J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2007 Oct;48(10):1415-1418. 10.3341/jkos.2007.48.10.1415.
A Case of Fungal Keratitis as a Complication of Orthokeratology Contact Lens
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, Pusan National University1, Pusan, Korea. Jiel75@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2210997
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2007.48.10.1415
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To present a case report of fungal keratitis related to prolonged overnight use of orthokeratology contact lenses.
METHODS
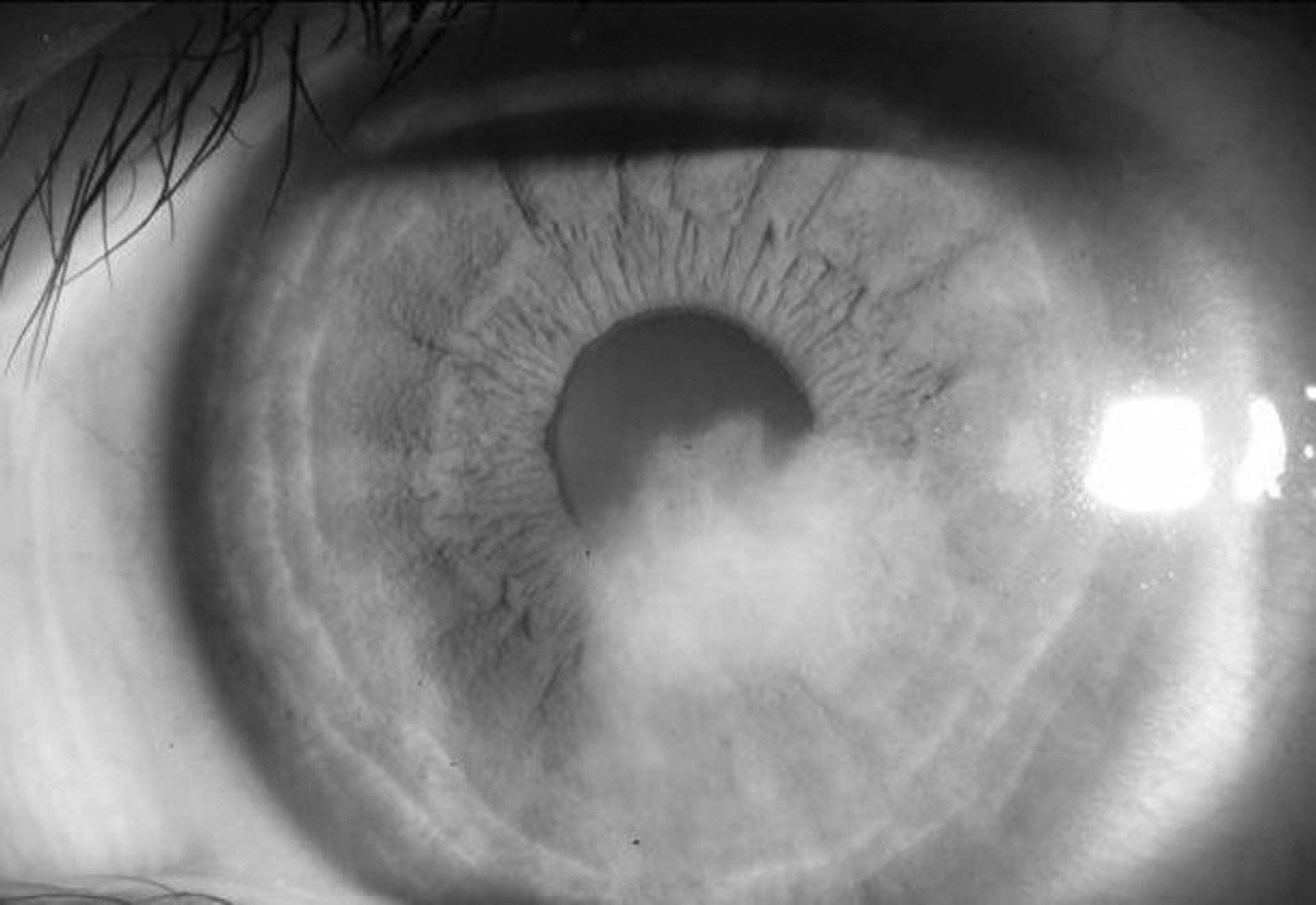
A 13 year-old girl presented with a corneal ulcer in her left eye refractory to antibacterial medication. She had a history of wearing orthokeratology contact lenses overnight for seven months.
RESULTS
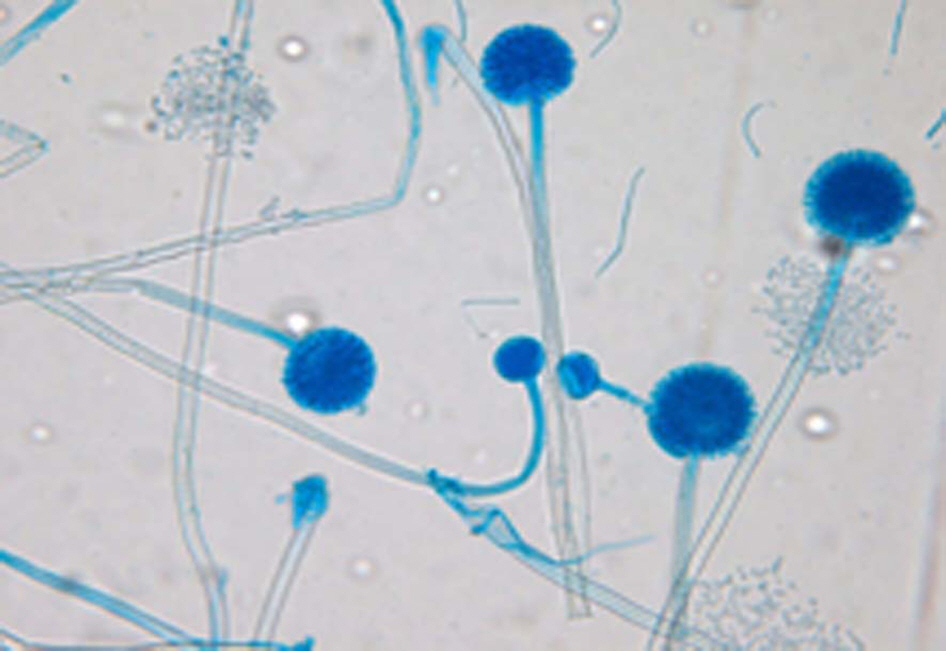
The organism Aspergillus was isolated by corneal scraping, the contact lens itself, and from the storage case. The patient was treated with topical fluconazole and Natamycin pimaricin in addition to oral itraconazole, resulting in a resolution of the ocular lesion.
CONCLUSIONS
The risk of fungal infection as a potential complication of the use of overnight orthkeratology contact lenses should be considered when using these lenses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Contact Lens and Amblyopia Treatment in Children With Unilateral High Myopic Anisometropia
Byung Joo Lee, Jeong Hun Kim, Young Suk Yu
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010;51(1):88-94. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2010.51.1.88.
Reference
-
References
1. Wilson DR, Keeney AH. Corrective measures of myopia. Surv Ophthalmol. 1962; 34:294–304.2. Alhharbi A, Swarbrick H. The effects of overnight orthokeratology lens wear on corneal thickness. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:2518–23.3. Liesegang TJ. Contact lens-related microbial keratitis. Cornea. 1997; 16:125–31.
Article4. Berstein HN. Fungal growth into a Bionite hydrophilic contact lens. Ann Ophthalmol. 1973; 5:317–22.5. Xuguang S, Huiying Zhao, Shijing Deng, et al. Infectious keratitis related to orthokeratology. Ophthal Physiol Opt. 2006; 26:133–6.6. Wilson DR, Keeney AH. Corrective measures for myopia. Sur Ophthalmol. 1990; 34:294–5.
Article7. Lee YB, Tchah H. A case of microbial keratitis as a complication of orthokeratology contact lens wear. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:1401–4.8. Xuguang S, Lin C, Yan Z, et al. Acanthamoeba keratitis as a complication of orthokeratology. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 136:1151–9.
Article9. Roth HW. The etiology of ocular irritation in soft lens wearers; distribution in a large clinical sample. Contact Intraocular Lens Med J. 1978; 4:38–47.10. Eriken SP. Hydrophilic soft lens sterility and disinfection. In : Ruben M, editor. Soft Contact Lenses : Clinical and Applied Technology. 1st ed.New York: Wiley;1978. chap. 5.11. Wilson LA, Ahearn DG. Association of fungi with extended-wear soft lenses. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986; 101:434–6.12. Hammeke JC, Ellis PP. Mycotic flora of the conjunctiva. Am J Ophthalmol. 1960; 49:1174–8.
Article13. Lau LI, Wu CC, Lee SM, et al. Pseudomonas corneal ulcer related to overnight orthokeratology. Cornea. 2003; 22:262–4.
Article14. Young AL, Leung AT, Cheung EY, et al. Orthokeratology lens-related pseudomonas aeruginosa infectious keratitis. Cornea. 2003; 22:265–6.
Article15. Young AL, Leung AT, Cheung LL, et al. Orthokeratology lens-related corneal ulcers in children: a case series. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:590–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Microbial Keratitis as a Complication of Orthokeratology Contact Lens Wear
- Proper Management for Rigid Gas Permeable Contact and Orthokeratology Lens
- Major Complications of Overnight Orthokeratology Lens for Myopic Correction
- Orthokeratology Lenses and Myopia Control
- Pseudomonas Keratitis Due to Mishandling of Soft Contact lenses