J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2010 Dec;14(2):126-133. 10.13104/jksmrm.2010.14.2.126.
Three-Dimensional Brain Surface Rendering Imaging of Cortical Dysplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chonbuk National University Medical School Jeonju, Jeonbuk, Korea. chunggh@chonbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2206910
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2010.14.2.126
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The study was to evaluate the localization of the abnormal gyral and sulcal patterns obtained by means of brain surface rendering imaging.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
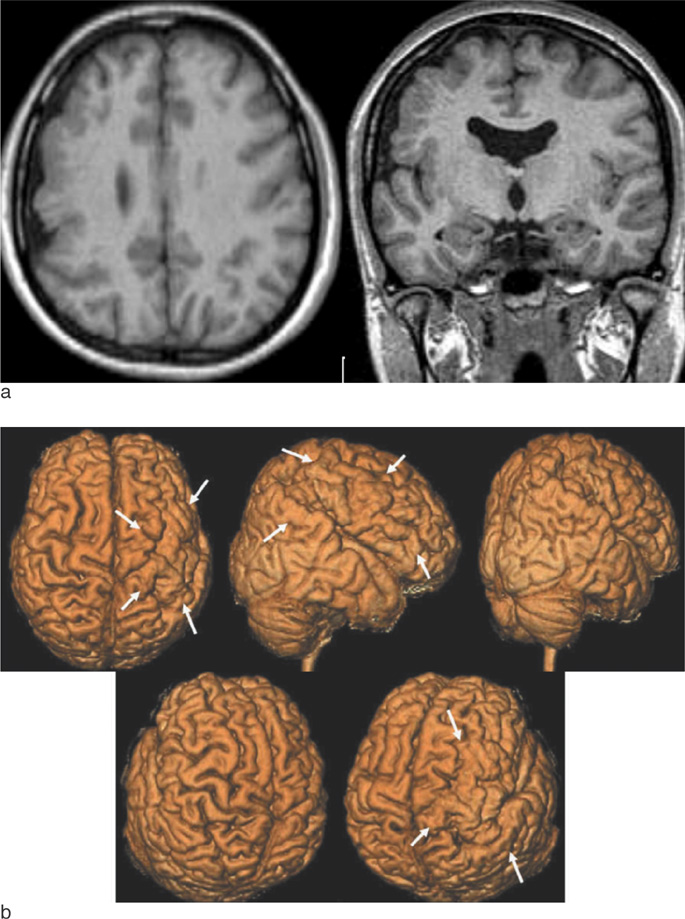
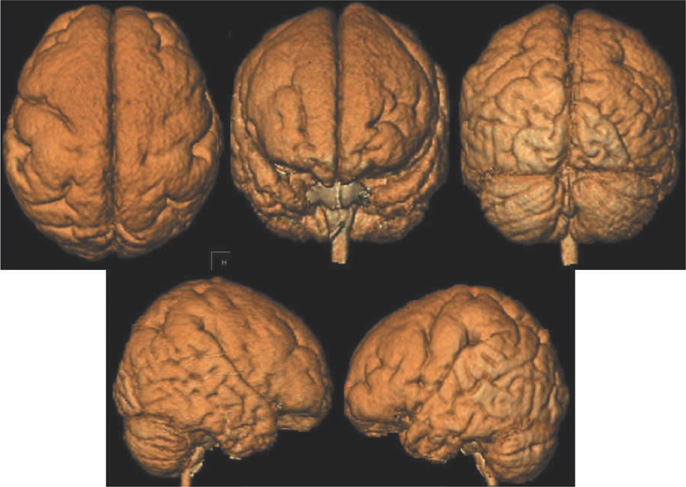
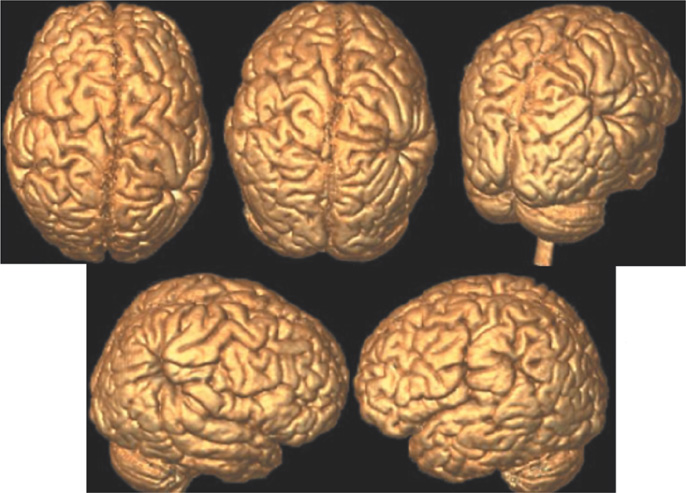
Nineteen patients with cortical dysplasia who underwent brain surface rendering MR imaging were included in this study. We acquired MP-RAGE sequence and created the 3-D surface rendering MR images by using VoxelPlus(R). Anatomical locations and configurations of abnormal gyri and sulci were reviewed.
RESULTS
Abnormal gyral and sulcal patterns were seen 18 in 19 patients. The configuration and orientation of affected gyri and sulci were clearly evaluated in the brain surface rendering images. In a lissencephaly, the a cortex was not delineated and showed markedly thick and smooth gyral pattern. In a schizencephaly, there were wheel shaped broad gyral pattern around the cleft. In a hemimegalencephaly, an affected hemisphere were enlarged and displayed thick and wide gyral pattern. In CBPS, the insular cortex was exposed and the gyri of the lesion were thickened. In focal cortical dysplasia, there were irregular serrated or thick and enlarged gyri.
CONCLUSION
Brain surface rendering MR imaging is useful for the evaluation of a detailed gyral pattern and accurate involvement site of abnormal gyri.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Keränen T, Riekkinen P. Severe epilepsy: diagnostic and epidemiological aspects. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1988. 117:7–14.2. Palmini A, Andermann F, Olivier A, Tampieri D, Robitaille Y, Andermann E, et al. Focal neuronal migration disorders and intractable partial epilepsy: a study of 30 patients. Ann Neurol. 1991. 30:741–749.3. Vital A, Marchal C, Loiseau H, Rougier A, Pedespan JM, Rivel J, et al. Glial and neuronoglial malformative lesions associated with medically intractable epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol. 1994. 87:196–201.4. Pedespan JM, Loiseas H, Vital A, Marchal C, Fontan D, Rougier A. Surgical treatment of an early epileptic encephalopathy with suppression bursts and focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsia. 1995. 36:37–40.5. Palmini A, Andermann F, Olivier A, Tampieri D, Robitaille Y. Focal neuronal migration disorders and intractable partial epilepsy: results of surgical treatment. Ann Neurol. 1991. 30:750–757.6. Devaux B, Chassoux F, Landre E, Turak B, Abou-Salma Z, Mann M, et al. Surgical resections in functional areas: report of 89 cases. Neurochirurgie. 2008. 54:409–417.7. Spencer SS, Berg AT, Victrey BG, Sperling MR, Bazil CW, Shinnar S, et al. Initial outcomes in the multicenter study of epilepsy surgery. Neurology. 2003. 61:1680–1685.8. Lee BC, Schmidt RE, Hatfield GA, Bourgeois B, Park TS. MRI of focal cortical dysplasia. Neuroradiology. 1998. 40:675–683.9. Kuzniecky R, Garcia JH, Faught E, Morawetz RB. Cortical dysplasia in temporal lobe epilepsy: magnetic resonance imaging correlations. Ann Neurol. 1991. 29:293–298.10. Hattingen E, Good C, Weidauer S, Herminghaus S, Raab P, Marquardt G, et al. Brain surface reformatted images for fast and easy localization of perirolandic lesions. J Neurosurg. 2005. 102:302–310.11. Araujo D, Machado HR, Oliveira RS, Terra-Bustamante V, Barros de Araujo D, Santos AC, et al. Brain surface reformatted imaging (BSRI) in surgical planning for resections around eloquent cortex. Childs Nerv Syst. 2006. 22:1122–1126.12. Mugler JP III, Brookeman JR. Rapid three-dimensional T1-weighted MR imaging with the MP-RAGE sequence. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1991. 1:561–567.13. Kulynych JJ, Vladar K, Jones DW, Weinberger DR. Three-dimensional surface rendering in MRI morphometry: a study of the planum temporale. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1993. 17:529–535.14. Levin DN, Hu XP, Tan KK, Galhotra S. Surface of the brain: three-dimensional MR images created with volume rendering. Radiology. 1989. 171:227–280.15. Gong X, Fang M, Wang J, Sun J, Zhang X, Kwong WH, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of brain surface anatomy based on magnetic resonance imaging diffusion weighted imaging: a new approach. J Biomed Sci. 2004. 11:711–716.16. Lee BCP, Hatfield G, Park TS, Kaufman BA. MR imaging surface display of the cerebral cortex in children. Pediatr Radiol. 1997. 27:199–206.17. Abdel Razek AAK, Kandell AY, Elsorogy LG, Elmongy A, Basett AA. Disorders of cortical formation: MR imaging features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. 30:4–11.18. Byrd SE, Osborn RE, Bohan TP, Naidich TP. The CT and MR evaluation of migrational disorders of the brain. Part I. lissencephaly and pachygyria. Pediatr Radiol. 1989. 19:151–156.19. de Rijk-van Andel JF, van der Knaap MR, Valk J, Arts WF. Neuroimaging in lissencephaly type I. Neuroradiology. 1991. 33:230–233.20. Barkovich AJ, Kjos BO. Schizencephaly: correlation of clinical findings with MR characteristics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992. 13:85–94.21. Lopes CF, Cendes F, Piovesana AM, Torres F, Lopes-Cendes I, Montenegro MA, et al. Epileptic features of patients with unilateral and bilateral schizencephaly. J Child Neurol. 2006. 21:757–760.22. Packard AM, Miller VS, Delgado MR. Schizencephaly: correlations of clinical and radiologic features. Neurology. 1997. 48:1427–1434.23. Nakahashi M, Sato N, Yagishita A, Ota M, Saito Y, Surgai K, et al. Clinical and imaging characteristics of localized megalencephaly: a retrospective comparison of diffuse hemimegalencephaly and multilobar cortical dysplasia. Neuroradiology. 2009. 51:821–830.24. Flores-Sarnat L. Hemimegalencephaly: part 1. Genetic, clinical, and imaging aspects. J Child Neurol. 2002. 17:373–384.25. Donders J, Mullarkey SK, Allchin J. Congenital bilateral perisylvian syndrome: a case study. Clin Neuropsychol. 2009. 23:276–285.26. Margari L, Presicci A, Ventura P, Buttiglione M, Andreula C, Perniola T. Congenital bilateral perisylvian syndrome with partial epilepsy. Case report with long term follow up. Brain Dev. 2005. 27:53–57.27. Luat AF, Bernardi B, Chygani HT. Congenital perisylvian syndrome: MRI and glucose PET correlations. Pediatr Neurol. 2006. 35:21–29.28. Koutsouraki E, Timplalexi G, Papadopoulou Z, Costa V, Baloyannis S. A case of intractable epilepsy in a double cortex syndrome. Int J Neurosci. 2008. 118:343–348.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three-Dimensional Surface Rendering Image of Cerebral Cortical Disease
- Curved Planar Reconstruction of MR Images in Focal Cortical Dysplasia of the Brain
- Bilateral Cerebellar Cortical Dysplasia without Other Malformations: A Case Report
- Evaluation of accuracy of 3D reconstruction images using multi-detector CT and cone-beam CT
- Can Three-Dimensional Reconstructed Image Replace Medical Photograph?