J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2012 Jul;53(7):988-995. 10.3341/jkos.2012.53.7.988.
Comparison of Rebound Tonometer, Non-Contact Tonometer, Goldmann Applanation Tonometer and the Relationship to Central Corneal Thickness
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea. goddns76@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2215858
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2012.53.7.988
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the level of accuracy of intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements of a rebound tonometer (RT) Icare(R), and non-contact tonometer (NCT), using Goldmann Applanation tonometer (GAT) as a reference to evaluate the influence of central corneal thickness (CCT) on IOP readings in the Korean population.
METHODS
In a prospective study of 273 eyes, IOP was measured with RT, GAT, and NCT and compared to CCT measurements. Patients were assigned to one of 3 groups based on IOP measurements of GAT and 1 of 2 groups based on CCT. The comparison of the IOP values of RT, GAT, and NCT was performed between the IOP and CCT groups, and the differences among tonometers were evaluated.
RESULTS
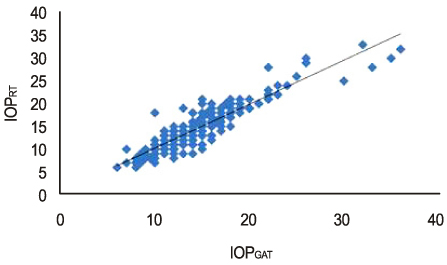
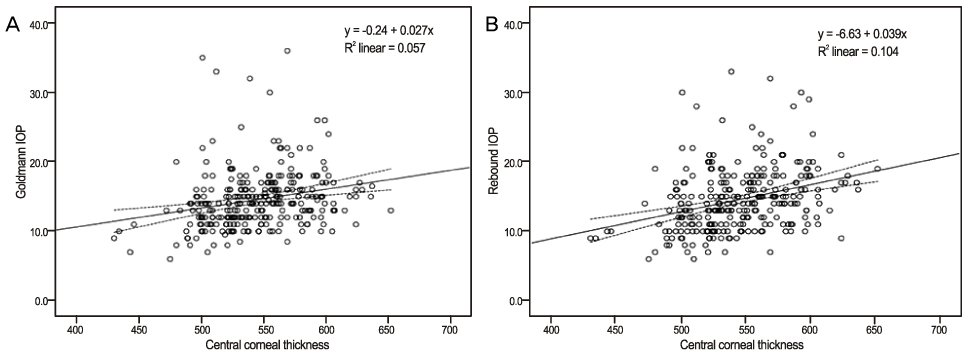
The RT showed statistically significant correlation with the GAT compared to the NCT. The CCT was related to RT measurements. The RT values compared to the GAT was underestimated in thin corneas and overestimated in thick corneas.
CONCLUSIONS
There was a significant correlation between the RT and the GAT measurements compared with the NCT. However, RT is influenced by CCT and correlates less with GAT in low IOP ranges, suggesting that corneal thickness should be taken into consideration during such measurements.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of Intraocular Pressures According to Position Using Icare Rebound Tonometer
Hae Jin Kim, Kayoung Yi
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(7):1049-1055. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.7.1049.
Reference
-
1. Landers J, Goldberg I, Graham SL. Analysis of risk factors that may be associated with progression from ocular hypertension to primary open angle glaucoma. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2002. 30:242–247.2. Johnson M, Kass MA, Moses RA, Grodzki WJ. Increased corneal thickness simulating elevated intraocular pressure. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978. 96:664–665.3. Stodtmeister R. Applanation tonometry and correction according to corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1998. 76:319–324.4. Doughty MJ, Zaman ML. Human corneal thickness and its impact on intraocular pressure measures: a review and meta-analysis approach. Surv Ophthalmol. 2000. 44:367–408.5. Nakamura M, Darhad U, Tatsumi Y, et al. Agreement of rebound tonometer in measuring intraocular pressure with three types of applanation tonometers. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006. 142:332–334.6. Fernandes P, Díaz-Rey JA, Queirós A, et al. Comparison of the ICare rebound tonometer with the Goldmann tonometer in a normal population. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2005. 25:436–440.7. Jorge J, Fernandes P, Queirós A, et al. Comparison of the IOPen and iCare rebound tonometers with the Goldmann tonometer in a normal population. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2010. 30:108–112.8. Brusini P, Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M, et al. Comparison of ICare tonometer with Goldmann applanation tonometer in glaucoma patients. J Glaucoma. 2006. 15:213–217.9. Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Castillo A, Garcia-Sanchez J. Reproducibility and clinical evaluation of rebound tonometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. 46:4578–4580.10. Flemmons MS, Hsiao YC, Dzau J, et al. Icare rebound tonometry in children with known and suspected glaucoma. J AAPOS. 2011. 15:153–157.11. Lee ES, Kim CY, Ha SJ, et al. Central corneal thickness of Korean patients with glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2007. 114:927–930.12. Dielemans I, Vingerling JR, Hofman A, et al. Reliability of intraocular pressure measurement with the Goldmann applanation tonometer in epidemiological studies. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1994. 232:141–144.13. Wessels IF, Oh Y. Tonometer utilization, accuracy, and calibration under field conditions. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990. 108:1709–1712.14. Moreno-Montañés J, Gosende I, Caire J, García-Granero M. Comparation of the new rebound tonometer IOPen and the Goldmann tonometer, and their relationship to corneal properties. Eye (Lond). 2011. 25:50–56.15. Moreno-Montañés J, García N, Fernández-Hortelano A, García-Layana A. Rebound tonometer compared with goldmann tonometer in normal and pathologic corneas. Cornea. 2007. 26:427–430.16. Ahn SK, Kim BH, Cho HK, Shyn KH. Comparison between intraocular pressures measured by non-contact tonometer and goldmann applanation tonometer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994. 35:700–703.17. Forbes M, Pico G Jr, Grolman B. A noncontact applanation tonometer. Description and clinical evaluation. Arch Ophthalmol. 1974. 91:134–140.18. Koçak I, Orgül S, Saruhan A, et al. Measurement of intraocular pressure with a modern noncontact tonometer. Ophthalmologica. 1998. 212:81–87.19. Kontiola AI. A new induction-based impact method for measuring intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2000. 78:142–145.20. Kontiola AI, Goldblum D, Mittag T, Danias J. The induction/impact tonometer: a new instrument to measure intraocular pressure in the rat. Exp Eye Res. 2001. 73:781–785.21. Abraham LM, Epasinghe NC, Selva D, Casson R. Comparison of the ICare rebound tonometer with the Goldmann applanation tonometer by experienced and inexperienced tonometrists. Eye (Lond). 2008. 22:503–506.22. Rehnman JB, Martin L. Comparison of rebound and applanation tonometry in the management of patients treated for glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2008. 28:382–386.23. Davies LN, Bartlett H, Mallen EA, Wolffsohn JS. Clinical evaluation of rebound tonometer. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2006. 84:206–209.24. Chui WS, Lam A, Chen D, Chiu R. The influence of corneal properties on rebound tonometry. Ophthalmology. 2008. 115:80–84.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Influence of Central Corneal Thickness on Intraocular Pressures Measured with Goldmann Applanation Tonometer and Non-contact Tonometer
- Clinical Evaluation of A Noncontact Applanation Tonometer
- Clinical Comparision of the ProTon and the Goldmann Applanation Tonometer
- Comparison of Portable Tonometers and Goldmann Applanation Tonometer for Intraocular Pressure Measurement
- Comparison of Intraocular Pressures According to Position Using Icare Rebound Tonometer