-Borja M, Blanco-Rodríguez M, Sanchez-Granados JM, et al. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (RosaiDorfman disease): clinico-pathological study of three cases. Eur J Pediatr. 2006; 165:536–9.
Article14. Bist SS, Bisht M, Varshney S, Kishore S. Rosai-Dorfman disease. Ear Nose Throat J. 2008; 87:16–7.
Article15. Cossor F, Al-Khater AH, Doll DC. Laryngeal obstruction and hoarseness associated with Rosai-Dorfman disease. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:1953–5.
Article16. Gaitonde S. Multifocal, extranodal sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: an overview. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007; 131:1117–21.
Article17. Finger PT, Perry HD, Kempin S, Iacob CE. High-frequency ultra-sound of extranodal limbal Rosai-Dorfman disease: affecting the conjunctiva, sclera, and cornea. Cornea. 2007; 26:888–90.18. Kala C, Agarwal A, Kala S. Extranodal manifestation of RosaiDorfman disease with bilateral ocular involvement. J Cytol. 2011; 28:131–3.
Article19. Kumar B, Karki S, Paudyal P. Diagnosis of sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease) by fine needle aspiration cytology. Diagn Cytopathol. 2008; 36:691–5.
Article20. Levine PH, Jahan N, Murari P, et al. Detection of human herpesvirus 6 in tissues involved by sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease). J Infect Dis. 1992; 166:291–5.
Article21. Pulsoni A, Anghel G, Falcucci P, et al. Treatment of sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): report of a case and literature review. Am J Hematol. 2002; 69:67–71.
Article22. Aluffi P, Prestinari A, Ramponi A, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease of the larynx. J Laryngol Otol. 2000; 114:565–7.
Article23. Komp DM. The treatment of sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease). Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990; 7:83–6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman Disease Enlarged in Size after Punch Biopsy
- Rosai-Dorfman Disease in the Neck and Subglottis
- A Case of Rosai-Dorfman Disease Limited to the Lip
- Rapidly Growing Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman Disease Successfully Treated with Surgical Excision
- A Case of Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman Disease on the Face Well Improved with Low-dose Systemic Corticosteroid