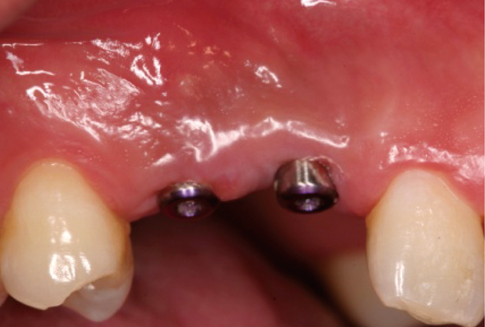
I-shaped incisions for papilla reconstruction in second stage implant surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Kyung Hee University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. chungjh@khu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Oral Biology, Kyung Hee University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2212141
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2010.40.3.139
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Pink gingival esthetic especially on the anterior teeth has been an important success criterion in implant-supported restoration. Inter-implant papillae are a critical factor for implant esthetics, and various techniques for inter-implant papilla reconstruction have been introduced. The aim of this study is to suggest and evaluate a surgical technique for reconstructing inter-implant papillae.
METHODS
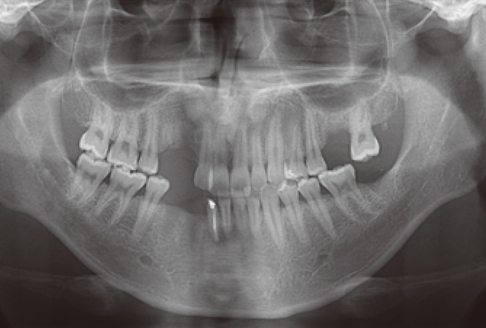
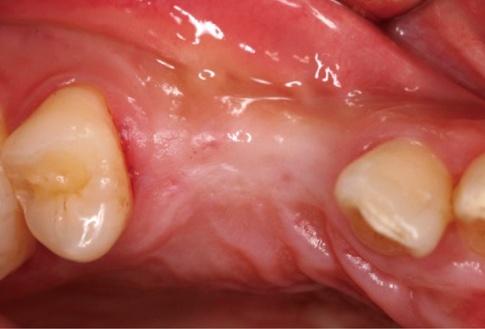
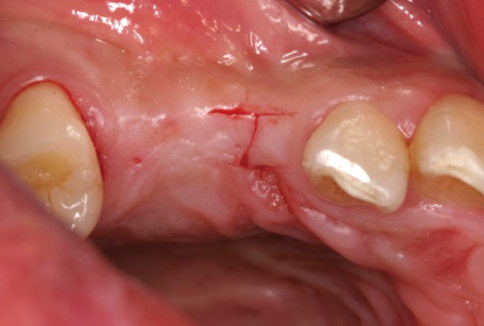
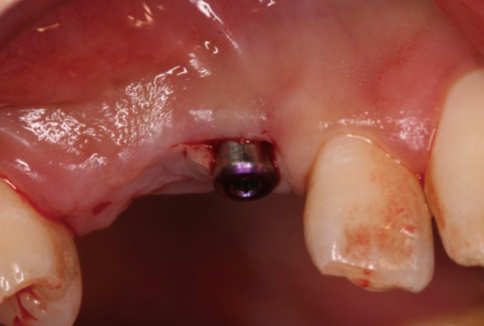
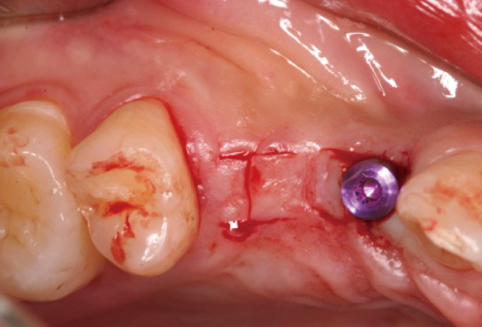
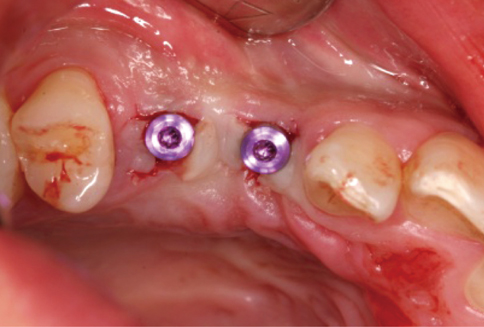
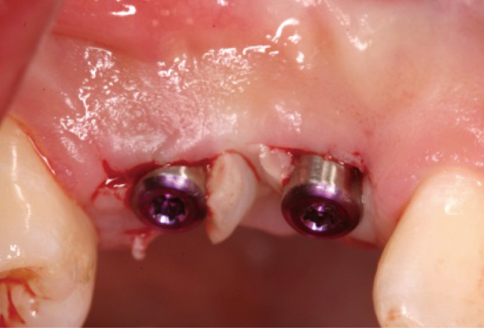
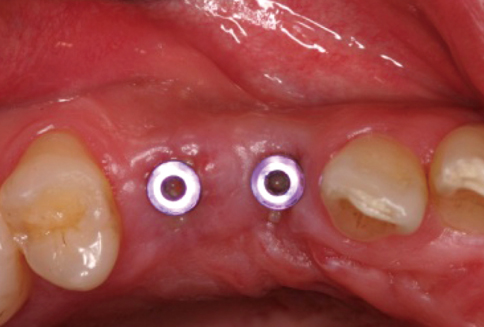
A 28-year-old man had an implant placed on the #13 and #14 area. Four months after implant placement, a second stage surgery was planned for inter-implant papilla reconstruction. At the time of the abutment connection, I-type incisions were performed on the #13i & #14i area followed by full-thickness flap elevation and connection of a healing abutment on underlying fixtures without suture.
RESULTS
Two weeks after the second stage implant surgery, soft tissue augmentation between the two implants was achieved.
CONCLUSIONS
I-shaped incisions for papilla reconstruction performed during the second stage implant surgery were useful for inter-implant papilla reconstruction and showed a good esthetic result.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
Seung-Yun Shin, Seung-Boem Kye, Jongrak Hong, Jun-Young Paeng, Seung-Min Yang
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2012;42(1):20-24. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20.The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
Seung-Yun Shin, Seung-Boem Kye, Jongrak Hong, Jun-Young Paeng, Seung-Min Yang
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2012;42(1):20-24. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20.The association between radiographic embrasure morphology and interdental papilla reconstruction using injectable hyaluronic acid gel
Won-Pyo Lee, Yo-Seob Seo, Hee-Jung Kim, Sang-Joun Yu, Byung-Ock Kim
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016;46(4):277-287. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2016.46.4.277.
Reference
-
1. Albrektsson T, Dahl E, Enbom L, Engevall S, Engquist B, Eriksson AR, et al. Osseointegrated oral implants: a Swedish multicenter study of 8139 consecutively inserted Nobelpharma implants. J Periodontol. 1988. 59:287–296.2. Grunder U. The inlay-graft technique to create papillae between implants. J Esthet Dent. 1997. 9:165–168.
Article3. Palacci P. Palacci P, Ericsson I, Engstrand P, Rangert B, editors. Papilla regeneration technique. Optimal implant positioning & soft tissue management for the Branemark system. 1995. Chicago: Quintessence Pub. Co.;59–70.4. Nemcovsky CE, Moses O, Artzi Z. Interproximal papillae reconstruction in maxillary implants. J Periodontol. 2000. 71:308–314.
Article5. Tarnow DP, Eskow RN. Considerations for single-unit esthetic implant restorations. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 1995. 16:778–788.6. Gastaldo JF, Cury PR, Sendyk WR. Effect of the vertical and horizontal distances between adjacent implants and between a tooth and an implant on the incidence of interproximal papilla. J Periodontol. 2004. 75:1242–1246.
Article7. Tarnow DP, Magner AW, Fletcher P. The effect of the distance from the contact point to the crest of bone on the presence or absence of the interproximal dental papilla. J Periodontol. 1992. 63:995–996.
Article8. Tarnow DP, Cho SC, Wallace SS. The effect of inter-implant distance on the height of inter-implant bone crest. J Periodontol. 2000. 71:546–549.
Article9. Grossberg DE. Interimplant papilla reconstruction: assessment of soft tissue changes and results of 12 consecutive cases. J Periodontol. 2001. 72:958–962.
Article10. Jemt T. Regeneration of gingival papillae after single-implant treatment. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1997. 17:326–333.11. Beagle JR. Surgical reconstruction of the interdental papilla: case report. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1992. 12:145–151.12. Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K. Site development for anterior single implant esthetics: the dentulous site. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2001. 22:221–232.13. Azzi R, Etienne D, Takei H, Fenech P. Surgical thickening of the existing gingiva and reconstruction of interdental papillae around implant-supported restorations. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2002. 22:71–77.14. Misch CE, Al-Shammari KF, Wang HL. Creation of inter-implant papillae through a split-finger technique. Implant Dent. 2004. 13:20–27.
Article15. Tinti C, Benfenati SP. The ramp mattress suture: a new suturing technique combined with a surgical procedure to obtain papillae between implants in the buccal area. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2002. 22:63–69.16. Shahidi P, Jacobson Z, Dibart S, Pourati J, Nunn ME, Barouch K, et al. Efficacy of a new papilla generation technique in implant dentistry: a preliminary study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008. 23:926–934.17. Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Umezu K, Kois JC. Dimensions of peri-implant mucosa: an evaluation of maxillary anterior single implants in humans. J Periodontol. 2003. 74:557–562.
Article18. Pradeep AR, Karthikeyan BV. Peri-implant papilla reconstruction: realities and limitations. J Periodontol. 2006. 77:534–544.
Article19. Berglundh T, Lindhe J, Jonsson K, Ericsson I. The topography of the vascular systems in the periodontal and peri-implant tissues in the dog. J Clin Periodontol. 1994. 21:189–193.
Article20. Hurzeler MB, Weng D. Periimplant tissue management: optimal timing for an aesthetic result. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent. 1996. 8:857–869.21. Flanagan D. An incision design to promote a gingival base for the creation of interdental implant papillae. J Oral Implantol. 2002. 28:25–28.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Breast Reconstruction with an Anatomical Expander and Implant: our clinical experience
- Retroauricular Hairline Incision and V-Shaped Incision for Parotidectomy
- The association between radiographic embrasure morphology and interdental papilla reconstruction using injectable hyaluronic acid gel
- Differences in complications and asymmetry in patients who did not receive a balancing procedure in two-stage and direct-to-implant breast reconstruction
- Technical approach and clinical outcomes of delayed two-stage tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction: a single-institution experience