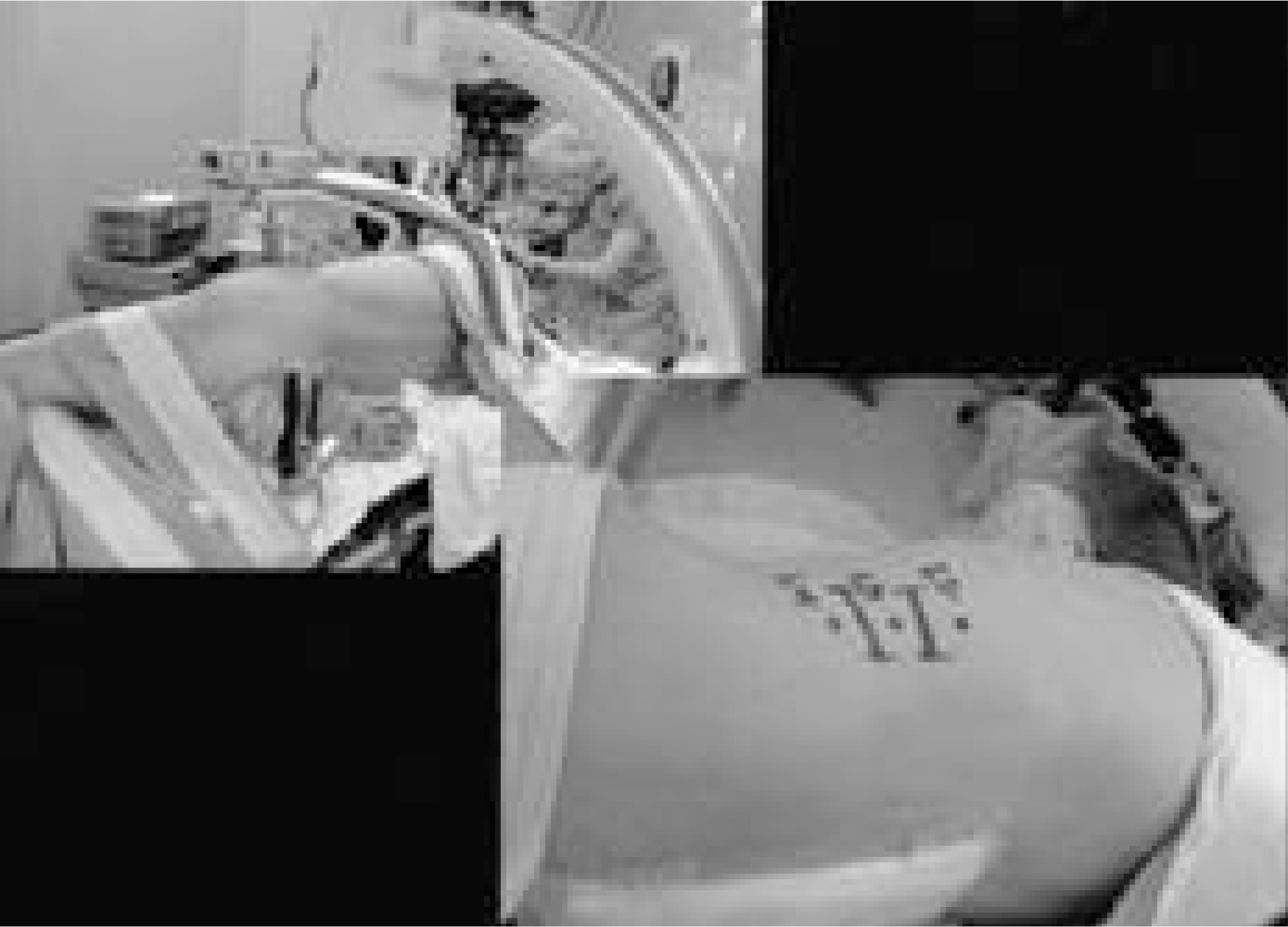
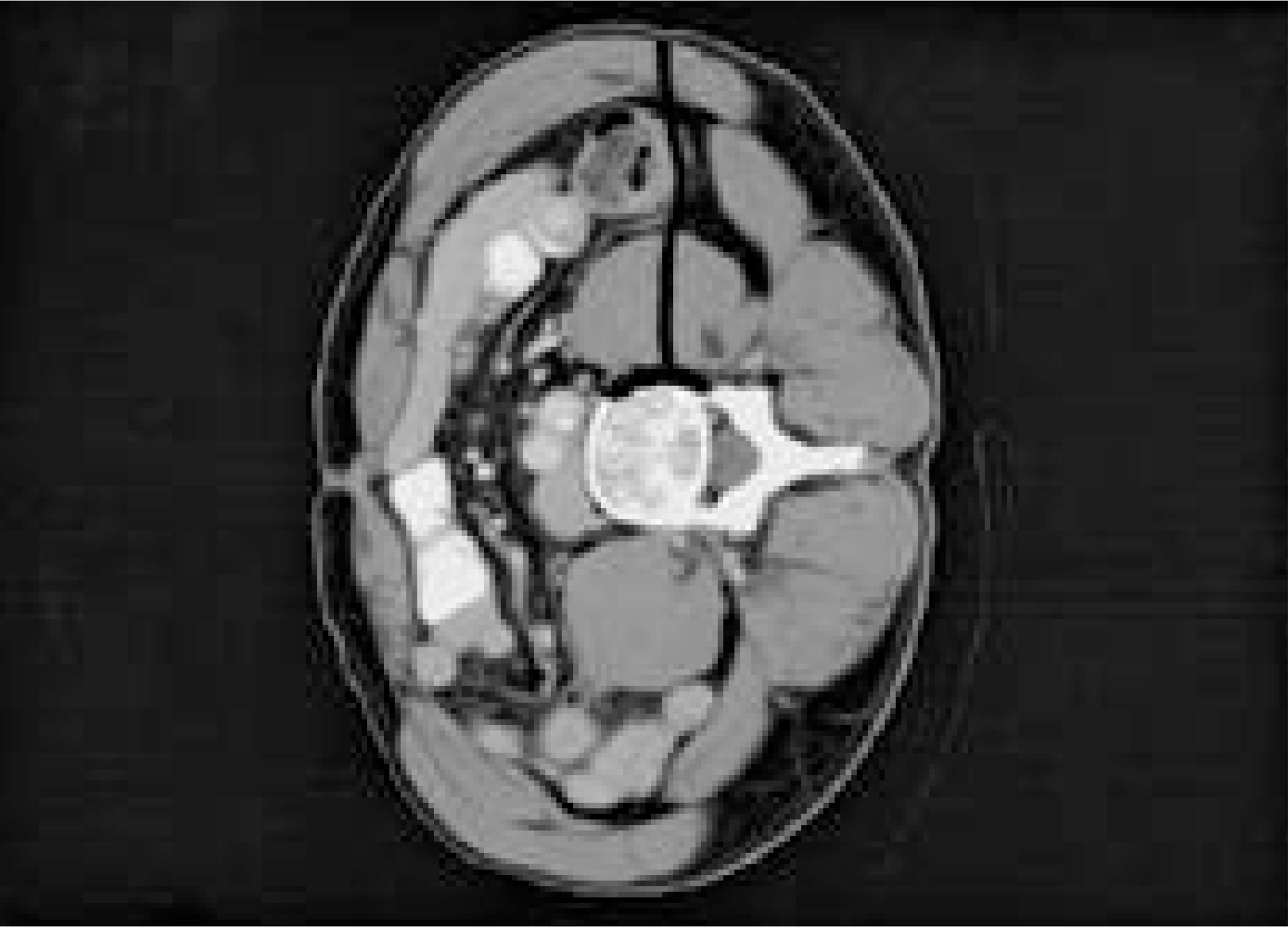
J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2002 Dec;9(4):341-346. 10.4184/jkss.2002.9.4.341.
Laparoscopy Assisted Miniopen Lateral Approach for Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea. csl@smc.samsung.co.kr
- KMID: 2209716
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2002.9.4.341
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: A new approach to anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF).
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the advantages, technical pitfalls and complications of the laparoscopy assisted miniopen lateral approach. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Several kinds of miniopen approach or laparoscopy are now used for ALIF.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-five patients with various disease entities were included. Blood loss, operation time, incision size, postoperative time to mobilization, length of hospital stay, technical problems and complications were analyzed.
RESULTS
Using this approach, T12 to L5 can be reached sub-diaphragmatically. Blood loss and operation time were 45.7 cc and 82.8 minutes for 1 level, 103.2 cc and 107.6 minutes for two levels, 272.5 cc and 150 minutes for three levels, and 520 cc and 190 minutes for four-level-fusion, respectively, The incision sizes were on average 4.1cm for 1 level, 6.2 cm for 2 levels, 8.2 cm for 3 levels and 10.1 cm for four-level-fusion. Complications were retroperitoneal hematoma in 2 cases, pneumonia in 1 case and transient lumbosacral plexus palsy in 3 cases.
CONCLUSION
The laparoscopy assisted miniopen lateral approach is an advantageous approach with a very short learning curve. However, special attention is required if complications such as transient lumbosacral plexus palsy are to be avoided.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Dewald CJ, Millikan KW, Hammerberg KW, Doolas A and Dewald RL. An open, minimally invasive approach to the lumbar spine. The American Surgeon. 65:61–68. 1999.2). Levrant SG, Bieber EJ and Barnes RB. Ante rior abdominal wall adhesions after laparotomy or laparoscopy. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 4:353–356. 1997.3). Mathews HH, Evans MT, Molligan HJ, Long BH. Laparoscopic discectomy with anterior lumbar interbody fusion. A preliminary review. Spine. 20:1797–1802. 1995.4). Mayer HM. A new microsurgical technique for minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine. 22:691–700. 1997.
Article5). McAfee PC, Regan JJ, Zdeblick T, et al. The incidence of complication in endoscopic anterior thoracolumbar spinal reconstructive surgery: A prospective multicenter study comprising the first 100 consecutive cases. Spine. 20:1624–1632. 1995.6). McAfee PC, Regan JJ, Geis WP and Fedder IL. Minimally invasive anterior retroperitoneal approach to the lumbar spine: Emphasis on the lateral BAK. Spine. 23:1476–1484. 1998.7). Obenchain TG. Laparoscopic discectomy: Case report. J. Lparoendosc Surg. 1:145–149. 1991.8). Regan JJ, McAfee PC, Mack MJ. Atlas of endoscopic spine surgery. St. Louis: MO. Quality Medical Publishing, Inc.;1995.9). Regan JJ, Yuan H and McAfee PC. Lap a r osc o pic fusion of the lumbar spine: Minimally invasive spine surgery: A prospective multicenter study evaluating open and laparoscopic lumbar fusion. Spine. 24:402–411. 1999.10). Tiusanen H, Seitsalo S, Osterman K and Soini J. Ret -rograde ejaculation after anterior interbody lumbar fusion. Eur Spine J. 4:339–342. 1995.11). Zdeblick TA and David SM. A prospective comparison of surgical approach for anterior L4-L5 fusion: Laparoscopic versus Mini anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine. 25:2682–2687. 2000.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Prospective Comparison of Surgical Approach for Lateral Retroperitoneal L4-5 Fusion: Laparoscopic Versus Mini-ALIF
- Minimally Invasive Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Indications, Outcomes and Complications
- Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- The Changes of the Dimension of Intervertebral Disc,-Neural Foramen and Spinal Canal after Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in the Lumbar Spine
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Minimally Invasive Anterior Interbody Fusion of the T11-T12 Level Using Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion Devices: A Case Report