J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2009 Dec;50(12):1789-1794. 10.3341/jkos.2009.50.12.1789.
Comparison of Aberrations in Korean Normal Eyes Measured With Two Different Aberrometers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. eyedr0823@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2212989
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.12.1789
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare ocular higher order aberrations measured by two different aberrometers in a sample of normal eyes.
METHODS
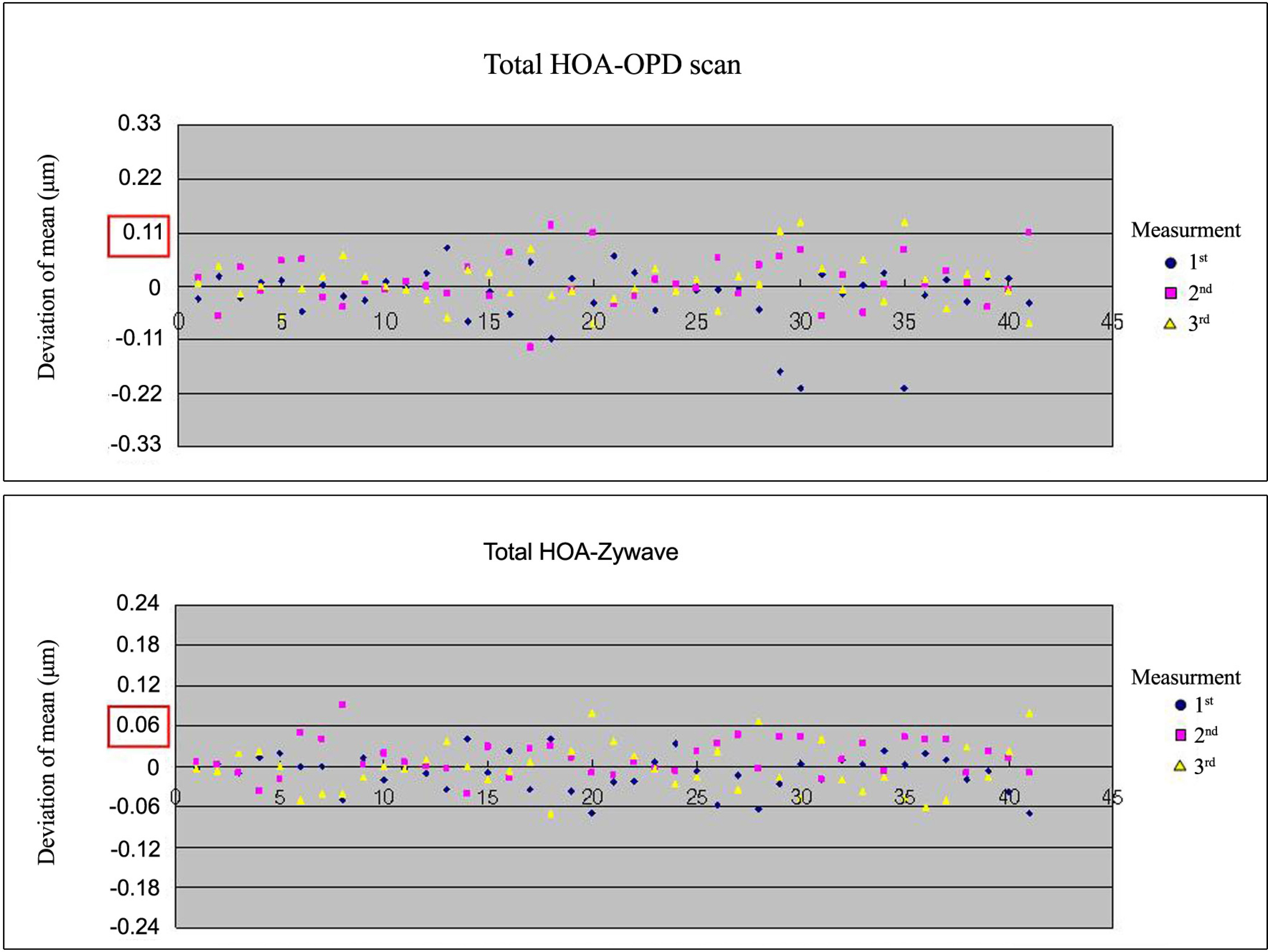
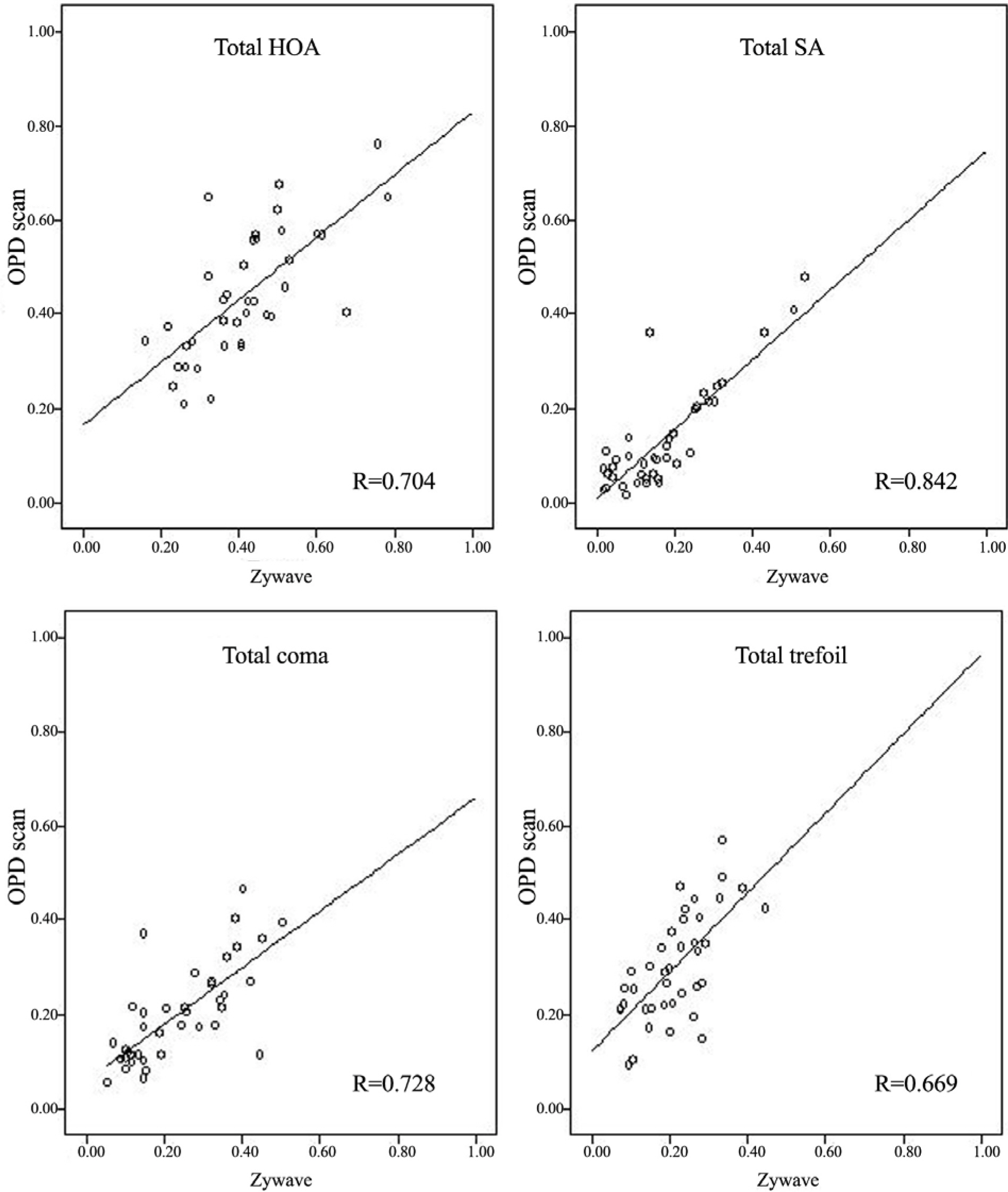
We included 41 normal eyes of Koreans in this study. Ocular aberration data were obtained through three measurements per eye using Zywave and OPD-Scan devices. Spherical equivalent and higher order aberrations calculated in the central 6 mm zone and expressed as root mean square (RMS) values were analyzed.
RESULTS
A comparison of measurements between the Zywave and OPD-Scan devices demonstrated no statistically significant differences in the RMS values of total higher order aberration (p=0.11), but significant differences were detected in the RMS values of total spherical aberration, total coma and total trefoil (p<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
The two different aberrometers that we tested are suitable for taking repeated measurements and are internally consistent, but not interchangeable.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Preoperative Ocular Aberrations Measured by Zywave® II Aberrometer in Individuals Screened for Refractive Surgery
Young Seung Kim, Byung Yi Ko
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(11):1680-1687. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.11.1680.Comparison of Corneal Higher-Order Aberrations Measured with Two Instruments Using Scheimpflug Camera System
Yeon Jung Choi, Na Hee Kang, Roo Min Jun
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(10):1497-1504. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.10.1497.
Reference
-
References
1. Born M. Principles of optics. New York: Pergamon Press;1975. p. 464–6.2. Rozema JJ, Van Dyck DE, Tassignon MJ. Clinical comparison of 6 aberrometers. Part 1: Technical specifications. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:1114–27.
Article3. Rozema JJ, Van Dyck DE, Tassignon MJ. Clinical comparison of 6 aberrometers. Part 2: statistical comparison in a test group. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:33–44.
Article4. Liang J, Grimm B, Goelz S, Bille JF. Objective measurement of wave aberrations of the human eye with the use of a Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 1994; 11:1949–57.
Article5. Thibos LN. Principles of Hartmann-Shack aberrometry. J Refract Surg. 2000; 16:563–5.
Article6. MacRae S, Fujieda M. Slit Skiascopic-guided ablation using the Nidek Laser. J Refract Surg. 2000; 16:576–80.
Article7. Molebny V, Pallikaris IG, Naoumidis LP, et al. Retina ray-tracing technique for eye refraction mapping. SPIE Proc. 1997; 2971:175–83.8. Navarro R, Moreno-Barriuso E. Laser ray-tracing method for optical testing. Opt Lett. 1999; 24:951–3.
Article9. Mrochen M, Kaemmerer M, Mierdel P, et al. Principles of Tscherning aberrometry. J Refract Surg. 2000; 16:570–1.
Article10. Mirshahi A, Buhren J, Gerhardt D, Kohnen T. In vivo and in vitro repeatability of Hartmann-Shack aberrometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:2295–301.
Article11. Hament WJ, Nabar VA, Nuijts RM. Repeatability and validity of Zywave aberrometer measurements. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:2135–41.
Article12. Durrie DS, Stahl ED. Comparing wavefront devices. Krueger RR, Applegate RA, MacRae SM, editors. Wavefront Customized Visual Correction: The Quest for Super Vision II. Thorofare, NJ: SLACK Inc;2004. 1:chap. 21.13. Jeong JH, Kim MJ, Tchah HW. Clinical Comparison of Laser Ray Tracing Aberrometer and Shack-Hartmann Aberrometer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1911–9.14. Altman DG, Bland JM. Measurements in medicine: the analysis of method comparison studies. Statistician. 1983; 32:307.15. Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurements. Lancet. 1986; 1:307–10.16. Bailey MD, Mitchell GL, Dhaliwal DK, et al. Patient satisfaction and visual symptoms after laser in situ keratomileusis. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:1371–8.
Article17. Marcos S. Aberrations and visual performance following standard laser vision correction. J Refract Surg. 2001; 17:596–601.
Article18. Burakgazi AZ, Tinio B, Bababyan A, et al. Higher order aberrations in normal eyes measured with three different aberrometers. J Refract Surg. 2006; 22:898–903.
Article19. Rodriguez P, Navarro R, Gonzalez L, Hernández JL. Accuracy and reproducibility of Zywave, Tracey and experimental aberrometers. J Refract Surg. 2004; 20:810–7.
Article20. Cerviño A, Hosking SL, Montés-Micó R. Comparison of higher order aberrations measured by NIDEK OPD-Scan dynamic skiascopy and Zeiss WASCA Hartmann-Shack aberrometers. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:790–6.
Article21. Kim DS, Narváez J, Krassin J, Bahjri K. Comparison of the VISX wavescan and NIDEK OPD-scan aberrometers. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25:429–34.
Article22. Liang CL, Juo SH, Chang CJ. Comparison of higher-order wavefront aberrations with 3 aberrometers. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:2153–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Internal and Total Optical Aberrations for 2 Aberrometers: iTrace and OPD Scan
- Comparison of Higher-order Aberrations Outcomes between Sutured Scleral Fixation and Modified Yamane Sutureless Scleral Fixation
- Higher-order Aberrations in Pseudophakia with Different Intraocular Lenses
- Wavefront Aberration Changes after the Instillation of Artificial Tear in Dry Eyes
- Relationship between Dry Eye Parameters and Anterior Corneal Higher-Order Aberrations Measured by Two Different Instruments