J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Jun;78(6):419-422. 10.4174/jkss.2010.78.6.419.
Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma in the Male Breast
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drjh.yang@samsung.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Deagu, Korea.
- KMID: 2211974
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.78.6.419
Abstract
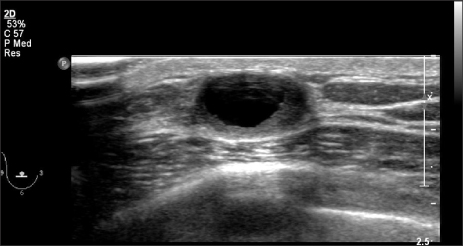
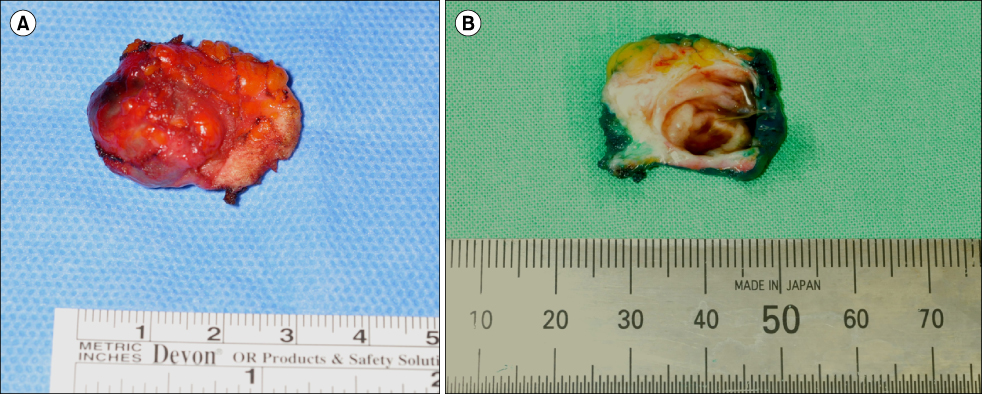
- Intracystic papillary carcinoma (IPC) is an extremely rare disease in the male breast with a few case reports. We present a case of a 61-year-old male who had IPC and review regarding diagnosis, characteristics and treatment. He had a chief complaint of a subareolar mass. It was diagnosed as a benign cystic intraductal papilloma by fine needle aspiration outside hospital. His radiologic studies including mammography and ultrasonography showed a suspicious malignant mass categorized as a BIRADS 4A in the right subareolar area. Therefore, the patient underwent wide excision without sentinel lymph node biopsy. The final pathologic results revealed a 1.6 cm sized intraductal papillary carcinoma of low nuclear grade with clear resection margin. He has taken tamoxifen and received adjuvant radiation therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tan PH, Sng IT. Male breast cancer: a retrospective study with immunohistochemical analysis of hormone receptor expression. Pathology. 1997. 29:2–6.2. Romics L Jr, O'Brien ME, Relihan N, O'Connell F, Redmond HP. Intracystic papillary carcinoma in a male as a rare presentation of breast cancer: a case report and literature review. J Med Case Reports. 2009. 3:13.3. Solorzano CC, Middleton LP, Hunt KK, Mirza N, Meric F, Kuerer HM, et al. Treatment and outcome of patients with intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast. Am J Surg. 2002. 184:364–368.4. Fentiman IS, Fourquet A, Hortobagyi GN. Male breast cancer. Lancet. 2006. 367:595–604.5. Dragoumis DM, Tsiftsoglou AP. Intracystic papillary carcinoma associated with ductal carcinoma in situ in a male breast. J Postgrad Med. 2008. 54:39–40.6. Sinha S, Hughes RG, Ryley NG. Papillary carcinoma in a male breast cyst: a diagnostic challenge. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2006. 88:W3–W5.7. Kinoshita T, Fukutomi T, Iwamoto E, Takasugi M, Akashi-Tanaka S, Hasegawa T. Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast in a male patient diagnosed by core needle biopsy: a case report. Breast. 2005. 14:322–324.8. Carter D, Orr SL, Merino MJ. Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast. After mastectomy, radiotherapy or excisional biopsy alone. Cancer. 1983. 52:14–19.9. Grabowski J, Salzstein SL, Sadler GR, Blair S. Intracystic papillary carcinoma: a review of 917 cases. Cancer. 2008. 113:916–920.10. Lefkowitz M, Lefkowitz W, Wargotz ES. Intraductal (intracystic) papillary carcinoma of the breast and its variants: a clinicopathological study of 77 cases. Hum Pathol. 1994. 25:802–809.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma in the Male Breast: A Case Report
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast
- Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma with Extensive Hemorrhage of the Breast: Sonographic and Advanced MR Findings: A Case Report
- Case of an Intracystic (Encysted) Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast
- Experience with Intracystic Papillary Carcinoma of the Breast at a Single Institute in Korea