Korean J Ophthalmol.
2008 Dec;22(4):210-213. 10.3341/kjo.2008.22.4.210.
Comparison of Internal and Total Optical Aberrations for 2 Aberrometers: iTrace and OPD Scan
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Institute of Vision Research, Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. biniya73@daum.net
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Soon-Chun-Hyang University College of Medicine, Bu-Cheon, Gyeonggido, Korea.
- 3Siloam Eye Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1084206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2008.22.4.210
Abstract
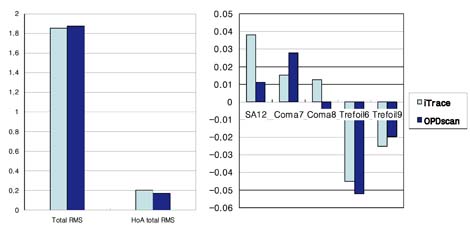
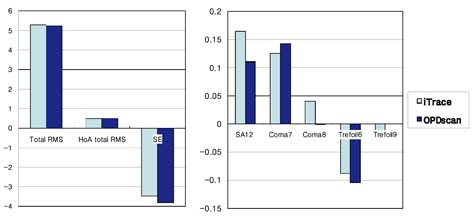
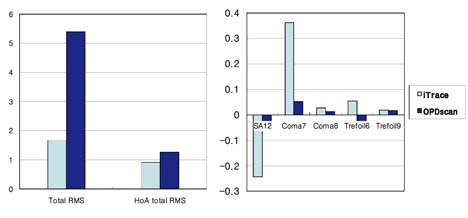
- PURPOSE: To compare and evaluate the total and internal aberrations measured by two aberrometers: the laser ray tracing aberrometer (iTrace, Tracey Technology) and the automatic retinoscope aberrometer (OPD Scan, Nidek). METHODS: A total of 54 healthy eyes were enrolled in the study. Following pupil dilation, aberrations were measured with the iTrace and OPD Scan. We compared the aberrations obtained from measurements obtained at pupillary diameters of 4 mm and 6 mm with the OPD Scan and iTrace. Aberrations of internal optics and total aberrations were compared for the two aberrometers. For each aberrometer and each eye, the averaged Zernike data were used to calculate various root-mean-square (RMS) data. These parameters, together with the refractive parameters, were then analyzed and complimented by paired t-tests. RESULTS: At a pupil diameter of 4 mm, the number of total aberrations in the entire eye showed significant differences for the mean values of spherical aberrations (Z4,0) obtained with the OPD Scan and iTrace aberrometers (p=0.001). Aberrations of the internal optics showed significant differences in the mean values of total RMS, coma (Z3,-1), and trefoil (Z3,3) between the iTrace and OPD Scan (p<0.001, p=0.01, p<0.001) for the same pupil diameter of 4 mm. At a pupil diameter of 6 mm, the two instruments showed a similar number of total aberrations. Aberrations of the internal optics showed significant differences in the mean values of total RMS, spherical aberration (Z4,0), and coma (Z3,-1) between the two devices (p<0.001, p=0.01, p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: The iTrace and OPD Scan showed the largest number of differences for aberrations of internal optics rather than total aberrations for both pupil diameters. These results suggest that in healthy eyes, the two aberrometers may vary in some details. The aberrometers showed more agreement at a pupil diameter of 6 mm compared to 4 mm.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Helmholtz H. Handbuch der physiologischen optic. 1867. Leipzig: Leopold Voss;137–147.2. Born M, Wolf E. Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference, and Diffraction of Light. 1975. New York: Pergamon Press;464–466.3. Seiler T, Kaemmerer M, Miderdel P, Krinke HE. Ocular optical aberrations after photorefractive keratectomy for myopia and myopic astigmatism. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000. 118:17–21.4. Charman WN. Wavefront aberration of the eye: a review. Optometry&Vision Science. 1991. 68:574–583.5. Thibos LN, Hong X, Bradley A, Cheng X. Statistical variation of aberration structure and image quality in a normal population of healthy eyes. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2002. 19:2329–2348.6. Wang L, Koch DD. Ocular higher-order aberrations in individuals screened for refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003. 29:1896–1903.7. Cheng X, Himebaugh NL, Kollbaum PS, et al. Test-retest reliability of clinical Shack-Hartmann measurements. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004. 45:351–360.8. Mirshahi A, Buhren J, Gerhardt D, Kohnen T. In vivo and in vitro repeatability of Hartmann-Shack aberrometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003. 29:2295–2301.9. Rozema JJ, Van Dyck DE, Tassignon MJ. Clinical comparison of 6 aberrometers Part 2: Statistical comparison in a test group. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006. 32:33–44.10. Liang CL, Juo SH, Chang CJ. Comparison of higher-order wavefront aberrations with 3 aberrometers. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. 31:2153–2156.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Aberrations in Korean Normal Eyes Measured With Two Different Aberrometers
- Clinical Comparison of Laser Ray Tracing Aberrometer and Shack-Hartmann Aberrometer
- Analysis of Internal Optical Aberrations in Eyes with Different Types of Cataract
- Comparison of Corneal Higher-order Aberrations Measured by Scheimpflug Camera and Placido Disc-based Topography in Korean Patients
- Changes in High-order Aberrations after Phacotrabeculectomy Surgery