J Korean Surg Soc.
2013 Dec;85(6):302-304. 10.4174/jkss.2013.85.6.302.
Torsion of the gallbladder in pregnancy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. selee508@cau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2212557
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2013.85.6.302
Abstract
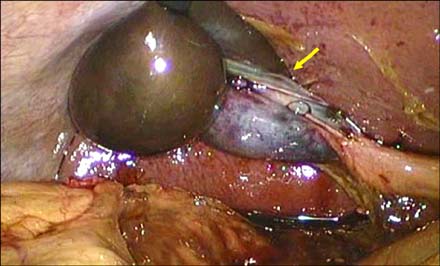
- Torsion of the gallbladder is a rare condition that is difficult to diagnose preoperatively, but prompt surgical intervention is necessary to avoid possible sepsis and death. A 36-year-old pregnant woman presented to Emergency Department with a constant epigastric pain at 17 weeks of gestation. Abdominal ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated a distended gallbladder that contained no stones but had mild wall thickening. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy using three ports was performed under the impression of an acalculous cholecystitis. The gallbladder was found to be rotated 180 degrees clockwise on gallbladder mesentery and to be gangrenous. The postoperative course was uneventful and the patient was discharged on the 4th day after surgery. It is important to keep in mind gallbladder torsion in the differential diagnosis from acute cholecystitis when the patient has an acute onset of abdominal pain and a severely distended gallbldder. Prompt cholecystectomy via a laparoscopic approach should be performed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nakao A, Matsuda T, Funabiki S, Mori T, Koguchi K, Iwado T, et al. Gallbladder torsion: case report and review of 245 cases reported in the Japanese literature. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999; 6:418–421.2. McHenry CR, Byrne MP. Gallbladder volvulus in the elderly: an emergent surgical disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1986; 34:137–139.3. Nguyen T, Geraci A, Bauer JJ. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy for gallbladder volvulus. Surg Endosc. 1995; 9:519–521.4. Ikematsu Y, Yamanouchi K, Nishiwaki Y, Kida H, Waki S, Okawada T, et al. Gallbladder volvulus: experience of six consecutive cases at an institute. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2000; 7:606–609.5. Schroder DM, Cusumano DA 3rd. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy for gallbladder torsion. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1995; 5:330–334.6. Vosswinkel JA, Colantonio AL. Torsion of the gallbladder: laparoscopic identification and treatment. Surg Endosc. 1999; 13:1154–1156.7. Losken A, Wilson BW, Sherman R. Torsion of the gallbladder: a case report and review of the literature. Am Surg. 1997; 63:975–978.8. Carter R, Thompson RJ Jr, Brennan LP, Hinshaw DB. Volvulus of the gallbladder. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1963; 116:105–108.9. Safadi RR, Abu-Yousef MM, Farah AS, al-Jurf AS, Shirazi SS, Brown BP. Preoperative sonographic diagnosis of gallbladder torsion: report of two cases. J Ultrasound Med. 1993; 12:296–298.10. Usui M, Matsuda S, Suzuki H, Ogura Y. Preoperative diagnosis of gallbladder torsion by magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000; 35:218–222.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Necrotizing Gallbladder Torsion Masking as Acalculous Cholecystitis: A Review of Two Cases Treated with Successful Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
- Imaging Findings of Acute Torsion of the Gallbladder: Case Report
- Acute Choleystitis due to Torsion of the Gallbladder
- Torsion of the Gallbladder
- Gallbladder Torsion: A Case Report and a Review of the Literature