Morphological Changes of the Eyelid According to Age
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Dong-A University, College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. hbahn@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2212761
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.10.1461
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The morphological changes of the eyelids according to gender among different age groups in Korea were analyzed.
METHODS
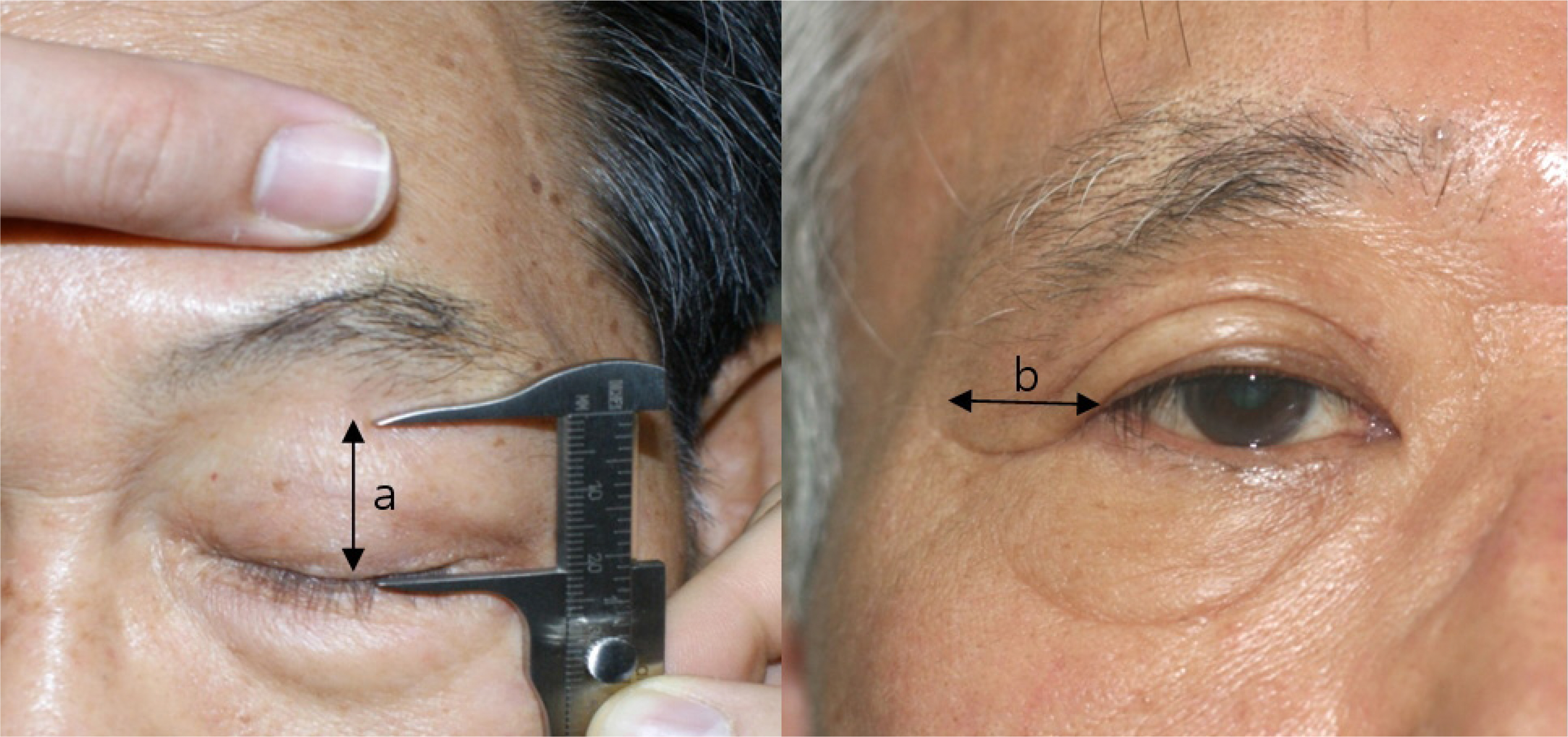
Six-hundred adults without any ocular disease were selected, and sorted by age (ranging from 20 to 79 years), and gender. Each group consisted of 50 adults. Interpalpebral fissure (IPF), marginal reflex distance 1 (MRD1), amount of the upper lid, degree of browptosis, lateral hood width of the eyelid, and protrusion of the eyelid fat were measured. The measured values were analyzed to determine changes related to the aging process. Other age groups were analyzed and compared with the subjects between 20 and 30 years old, using the Student's t-test with SPSS.
RESULTS
MRD 1 and IPF slightly decreased with age, but there was no statistical significance. The upper lid amount showed a statistically significant increase at the 7th and 8th decade. The degree of browptosis showed a statistically significant increase from the 7th decade of age in men, and from the 6th decade in women. In particular, the lateral browptosis was more drooped than the center browptosis. The lateral hood width of the eyelid showed a statistically significant increase from the 7th decade of age in men, and from the 6th decade in women. Eyelid fat was most protruded at the central lower part, but there was no statistical significance.
CONCLUSIONS
It is important to understand the change related to aging in the study of eyelid morphology and eyelid operation. The results from present study may be used to determine standard for the safe amount of skin resection in Korean eyelid operations.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
Upper and Lower Eyelid Positions in Several Korean Age Groups
Sukyeon Lee, Jinhwan Park, Janghoon Lee, Jaehoon Na, Hwa Lee, Sehyun Baek
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(7):606-612. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.7.606.Exploring Brow Position Changes with Age in Koreans
Noh Seung Yoon, Hee Bae Ahn
Korean J Ophthalmol. 2019;33(1):91-94. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2018.0013.Periorbital changes with aging
Ho-Kyung Choung
J Korean Med Assoc. 2013;56(11):1012-1016. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2013.56.11.1012.Analysis of Upper Eyelid Fat Pad Changes with Aging and Body Mass Index in Korean
Jae Moon Ahn, Hwa Lee, Jung Wan Kim, Min Wook Jang, Tae Soo Lee, Se Hyun Baek
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(4):562-567. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.4.562.Clinical Features of Dry Eye in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy According to Disease Activity
Jun Young Ha, Won Choi, Kyung Chul Yoon
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016;57(7):1037-1043. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.7.1037.Changes in Lower Eyelid Positions after Individualized Lower Blepharoplasty
Young Je Sung, Jong Seo Park, Helen Lew
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(12):1831-1839. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.12.1831.
Reference
-
References
1. Sanke RF. Relationship of senile ptosis to age. Ann Ophthalmol. 1984; 16:928–931.2. Goldberg B, Rabinovitch M. Connective tissue, in Histology. 4th ed.New York: McGraw-Hill;1977. p. 145–78.3. Bailey AJ, Duance VC. Collagen in acquired connective tissue disease: An active or passive role? Eur J Clin Invest. 1980; 10:1–5.4. Na KS. Upper blepharoplasty. Journal Korean Society of Plastic Reconstructive Surgery. 2004; 135.5. Kim IS, Choi JB, Rah SH, Lee SY. Classification of ptosis in Korea. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1262–9.6. Park DM, Song JW, Han KH, Kang JS. Anthropometry of normal Korean eyelids. Journal Korean Society of Plastic Reconstructive Surgery. 1990; 17:822–34.7. Song WS, Kim YH, Lee SJ. Morphologic study of upper eyelid contour and functional evaluation of levator palpebrae superiors muscle in adult and young people. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:1523–9.8. Lee JS, On KK, Kim JD. Superior visual field on MRD1 and aging changes of MRD1. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:884–8.9. Yim HK, Son MS. A statistical study on the palprbral fissure in Korean. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1981; 22:333–40.10. van den Bosch WA, Leenders I, Mulder P. Topographic anatomy of the eyelids, and the effects of sex and age. Br J Ophthalmol. 1999; 83:347–52.
Article11. Park JW, Lee BH, Jeong SK, Kim JB. Morphological evaluation of upper eyelid in Korean. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:879–85.12. Kim KC, Kim YW, Kim HB. The levator action in Korean. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1986; 27:995–9.13. Park CY, Jeon SL, Woo KI, Chang HR. The frequency and aspects of ptosis in Korean old age. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:205–10.14. Moses RA. The eyelid. Moses RA, Adler's physiology of the eye, clinical application. 8th ed.St. Louis: Mosby;1987. p. 11–36.15. Beard C. The surgical treatment of blepharoptosis: A quantitative approach. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1966; 64:404.16. Cartwright MJ, Kurumetry UR, Nelson CC, et al. Measurements of upper eyelid and eyebrow dimentions in healthy white in-divisuals. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994; 117:231–4.17. Moon CS, Moon SH, Jang JW. Topographic anatomic difference of the eyelid according to age in Korean. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:1865–71.18. Kunjur J, Sabesan T, Ilankovan V. Anthropometric analysis of eyebrow and eyelids: An inter-racial study. Br J Oral Maxillo-facial Surg. 2005; 44:89–93.19. Hoenig JA. Comprehensive management of eyebrow and forehead ptosis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2005; 38:947–84.
Article20. Brooth AJ, Murray A, Tyers AG. The direct brow lift: efficacy, complications, and patient satisfaction. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:688–91.21. Scott M, Goldstein SM, Katowitz JA. The male eyebrow: a topographic anastomic analysis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 21:285–91.22. Har-Shai Y, Hirshowitz B. Extended upper blepharoplasty for lateral hooding of the upper eyelid using a scalpel-shaped excision: a 13-year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 113:1028–35.
Article23. Shore JW, McCord CD Jr. Anatomic changes in involutional blepharoptosis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984; 98:21–7.
Article24. Kim SY, Chung WS. Analysis of the cause of ptosis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:1649–54.25. Camirand A, Doucet J, Harris J. Eyelid aging: the historical evolution of its management. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2005; 29:65–73.
Article26. Goldberg RA, McCann JD, Fiaschetti D, Ben Simon GJ. What causes eyelid bags? Analysis of 114 consecutive patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 115:1395–402.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Morphological and Functional Characteristics of Eyelid in Korean Children
- Changes in Lower Eyelid Positions after Individualized Lower Blepharoplasty
- Morphological Evaluation of Upper Eyelid in Korean Children
- Age-related eyelid changes
- The Lower Eyelid Movement by Inferior Oblique Muscle Action According to the Age