J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2013 Mar;20(1):22-27. 10.4184/jkss.2013.20.1.22.
The Result of Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Low Grade Spondylolisthesis - Minimum 2 Years Follow Up -
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Busan Bumin Hospital, Busan, Korea. moon_chan@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2209497
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2013.20.1.22
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGNS: A retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
To analyze the clinical and radiological outcomes of spontaneous reduction via minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (Mini-TLIF) as the treatment for low-grade symptomatic spondylolisthesis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Although minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion is technically demanding, this procedure is an effective method for spontaneous reduction of low grade spondylolisthesis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyzed consecutive series of 41 patients with low grade spondylolisthesis who underwent minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion, between April 2008 and July 2009. The minimum follow-up period was 2 years. Clinical evaluation was performed by an analysis of Visual Analogue Scale and Oswestry Disability Index. For the radiological evaluation, disc space height, slip percentage, and slip angle were analyzed. At the final follow-up, the fusion rate was analyzed according to the Bridwell's anterior fusion grade.
RESULTS
For the evaluation of clinical outcomes, the Visual Analogue Scale for back pain decreased from 6.8+/-1.2 to 2.0+/-1.1, and that for radiating pain decreased from 7.9+/-1.3 to 1.7+/-1.1. Oswetry Disability Index decreased from 38.5+/-8.4 to 13.4+/-6.1. For the radiological evaluation, disc space height increased from 8.4+/-2.14mm to 11.8+/-1.54mm(P<0.05), slip percentage was reduced from 18.4+/-5.1% to 13.3+/-3.1%(P<0.05) and slip angle decreased from 10.6+/-4.5degrees to 6.2+/-3.4degrees (P<0.05). At the final follow-up, radiological union was obtained in 38 cases (92.7%).
CONCLUSIONS
We conclude that minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion appears to be an effective method for spontaneous reduction of low grade spondylolisthesis if the surgeon becomes familiar with this method.
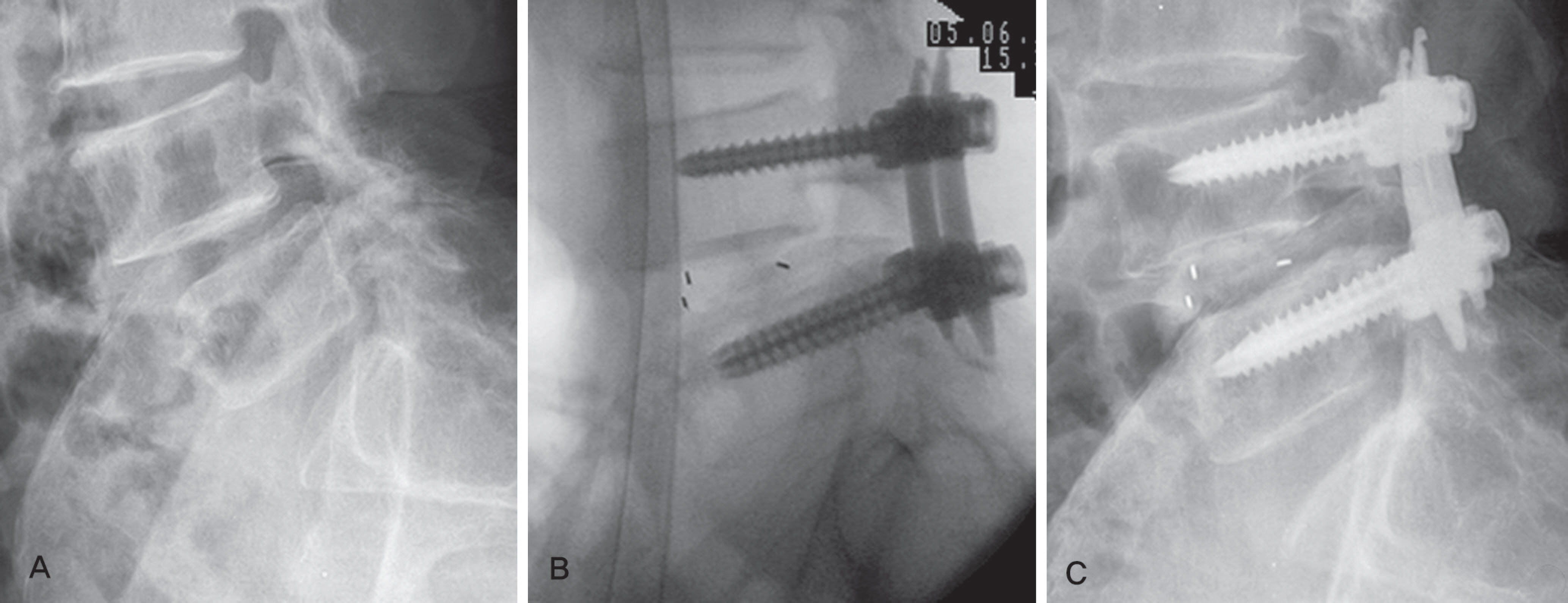
Figure
Reference
-
1.Thomsen K., Christensen FB., EISkjaer SP., Hansen ES., Fru-ensuaard S., Bü nger CE. The effects of pedicle screw instrumentation on functional outcome and fusion rates in pos-terolateral lumbar spinal fusion: a prospective, randomized, clinical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997. 22:2813–22.2.Steffee AD. Sitkowski DJ. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion and plates. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. 227:99–102.3.Foley KT., Holly LT., Schwender JD. Minimally invasive lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003. 28(15 Suppl):S26–35.
Article4.Schwender JD, Holly LT, Rouben DP, Foley KT. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: technical feasibility and initial results. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005. 18(Suppl):S1–6.5.Mulholland RC. Comment on topographic relations of neural and ligamentous structures of the lumbosacral junction: in vitro investigation. Spondylolisthesis- no reduction. Partial reduction or total reduction? Eur Spine J. 2001. 10:133–4.6.Bridwell KH., Lenke LG., McEnery KW., Baldus C., Blanke K. Anterior fresh frozen structural allografts in the tho-racic and lumbar spine. Do they work if combined with posterior fusion and instrumentation in adult patients with kyphosis or anterior column defects? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995. 20:1410–8.
Article7.Park P., Foley KT. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with reduction of spondylolisthesis: technique and outcomes after a minimum of 2 years follow up. Neurosurg Focus. 2008. 25:E16.8.Mulholland RC. Comments on tomographic relations of neural and ligamentous structures of lumbosacral junction: in vitro investigation. Spondylolisthesis-no reduction.partial reduction or total reduction? Eur Spine J. 2001. 10:133–4.9.Cho KJ., Moon KH., Lee DJ., Lee KY., KIM KH., Park SR. Factors affecting reduction of splippage in posterolateral fusion for spondylolytis spondylolisthesis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2006. 13:177–83.10.Molinari MR., Bridwell KH., Lenke LG., Baldus C. Anterior column support in surgery for high grade, isthmic spondy-lolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. 394:109–20.11.Bradford DS., Broachie-Adjei O. Treatment of severe spon-dylolisthesis by anterior and posterior reduction and stabili-zation. A long term follow up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990. 72:1060–6.12.Madan S., Boeree NR. Outcomes of posterior lumbar in-terbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion for spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002. 27:1536–42.13.Pan J., Li L., Qian L,et al. Spontaneous Slip Reduction of Low Grade Isthmic Spondylolisthesis Following Circum-ferential Release via Bilateral Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011. 36:283–9.14.Yan DL., Pei FX., Li J., Soo CL. Comparative study of PLIF and TLIF treatment in adult degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2008. 17:1311–6.15.Hackenberg L., Halm H., Bullmann V., Vieth V., Shneider M., Liljenqvist U. tranforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a safe technique with satisfactory three to five year results. Eur Spine J. 2005. 14:551–8.16.Park Y., Ha JW., Lee YT., Sung NY. The effect of a radio-graphic solid fusion on clinical outcomes after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 2011. 11:205–12.
Article17.Gong K., Wang Z., Luo Z. Reduction and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with posterior fixation versus transsacral cage fusion in situ with posterior fixation in the treatment of Grade 2 adult isthmic spondylolisthesis in the lumbosacral spine. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010. 13:394–400.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intraoperative Anteropulsion of an Interbody Fusion Cage During Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Case Report
- Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Patients with Low Grade Spondylolisthesis: Comparison of the Unilateral and Bilateral Approaches
- Surgical Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for the Treatment of Spondylolisthesis and Degenerative Segmental Instability
- Minimally Invasive Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Indications, Outcomes and Complications
- Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Percutaneous Instrumentation: A Technical Note