J Pathol Transl Med.
2016 Mar;50(2):147-154. 10.4132/jptm.2015.12.25.
Morphologic Analysis of Cytomegalovirus Infected Cells in Bronchial Washing Cytology: Comparison of Liquid-Based Preparation and Conventional Smear
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. syha@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2211382
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.12.25
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The cytopathic effects of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection have been well described since the virus was first reported; however, the morphology of CMV infection has not been clearly studied. We examined the difference in detailed cytologic findings in bronchial washing cytology between liquid-based and conventionally prepared smears.
METHODS
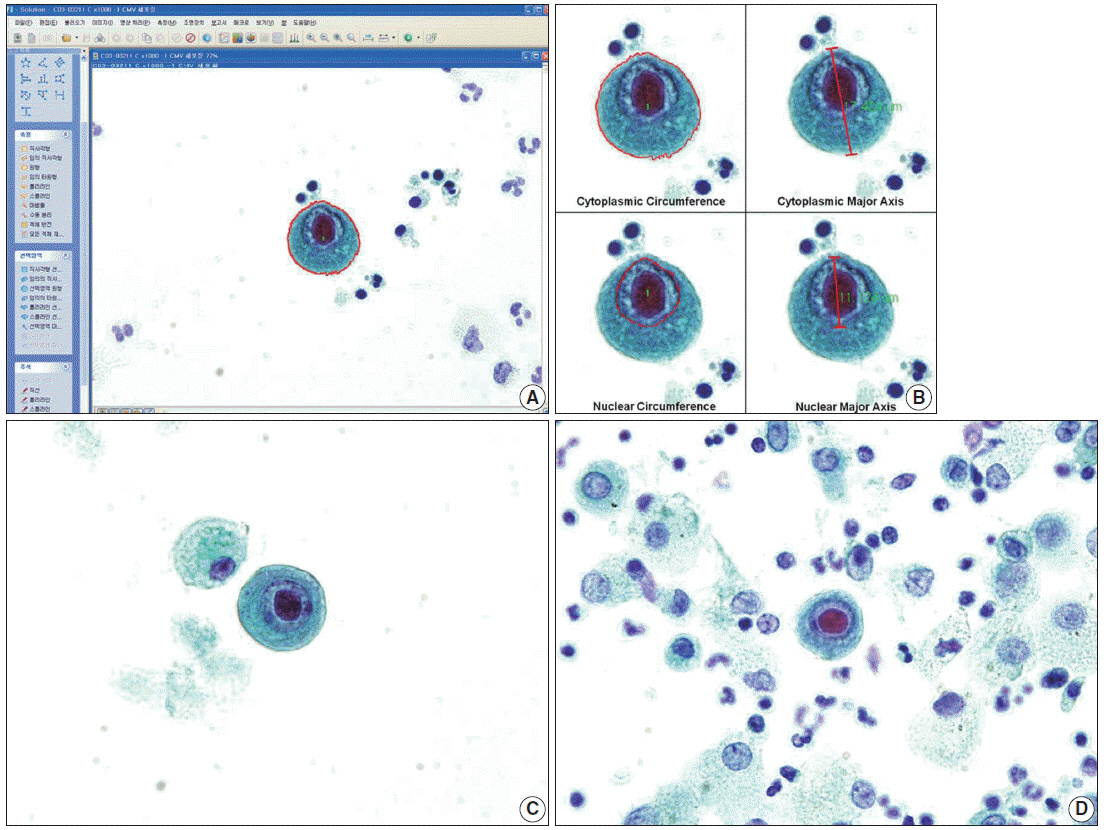
Bronchial washing cytology was processed using either the conventional preparation (CP) or liquid-based preparation (LBP). Sixty-nine cells with typical cytopathic effects of CMV infection were detected on CP slides and 18 cells on LBP slides. Using the image analyzer, area, circumference, major axis, and minor axis of the cytoplasm, nucleus, and intranuclear inclusion were measured in singly scattered CMV-infected cells, and histiocytes were used as a control.
RESULTS
The mean cytoplasmic area of CMV-infected cells was 1.47 times larger than that of histiocytes in CP and 2.92 times larger in LBP (p<.05). The mean nuclear area of CMV-infected cells was 2.61 times larger than that of histiocytes in CP and 4.25 times larger in LBP (p<.05). The nucleus to cytoplasm ratio and intranuclear inclusion to cytoplasm ratio of the mean area, circumference, major axis, and minor axis in CP were larger than those in LBP (p<.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The sizes of cytoplasm, nucleus, and intranuclear inclusion were larger in LBP than in CP, indicating that CMV-infected cells are easily detectable in LBP. However, the nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio was larger in CP, suggesting that differentiation from malignancy or regenerative atypia requires caution in CP.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ribbert H. Über protozoenartige Zellen in der Niere eines syphilitischen Neugeborenen und in der Parotis von Kindern. Zentralbl Allg Pathol. 1904; 15:945–8.2. Halwachs-Baumann G. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: epidemiology, diagnosis, therapy. Wien: Springer Vienna;2011.3. Jesionek A, Kiolemenoglou B. Ueber einen Befund von protozoenartigen Gebilden in den Organen eines hereditar-luetischen Foetus. Munch Med Wochenschr. 1904; 51:1905–7.4. Goodpasture EW, Talbot FB. Concerning the nature of “protozoan-like” cells in certain lesions of infancy. Am J Dis Child. 1921; 21:415–25.
Article5. Cole R, Kuttner AG. A filterable virus present in the submaxillary glands of guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1926; 44:855–73.
Article6. Craig JM, Macauley JC, Weller TH, Wirth P. Isolation of intranuclear inclusion producing agents from infants with illnesses resembling cytomegalic inclusion disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957; 94:4–12.7. Fetterman GH. A new laboratory aid in the clinical diagnosis of inclusion disease of infancy. Am J Clin Pathol. 1952; 22:424–5.
Article8. Warner NE, McGrew EA, Nanos S. Cytologic study of the sputum in cytomegalic inclusion disease. Acta Cytol. 1964; 8:311–5.9. An-Foraker SH, Haesaert S. Cytomegalic virus inclusion body in bronchial brushing material. Acta Cytol. 1977; 21:181–2.10. Frable WJ, Frable MA, Seney FD Jr. Virus infections of the respiratory tract cytopathologic and clinical analysis. Acta Cytol. 1977; 21:32–6.11. Martin WJ 2nd, McDougall JC. Cytomegalovirus infection with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis suggested by bronchoalveolar lavage. Chest. 1983; 84:500–2.12. Duggan MA, Pomponi C, Robboy SJ. Pulmonary cytology of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: an analysis of 36 cases. Diagn Cytopathol. 1986; 2:181–6.
Article13. Buchanan AJ, Gupta RK. Cytomegalovirus infection of the lung: cytomorphologic diagnosis by fine-needle aspiration cytology. Diagn Cytopathol. 1986; 2:341–2.
Article14. Selvaggi SM, Gerber M. Pulmonary cytology in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Diagn Cytopathol. 1986; 2:187–93.
Article15. Solans EP, Yong S, Husain AN, Eichorst M, Gattuso P. Bronchioloalveolar lavage in the diagnosis of CMV pneumonitis in lung transplant recipients: an immunocytochemical study. Diagn Cytopathol. 1997; 16:350–2.
Article16. Gideon K, Zaharopoulos P. Cytomegalovirus endocervicitis diagnosed by cervical smear. Diagn Cytopathol. 1991; 7:625–7.
Article17. Hunt JL, Baloch Z, Judkins A, LiVolsi VA, Montone KT, Gupta PK. Unique cytomegalovirus intracytoplasmic inclusions in ectocervical cells on a cervical/endocervical smear. Diagn Cytopathol. 1998; 18:110–2.
Article18. Henry-Stanley MJ, Stanley MW, Burton LG, Samuelson J. Cytologic diagnosis of cytomegalovirus in cervical smears. Diagn Cytopathol. 1993; 9:364–5.
Article19. Sekhon HS, Press RD, Schmidt WA, Hawley M, Rader A. Identification of cytomegalovirus in a liquid-based gynecologic sample using morphology, immunohistochemistry, and DNA real-time PCR detection. Diagn Cytopathol. 2004; 30:411–7.
Article20. Oei AL, Salet-van de Pol MR, Borst SM, van den Berg AP, Grefte JM. “Owl’s eye” cells in a cervical smear of a transplant recipient: don’t forget to inform the referring physician. Diagn Cytopathol. 2007; 35:227–9.
Article21. Venkataraman G, Kouria G, Mehrotra S, Hammadeh R, Wojcik EM, Booth CN. Cytomegalovirus inclusions on a cervical pap test: report of a well-known organism at an uncommon site. Diagn Cytopathol. 2007; 35:618–20.
Article22. Wax TD, Layfield LJ, Zaleski S, et al. Cytomegalovirus sialadenitis in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a potential diagnostic pitfall with fine-needle aspiration cytology. Diagn Cytopathol. 1994; 10:169–72.
Article23. Santiago K, Rivera A, Cabaniss D, Dhurhar N, Moroz K. Fine-needle aspiration of cytomegalovirus sialadenitis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: pitfalls of diff-quik staining. Diagn Cytopathol. 2000; 22:101–3.
Article24. Goodman ZD, Gupta PK, Frost JK, Erozan YS. Cytodiagnosis of viral infections in body cavity fluids. Acta Cytol. 1979; 23:204–8.25. Delfs-Jegge S, Dalquen P, Hurwitz N. Cytomegalovirus-infected cells in a pleural effusion from an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patient: a case report. Acta Cytol. 1994; 38:70–2.26. Armbruster C, Schalleschak J, Vetter N, Pokieser L. Pleural effusions in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: correlation with concomitant pulmonary diseases. Acta Cytol. 1995; 39:698–700.27. Katz RL, Alappattu C, Glass JP, Bruner JM. Cerebrospinal fluid manifestations of the neurologic complications of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Acta Cytol. 1989; 33:233–44.28. Teot LA, Ducatman BS, Geisinger KR. Cytologic diagnosis of cytomegaloviral esophagitis: a report of three acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related cases. Acta Cytol. 1993; 37:93–6.29. Zhang X, el-Sahrigy D, Elhosseiny A, Melamed MR. Simultaneous cytomegalovirus infection and Kaposi’s sarcoma of the thyroid diagnosed by fine needle aspiration in an AIDS patient: a case report and first cytologic description of the two entities occurring together. Acta Cytol. 2003; 47:645–8.30. Shi Q, Nilson E, Singh M, David O, Cabay RJ. Uncommon cervical viral cytopathic changes in a liquid-based cytology preparation. Diagn Cytopathol. 2012; 40:1088–9.
Article31. Son SM, Koo JH, Choi SY, et al. Evaluation of urine cytology in urothelial carcinoma patients: a comparison of CellprepPlus(R) liquidbased cytology and conventional smear. Korean J Pathol. 2012; 46:68–74.32. Takei H, Ruiz B, Hicks J. Cervicovaginal flora: comparison of conventional pap smears and a liquid-based thin-layer preparation. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006; 125:855–9.33. Konofaos P, Tomos P, Malagari K, et al. The role of ThinPrep cytology in the investigation of lung tumors. Surg Oncol. 2006; 15:173–8.
Article34. Lee KR, Papillo JL, St John T, Eyerer GJ. Evaluation of the ThinPrep processor for fine needle aspiration specimens. Acta Cytol. 1996; 40:895–9.
Article35. Astall E, Atkinson C, Morton N, Goddard MJ. The evaluation of liquid-based ‘Cyto-SED’ cytology of bronchioalveolar lavage specimens in the diagnosis of pulmonary neoplasia against conventional direct smears. Cytopathology. 2003; 14:143–9.36. Hayama FH, Motta AC, Silva Ade P, Migliari DA. Liquid-based preparations versus conventional cytology: specimen adequacy and diagnostic agreement in oral lesions. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2005; 10:115–22.37. Kobayashi Y, Uehara T, Ota H. Liquid-based thin-layer cytology can be routinely used in samples obtained via fiberoptic bronchoscope. Acta Cytol. 2011; 55:69–78.
Article38. Kim S, Owens CL. Analysis of ThinPrep cytology in establishing the diagnosis of small cell carcinoma of lung. Cancer. 2009; 117:51–6.
Article39. Lee JD, Oh YH, Lee SO, Kim JY. Comparison of diagnostic cytomorphology of atypical squamous cells in liquid-based preparations and conventional smears. Korean J Pathol. 2012; 46:365–9.
Article40. Norimatsu Y, Shigematsu Y, Sakamoto S, et al. Nuclear characteristics of the endometrial cytology: liquid-based versus conventional preparation. Diagn Cytopathol. 2013; 41:120–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of ThinPrep Cytology and Conventional Cytology in Bronchial Washing for Lung Cancer
- Comparison of Conventional Smear, Cell Block and Liquid-based Preparation in the Evaluation of Bronchial Washing Specimen in Lung Cancer Patients
- Evaluation of cytopathologic diagnosis of lung carcinoma
- Liquid-Based Cytology Using MonoPrep2(TM) System in Cervicovaginal Cytology: Comparative Study with Conventional Pap Smear and Histology
- Diagnostic Value of Urine Cytology in 236 cases; a Comparison of Liquid-Based Preparation and Conventional Cytospin Method