J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2009 May;50(5):677-683. 10.3341/jkos.2009.50.5.677.
Long-term Change in Corneal Endothelium After Iris-fixed Phakic Intraocular Lens Insertion
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Institute of Vision Research, Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. shadik@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2212297
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.5.677
Abstract
-
PURPOSE:To investigate long-term endothelial changes in phakic eyes implanted with iris-claw phakic intraocular lens (IOL) (Artisan(R) lens Ophtec, Groningen, Netherlands) and to identify the associated factors.
METHODS
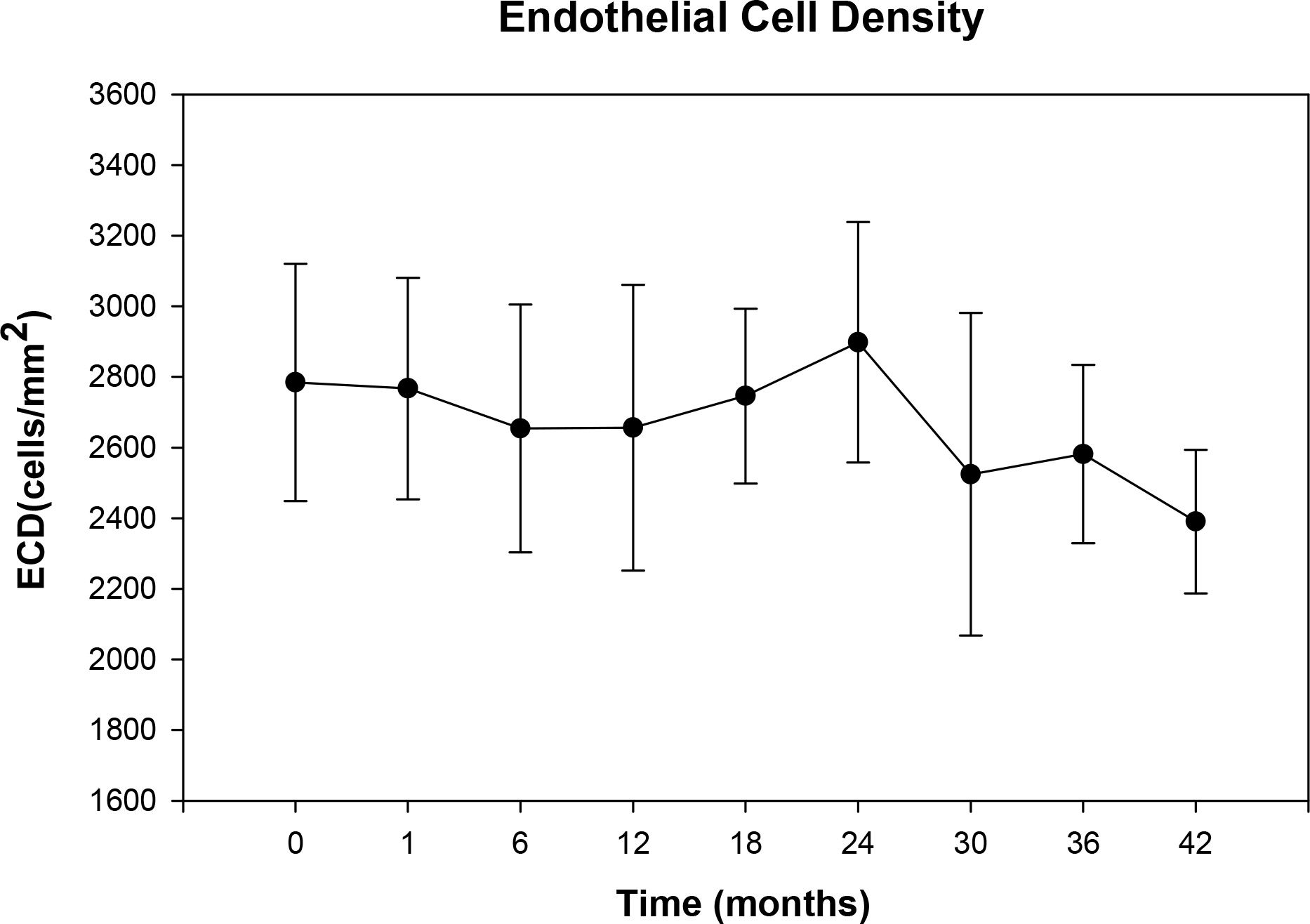
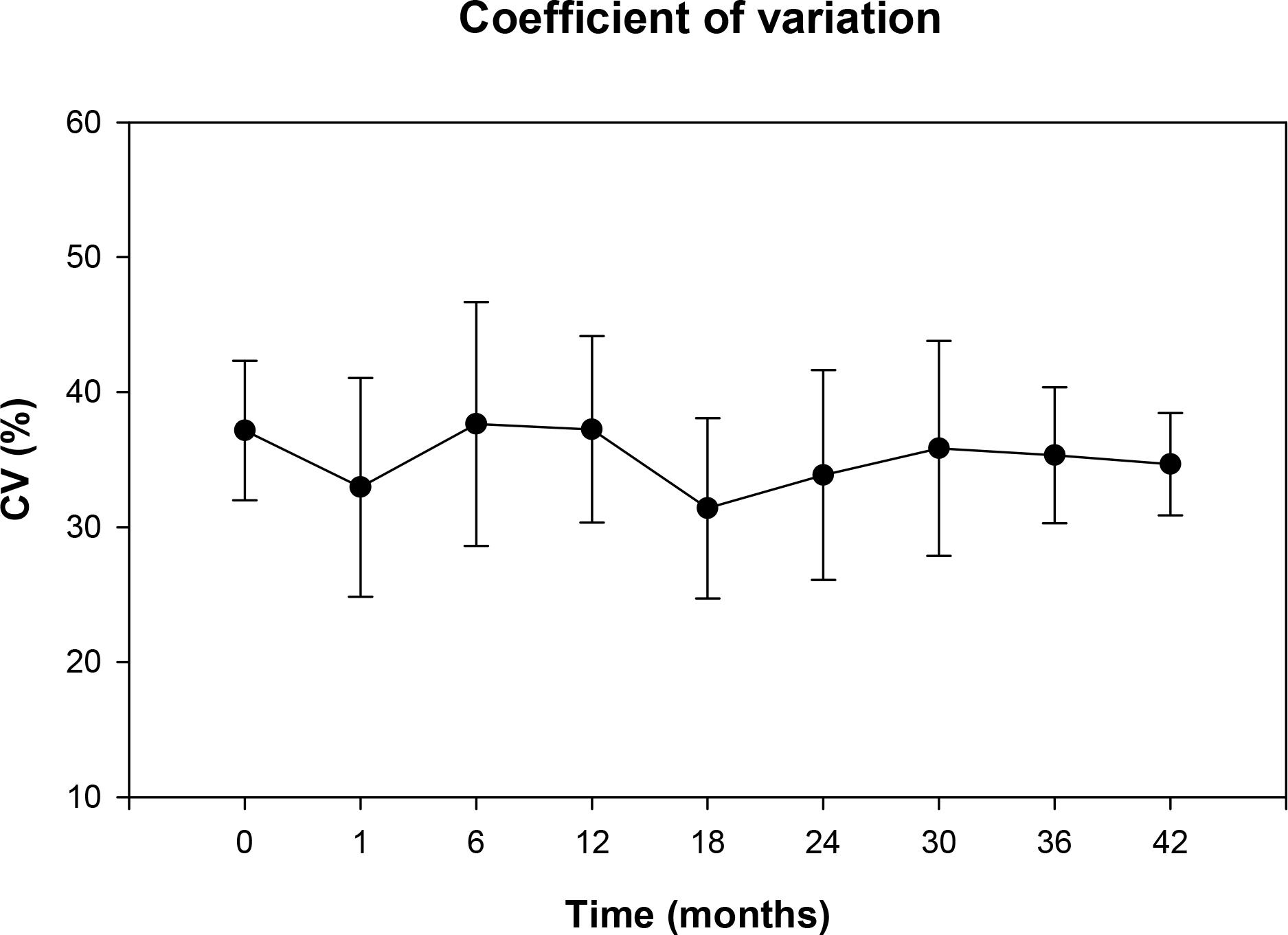
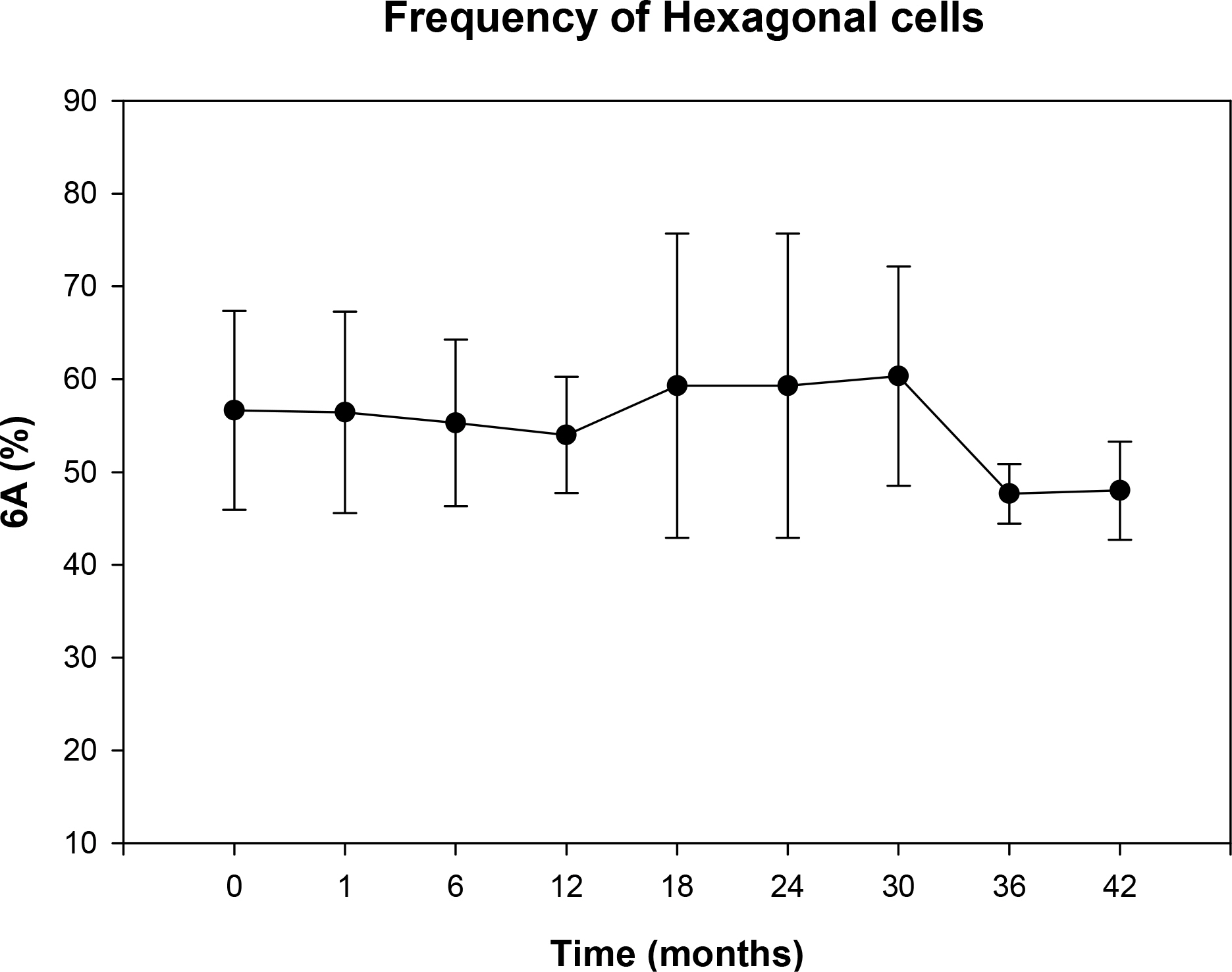
Thirty-one eyes of 18 patients underwent Artisan phakic IOL implantation and were followed up for over 1 year. The authors retrospectively examined the endothelial cell density, percentage of hexagonal cells and coefficient of variation using the result of non-contact specular microscope.
RESULTS
The mean endothelial cell loss was 0.9% at 23.9+/-9.44 months of the mean follow-up period. There was no statistically significant decrease in endothelial cell density (p=0.445). There was no statistically significant change in pleomorphism and polymegathism of the endothelial cells after the surgery. There was no statistically significant correlation between endothelial cell loss and anterior chamber depth (r2=0.0488, p=0.377).
CONCLUSIONS
No clinically significant endothelial damage occurred after iris-claw phakic IOL implantation. However, special attention should be given to patients with shallow anterior chamber depth for iris-claw phakic IOL insertion to avoid unintended endothelial damage and long-term endothelial checkups using a specular microscope are critical for long-term protection of endothelial cells.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Long Term Corneal Endothelial Cell Density Loss after Iris-fixed Phakic Intraocular Lens Implantation
Jae Sung Park, Byung Gun Park, Bong Joon Choi, Jong Soo Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2017;58(4):473-477. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.4.473.
Reference
-
References
1. Heitzmann J, Binder PS, Kassar BS, Nordan LT. The correction of high myopia using excimer laser. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111:1627–34.2. Geggel HS, Talley AR. Delayed onset keratectasia following laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999; 25:582–6.
Article3. Holladay JT, Dudeja DR, Chang J. Functional vision and corneal changes after laser in situ keratomileusis determined by contrast sensitivity, glare testing, and corneal topography. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999; 25:663–9.
Article4. Sanders DR, Doney K, Poco M. ICL in Treatment of Myopia Study Group. United States food and drug administration clinical trial of the implatable collamer lens (ICL) for moderate to high myopia. Three-year follow-up. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:1683–92.5. Sarikkola AU, Sen HN, Uusitalo RJ, Laatikainen L. Traumatic cataract and other adverse events with implantable contact lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:511–24.6. Smallman D, Probst L, Rafuse PE. Pupillary block glaucoma secondary to posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens implantation for high myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:905–7.
Article7. Kodjikian L, Gain P, Donate D, et al. Malignant glaucoma induced by a phakic posterior chamber intraocular lens for myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:2217–21.
Article8. Perez-Santonja JJ, Iradier MT, Sanz-Iglesias L, et al. Endothelial changes in phakic eyes with anterior chamber intraocular lenses to correct high myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:1017–22.9. Alio JL, de la Hoz F, Perez-Santonja JJ, et al. Phakic anterior chamber lenses for the correction of myopia: a 7-year cumulative analysis of complications in 263 cases. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:458–66.10. Allemann N, Chamon W, Tanaka HM, et al. Myopic angle-supported intraocular lenses: two-year follow-up. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:1549–54.
Article11. Guell JL, Vazquez M, Gris O. Adjustable refractive surgery: 6-mm Artisan lens plus laser in situ keratomileusis for the correction of high myopia. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:945–52.
Article12. Fink AM, Gore C, Rosen E. Cataract development after implantation of the Staar Collamer posterior chamber phakic lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999; 25:278–82.13. Budo C, Hessloehl JC, Izak M, et al. Multicenter study of the Artisan phakic intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000; 26:1163–71.
Article14. Menezo JL, Avino JA, Cisneros A, et al. Iris claw phakic intraocular lens for high myopia. J Refract Surg. 1997; 13:545–55.
Article15. Landesz M, van Rij G, Luyten G. Iris-claw phakic intraocular lens for high myopia. J Refract Surg. 2001; 17:634–40.
Article16. Asano-Kato N, Toda I, Hori-Komai Y, et al. Experience with the Artisan phakic intraocular lens in Asian eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:910–5.
Article17. Pop M, Payette Y. Initial results of endothelial cell counts after Artisan lens for phakic eyes An evaluation of the United States Food and Drug Administration Ophtec study. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:309–17.18. Jang BH, Lee DW, Cho NC, et al. Clinical Results of Anterior Chamber Phakic Intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:31–6.19. Kim M, Kim JK, Lee HK. Corneal endothelial decompensation after iris-claw phakic intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:517–9.
Article20. Menezo JL, Cisneros AL, Rodriguez-Salvador V. Endothelial study of iris-claw phakic lens: four year follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:1039–49.
Article21. Lee ES, Cho YJ, Kim EK. Short-term change in corneal endothelium after iris-fixed phakic intraocular lens insertion. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:410–5.22. Bourne WM, Nelson LR, Hodge DO. Central corneal endothelial cell changes over a ten-year period. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997; 38:779–82.23. Bartels MC, Santana NT, Budo C, et al. Toric phakic intraocular lens for the correction of hyperopia and astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:243–9.
Article24. Guell JL, Vazquez M, Malecaze F, et al. Artisan toric phakic intraocular lens for the correction of high astigmatism. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 136:442–7.25. Saxena R, Boekhoorn SS, Mulder PG, et al. Long-term follow-up of endothelial cell change after Artisan phakic intraocular lens implantation. Ophthalmology. 2008; 115:608–13.
Article26. Waring GO 3rd, Bourne WM, Edelhauser HF, Kenyon KR. The corneal endothelium. Normal and pathologic structure and function. Ophthalmology. 1982; 89:531–90.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Short-term Change in Corneal Endothelium after Iris-Fixed Phakic Intraocular Lens Insertion
- Long Term Corneal Endothelial Cell Density Loss after Iris-fixed Phakic Intraocular Lens Implantation
- Two-year Endothalial Changes after Iris Fixed Phakic Intraocular Lens Implantation in Korean
- Five-year Change in Corneal Endothelial Cell Density after Foldable Iris-fixed Lens Insertion
- Clinical Outcomes of Foldable Iris-Fixed Phakic Intraocular Lens and Change in Corneal Endothelial Cell Density