J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Nov;79(5):415-419. 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.5.415.
Synchronous Undifferentiated Carcinoma of Gallbladder in a Patient with Intrahepatic Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasia (b-IPMN)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kdh2109@eulji.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2212057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.79.5.415
Abstract
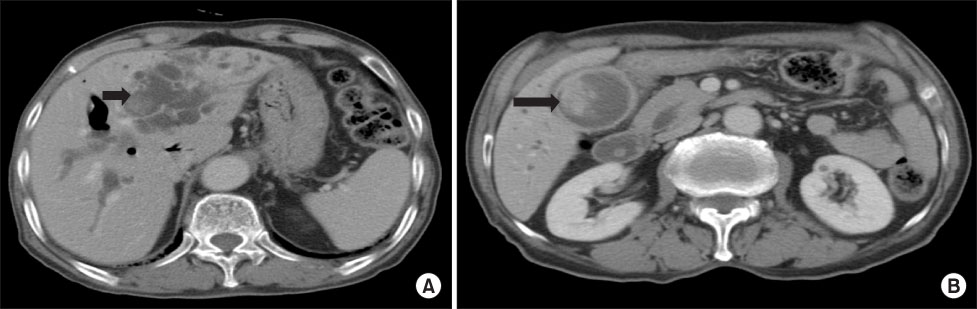
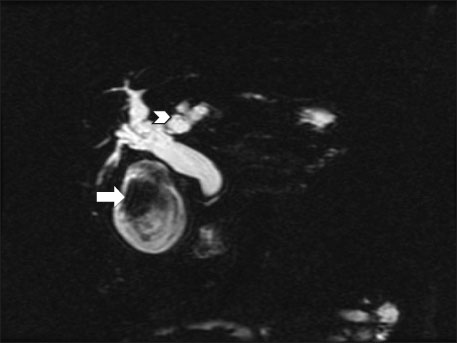
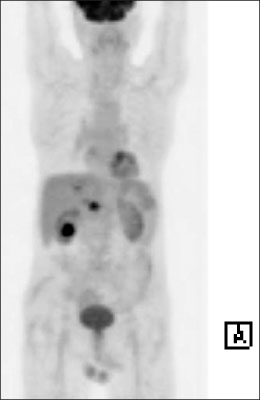
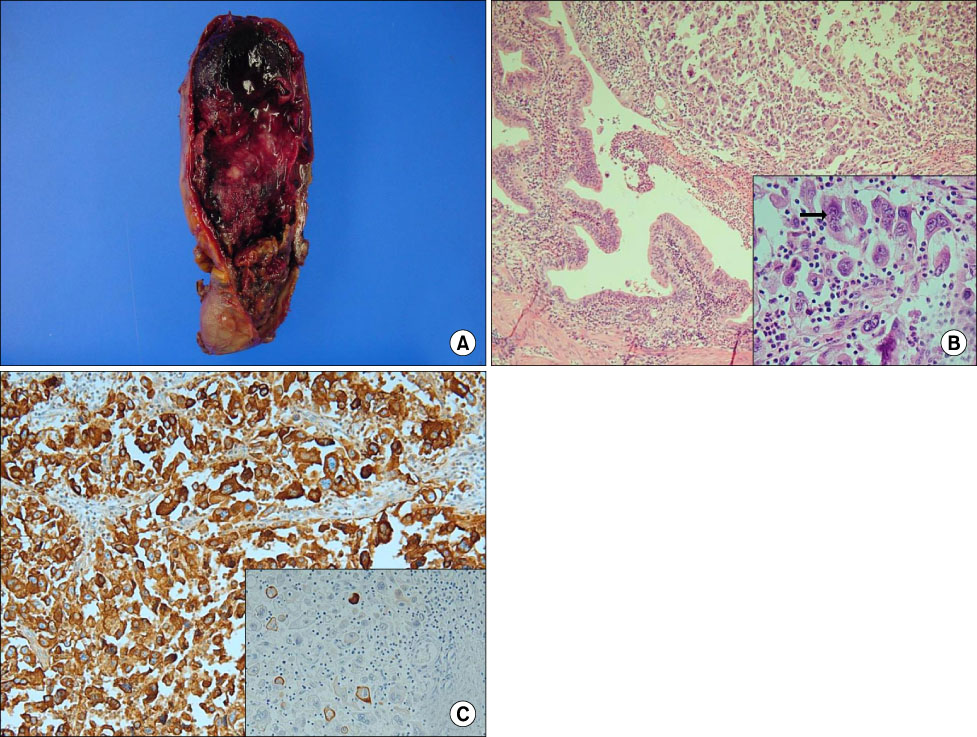
- Simultaneous development of intrahepatic bile duct and gallbladder carcinoma is extremely rare. We report herein the case of an 86-year-old man found to have double cancer of the gallbladder and intrahepatic bile duct. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography revealed a polypoid mass in the gallbladder and dilatation of the intrahepatic bile duct with intraductal papillary tumor in the left side of the liver. The patient underwent left hepatectomy, cholecystectomy with lymphadenectomy around the hepatoduodenal ligament. Pathological examination of the gallbladder revealed undifferentiated giant cell type carcinoma invading the muscularis propria. On the other hand, the liver tumor was intrahepatic intraductal papillary mucinous carcinoma in situ. Therefore, this was an extremely rare case of synchronous carcinoma of the gallbladder associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma, Mucinous
Aged, 80 and over
Bile Ducts, Intrahepatic
Carcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiopancreatography, Magnetic Resonance
Cholecystectomy
Dilatation
Gallbladder
Gallbladder Neoplasms
Giant Cells
Hand
Hepatectomy
Humans
Ligaments
Liver
Liver Neoplasms
Lymph Node Excision
Mucins
Cholangiocarcinoma
Liver Neoplasms
Mucins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kurosaki I, Watanabe H, Tsukada K, Hatakeyama K. Synchronous primary tumors of the extrahepatic bile duct and gallbladder. J Surg Oncol. 1997. 65:258–262.2. Fujii T, Kaneko T, Sugimoto H, Okochi O, Inoue S, Takeda S, et al. Metachronous double cancer of the gallbladder and common bile duct. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2004. 11:280–285.3. Taniai N, Onda M, Tajiri T, Yoshida H, Naitou Z. Synchronous carcinoma of the gallbladder in a patient with intrahepatic bile duct carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000. 47:121–124.4. Warren S, Gates O. Multiple primary malignant tumors. A survey of the literature and a statistical study. Am J Cancer. 1932. 16:1358–1414.5. Gertsch P, Thomas P, Baer H, Lerut J, Zimmermann A, Blumgart LH. Multiple tumors of the biliary tract. Am J Surg. 1990. 159:386–388.6. Fahim RB, McDonald JR, Richards JC, Ferris DO. Carcinoma of the gallbladder: a study of its modes of spread. Ann Surg. 1962. 156:114–124.7. Sozzi G, Miozzo M, Pastorino U, Pilotti S, Donghi R, Giarola M, et al. Genetic evidence for an independent origin of multiple preneoplastic and neoplastic lung lesions. Cancer Res. 1995. 55:135–140.8. Nees M, Homann N, Discher H, Andl T, Enders C, Herold-Mende C, et al. Expression of mutated p53 occurs in tumor-distant epithelia of head and neck cancer patients: a possible molecular basis for the development of multiple tumors. Cancer Res. 1993. 53:4189–4196.9. Habuchi T, Takahashi R, Yamada H, Kakehi Y, Sugiyama T, Yoshida O. Metachronous multifocal development of urothelial cancers by intraluminal seeding. Lancet. 1993. 342:1087–1088.10. Ogawa A, Sugo H, Takamori S, Kojima K, Fukasawa M, Beppu T, et al. Double cancers in the common bile duct: molecular genetic findings with an analysis of LOH. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2001. 8:374–378.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recurrent pancreatitis in the setting of gallbladder agenesis,ansa pancreatica, Santorinicoele and eventual intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia (IPMN)
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the pancreas with a pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: a case report
- Malignant Pancreatic Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm with Splenic Invasion: A Case Report
- Medical Management of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm
- Pathologic View of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm