J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 May;52(5):603-609. 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.5.603.
Retinal Changes in White Rabbits after Exposure to the Light of an Operating Microscope
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hkcho26@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2214581
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2011.52.5.603
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was performed to investigate the potential damage to white rabbit retinas caused by an operating microscope light.
METHODS
A total of 18 white rabbits were exposed to the light of an operating microscope for 60 minutes. Fundus examination, fluorescein angiography (FAG), and electroretinogram (ERG) were performed before exposure and 1 hr, 1 day, 7 days and 14 days afterward to allow for serial comparisons. Light and electron microscopic examinations were performed to evaluate the changes in the rabbit retinas over time.
RESULTS
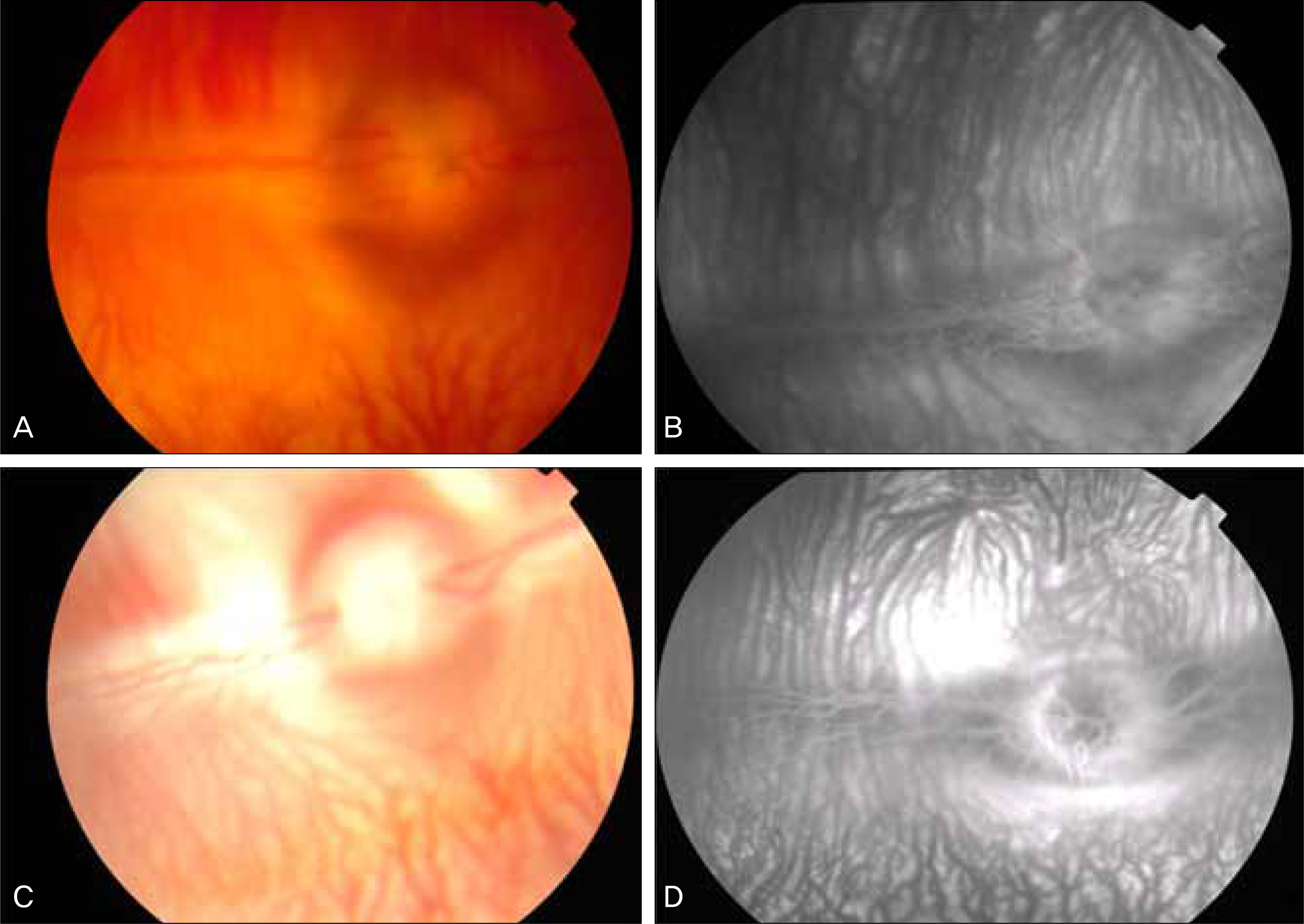
Signs of retinal damage upon fundus examination and FAG were not found before or after exposure to the light of an operating microscopy. ERG, however, showed significant reduction in the dark-adapted rod response 1 hour after light exposure, and significant decline in the amplitude of the maximal combined response a- and b-wave 1 day after light exposure in the rabbit retinas. ERG findings returned to the pre-exposure level after 2 weeks. Ultrastructural injury to the photoreceptor outer segments and the retinal pigmented epithelium, observed using transmission electron microscopy, recovered to the pre-exposure state after 2 weeks.
CONCLUSIONS
The risk of retinal damage should be considered as an early result of exposure to the light of an operating microscope, even in normal retinal findings.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sadun AC, Sadun AA, Sadun LA. Solar retinopathy. A biophysical analysis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984; 102:1510–2.2. Kim SH, Song JK. The effects of repeated prolonged indirect ophthalmoscopy on rabbit retina. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1984; 25:189–200.3. Jaffe GJ, Irvine AR, Wood IS, et al. Retinal phototoxicity from the operating microscope. The role of inspired oxygen. Ophthalmology. 1988; 95:1130–41.4. Michels M, Lewis H, Abrams GW, et al. Macular phototoxicity caused by fiberoptic endoillumination during pars plana vitrectomy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992; 114:287–96.
Article5. Noell WK, Walker VS, Kang BS, Berman S. Retinal damage by light in rats. Invest Ophthalmol. 1966; 5:450–73.6. McDonald HR, Irvine AR. Light-induced maculopathy from the operating microscope in extracapsular cataract extraction and intraocular lens implantation. Ophthalmology. 1983; 90:945–51.
Article7. Ham WT Jr, Ruffolo JJ Jr, Mueller HA, Guerry D 3rd. The nature of retinal radiation damage: dependence on wavelength, power level and exposure time. Vision Res. 1980; 20:1105–11.
Article8. Jeon SW, Park YH, Hahn DK. Experimental model of solar retinopathy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1991; 32:458–66.9. Sliney DH. Eye protective techniques for bright light. Ophthalmology. 1983; 90:937–44.
Article10. Boettner EA, Wolter JR. Transmission of the ocular media. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1962; 1:776–83.11. Lerman S. Chemical and physical properties of the normal and aging lens: spectroscopic (UV, fluorescence, phosphorescence, and NMR) analyses. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1987; 64:11–22.12. Arafat AF, Dutton GN, Wykes WN. Subclinical operating microscope retinopathy: the use of static perimetry in its detection. Eye (Lond). 1994; 8:467–72.
Article13. Yoon HM, Jang YJ, Kim JS, Ji NC. An ultrastructural study of recovery of photoreceptor layer from visible light-induced damage. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1993; 34:678–86.14. Ramirez J, Meyer U, Stoppa M, Wenzel M. Electrophysiological and morphological changes in rabbit retina after exposure to the light of the operating microscope. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1992; 230:380–4.
Article15. Shin JW, Kim YH, Kim SY. Two cases of photic retinopathy by ex-cessive exposure to light of sun and operating microscope. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:1362–6.16. Khwarg SG, Linstone FA, Danicls SA, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and morphology in operating microscope light retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1987; 103:225–63.
Article17. Byrnes GA, Chang B, Loose I, et al. Prospective incidence of photic maculopathy after cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995; 119:231–2.
Article18. Michels M, Sternberg P Jr. Operating microscope-induced retinal phototoxicity: pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and prevention. Surv Ophthalmol. 1990; 34:237–52.
Article19. Hochheimer BF, D’Anna SA, Calkins JL. Retinal damage from light. Am J Ophthalmol. 1979; 88:1039–44.
Article20. Lawwill T. Three major pathologic processes caused by light in the primate retina: a search for mechanisms. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1982; 80:517–79.21. Wiegand RD, Giusto NM, Rapp LM, Anderson RE. Evidence for rod outer segment lipid peroxidation following constant illumination of the rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1983; 24:1433–5.22. Glickman RD. The origin of photo-oxidative stress in the aging eye. Prog Brain Res. 2001; 131:699–712.23. Kremers JJ, van Norren D. Retinal damage in macaque after white light exposures lasting ten minutes to twelve hours. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989; 30:1032–40.24. Rapp LM, Tolman BL, Dhindsa HS. Separate mechanisms for retinal damage by ultraviolet-A and mid-visible light. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990; 31:1186–90.25. Hansson HA. Ultrastructural studies on rat retina damaged by visible light. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1970; 6:247–62.
Article26. Lanum J. The damaging effects of light on the retina. Empirical findings, theoretical and practical implications. Surv Ophthalmol. 1978; 22:221–49.
Article27. O'Steen WK, Shear CR, Anderson KV. Retinal damage after prolonged exposure to visible light. A light and electron microscopic study. Am J Anat. 1972; 134:5–21.28. Borsje RA, Vrensen GF, van Best JA, Oosterhuis JA. Fluorophotometric assessment of blood-retinal barrier function after white light exposure in the rabbit eye. Exp Eye Res. 1990; 50:297–304.
Article29. Wu J, Seregard S, Algvere PV. Photochemical damage of the retina. Surv Ophthalmol. 2006; 51:461–81.
Article30. Abe T, Saigo Y, Hojo M, et al. Protection of photoreceptor cells from phototoxicity by transplanted retinal pigment epithelial cells expressing different neurotrophic factors. Cell Transplant. 2005; 14:799–808.
Article31. Calkins JL, Hochheimer BF. Retinal light exposure from oph-thalmoscopes, slit lamps, and overhead surgical lamps. An analysis of potential hazards. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1980; 19:1009–15.32. Ham WT Jr, Mueller HA, Sliney DH. Retinal sensitivity to damage from short wavelength light. Nature. 1976; 260:153–5.
Article33. Calkins JL, Hochheimer BF. Retinal light exposure from operation microscopes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1979; 97:2363–7.
Article34. Sliney DH. Quantifying retinal irradiance levels in light damage experiments. Curr Eye Res. 1984; 3:175–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Histopathological Study for Chronic Photic Retinal injury After Atropinization for a Long Time
- Two Cases of Photic Retinopathy by Excessive Exposure to Light of Sun and Operating Microscope
- Comparison of Blood-Ocular-Barrier between White Rabbits and Colored Rabbits
- Photic Retinal Injury Induced by Endoillumination during Vitrectomy
- Experimental Subretinal Neovascularization Induced with Argon Laser in Pigmented Rabbits