J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2016 Feb;57(2):283-289. 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.2.283.
Mycophenolate Mofetil for Chronic Uveitis in Koreans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea. jlee@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2213670
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2016.57.2.283
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the therapeutic effect and safety of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) on chronic uveitis in Korean patients.
METHODS
This study included 25 patients with chronic uveitis who used MMF and were followed up more than 6 months in 2 referral centers from 2010 to 2014. The medical records were analyzed retrospectively. The therapeutic effect was assessed based on control of inflammation, corticosteroid sparing effects, and discontinuation of MMF, and the safety was assessed based on side effects. Control of inflammation was defined as no active inflammation observed on at least 2 consecutive visits 28 days apart or more.
RESULTS
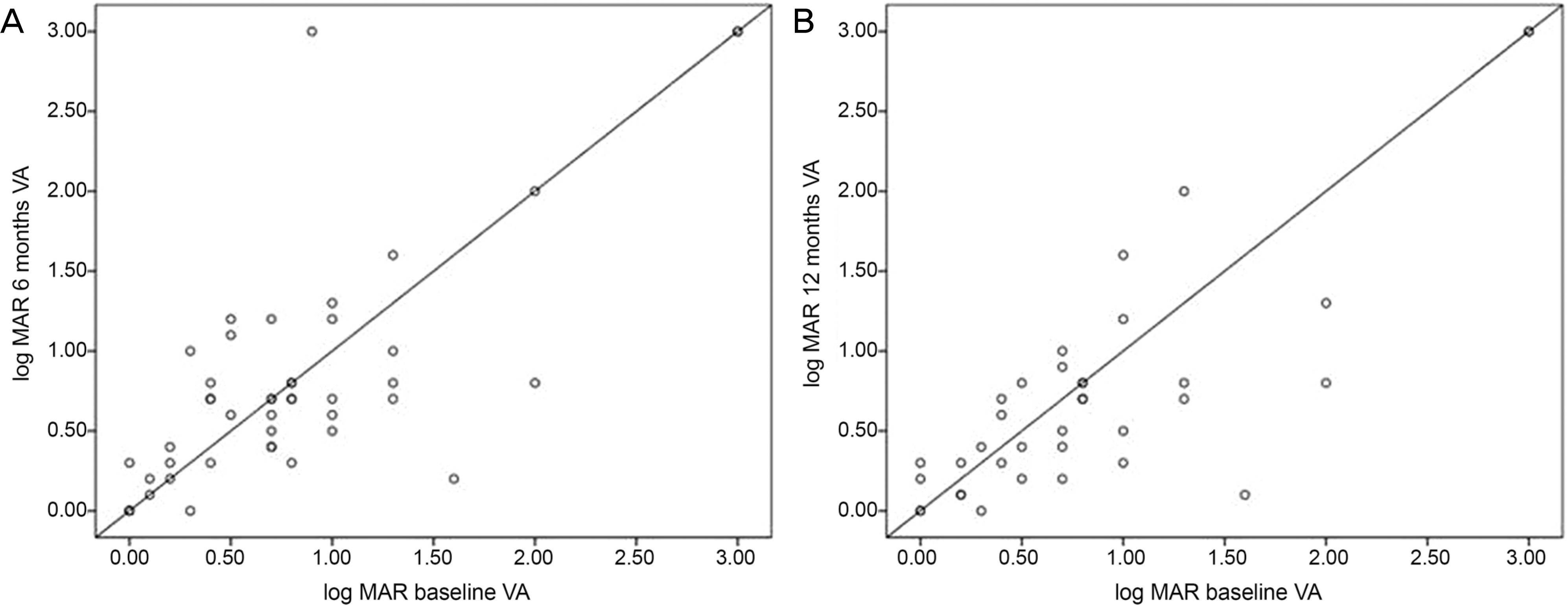
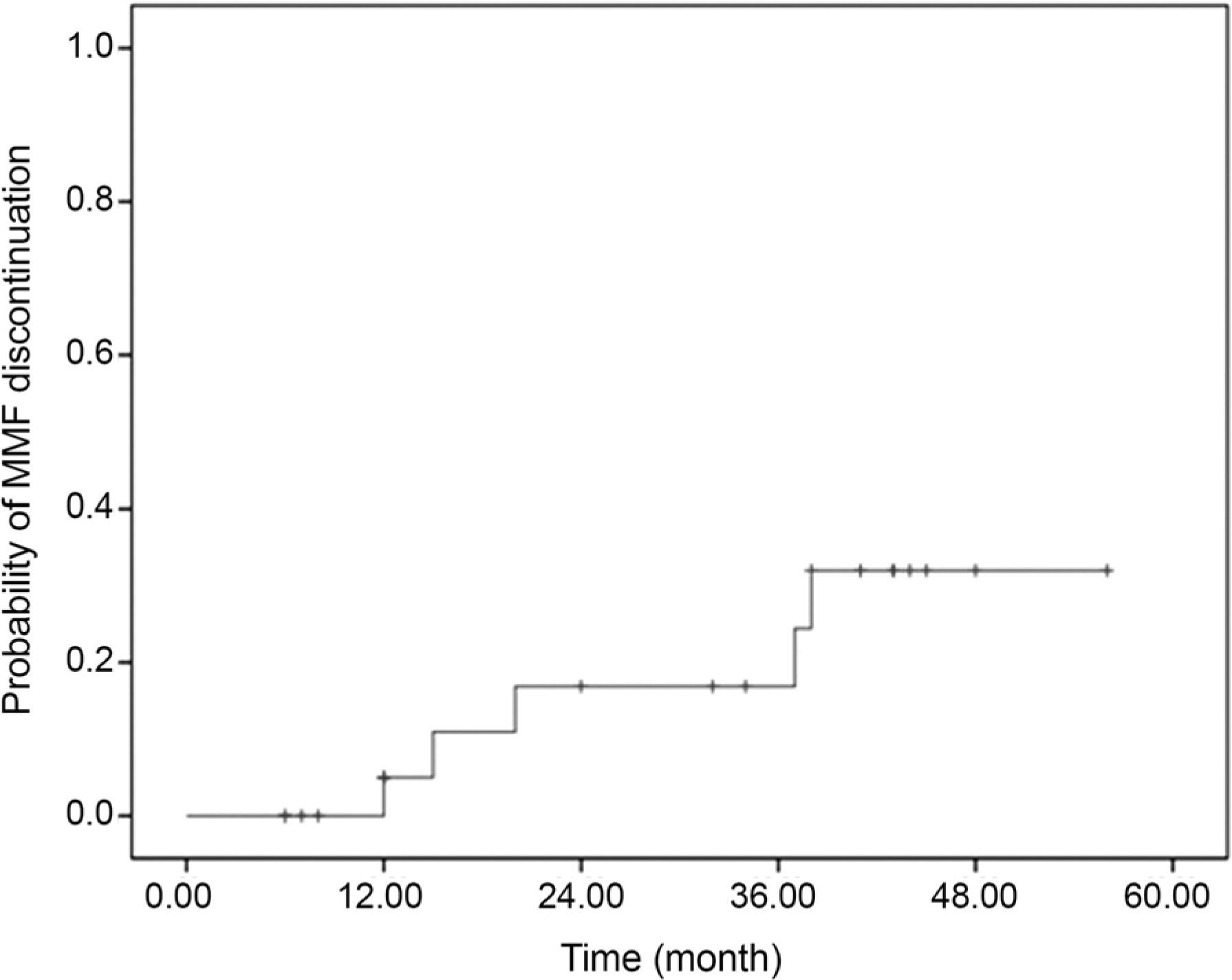
The 25 patients consisted of 18 males and 7 females. The mean age of the patients was 47.52 years. The etiology of uveitis was as follows: Behcet's disease in 15 patients (60%), Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease in 4 (16%), sympathetic ophthalmia in 2 (8%), systemic lupus erythematosus in 1 (4%), and idiopathic uveitis in 3 (12%). Anatomic classification was anterior uveitis in 20% and posterior uveitis or panuveitis in 80% of patients. Complete control of inflammation was achieved in 44% and 50% of patients within 6 months and 1 year, respectively. Systemic corticosteroid dosage was reduced to 10 mg of prednisone or less while maintaining sustained control of inflammation in 36% and 45% of patients for 6 months and 1 year, respectively. MMF was discontinued in 3 patients (12%) due to side effects and in 2 patients (8%) due to lack of effectiveness.
CONCLUSIONS
MMF was effective and side effects were uncommon when managing chronic uveitis in Korean patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Nussenblatt RB. The natural history of uveitis. Int Ophthalmol. 1990; 14:303–8.
Article2). Rothova A, Suttorp-van Schulten MS, Frits Treffers W, Kijlstra A. Causes and frequency of blindness in patients with intraocular inflammatory disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 1996; 80:332–6.
Article3). Jabs DA, Rosenbaum JT, Foster CS, et al. Guidelines for the use of immunosuppressive drugs in patients with ocular inflammatory disorders: recommendations of an expert panel. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 130:492–513.
Article4). Siepmann K, Huber M, Stübiger N, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil is a highly effective and safe immunosuppressive agent for the treatment of uveitis: a retrospective analysis of 106 patients. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006; 244:788–94.5). Baltatzis S, Tufail F, Yu EN, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil as an immunomodulatory agent in the treatment of chronic ocular inflammatory disorders. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:1061–5.
Article6). Allison AC, Eugui EM. Mycophenolate mofetil and its mechanisms of action. Immunopharmacology. 2000; 47:85–118.
Article7). Thorne JE, Jabs DA, Qazi FA, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil therapy for inflammatory eye disease. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1472–7.
Article8). Teoh SC, Hogan AC, Dick AD, Lee RW. Mycophenolate mofetil for the treatment of uveitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008; 146:752–60. 760.e1-3.
Article9). Daniel E, Thorne JE, Newcomb CW, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil for ocular inflammation. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 149:423–32. e1-2.
Article10). Jabs DA, Nussenblatt RB, Rosenbaum JT. Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) Working Group. Standardization of uveitis nomenclature for reporting clinical data. Results of the First International Workshop. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005; 140:509–16.11). Doycheva D, Zierhut M, Blumenstock G, et al. Long-term results of therapy with mycophenolate mofetil in chronic non-infectious uveitis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2011; 249:1235–43.
Article12). Rathinam SR, Babu M, Thundikandy R, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil for noninfectious uveitis. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:1863–70.
Article13). Galor A, Jabs DA, Leder HA, et al. Comparison of antimetabolite drugs as corticosteroid-sparing therapy for noninfectious ocular inflammation. Ophthalmology. 2008; 115:1826–32.
Article14). Filler G. Value of therapeutic drug monitoring of MMF therapy in pediatric transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2006; 10:707–11.
Article15). Connell WR, Kamm MA, Ritchie JK, Lennard-Jones JE. Bone marrow toxicity caused by azathioprine in inflammatory bowel disease: 27 years of experience. Gut. 1993; 34:1081–5.
Article16). Behrend M. Adverse gastrointestinal effects of mycophenolate mofetil: aetiology, incidence and management. Drug Saf. 2001; 24:645–63.17). Kitchin JE, Pomeranz MK, Pak G, et al. Rediscovering mycophenolic acid: a review of its mechanism, side effects, and potential uses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997; 37((3 Pt 1)):445–9.
Article18). Chang PI, Giuliari GP, Shaikh M, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil monotherapy in the management of paediatric uveitis. Eye (Lond). 2011; 25:427–35.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pretransplant mycophenolate mofetil reduces intrahepatic cholangiopathy related to laparoscopic donor hepatectomy in ABO-incompatible liver transplantation
- Application of mycophenolate mofetil for immune-mediated hemolytic anemia in two dogs
- Mycophenolate Mofetil for Treatment of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia and Nephrotic Syndrome after Cord Blood Transplantation
- Successful long-term management of late-stage precursor-targeted immune-mediated anemia with prednisolone and mycophenolate mofetil in a dog
- Optic Disc Neovascularization in Chronic Anterior Uveitis