J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Sep;63(3):201-203. 10.3348/jksr.2010.63.3.201.
Bilateral Cerebellar Cortical Dysplasia without Other Malformations: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Korea. jeeyoungkim@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2097893
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2010.63.3.201
Abstract
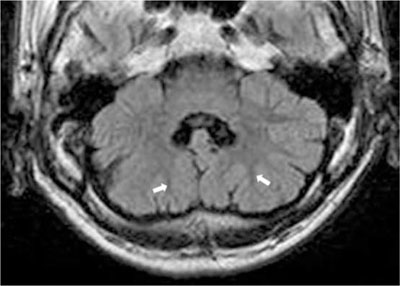
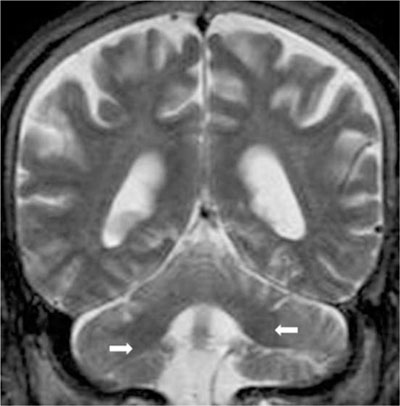
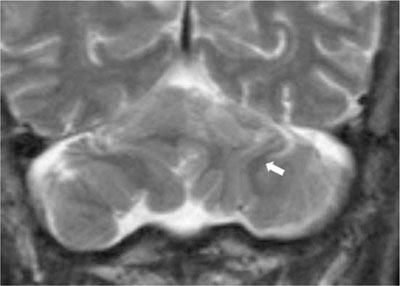
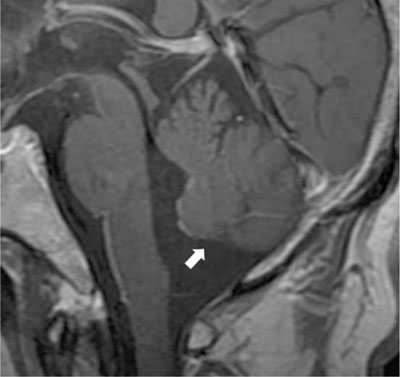
- Recent advances in MRI have revealed congenital brain malformations and subtle developmental abnormalities of the cerebral and cerebellar cortical architecture. Typical cerebellar cortical dysplasia as a newly categorized cerebellar malformation, has been seen in patients with Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy. Cerebellar cortical dysplasia occurs at the embryonic stage and is often observed in healthy newborns. It is also incidentally and initially detected in adults without symptoms. To the best of our knowledge, cerebellar dysplasia without any related disorders is very rare. We describe the MRI findings in one patient with disorganized foliation of both cerebellar hemispheres without a related disorder or syndrome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Soto-Ares G, Delmaire C, Deries B, Vallee L, Pruvo JP. Cerebellar cortical dysplasia: MR findings in a complex entity. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:1511–1519.2. Patel S, Barkovich AJ. Analysis and classification of cerebellar malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1074–1087.3. Sasaki M, Oikawa H, Ehara S, Tamakawa Y, Tohgi H. Disorganised unilateral cerebellar folia: a mild form of cerebellar cortical dysplasia? Neuroradiology. 2001; 43:151–155.4. Collin P. Embryology and development. In : Lawrence HB, Martin M, Patricia C, Mary D, Julian E, Mark WJF, editors. Gray's anatomy. 38th Ed. London: Churchill Livingstone;1995. p. 238–257.5. Berry MM, Standring SM, Bannister LH. Nervous system. In : Lawrence HB, Martin M, Patricia C, Mary D, Julian E, Mark WJF, editors. Gray's anatomy. 38th Ed. London: Churchill Livingstone;1995. p. 1027–1065.6. Demaerel P, Lagae L, Casaer P, Baert AL. MR of cerebellar cortical dysplasia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:984–986.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Disorganized Foliation of Unilateral Cerebellar Hemisphere as Cerebellar Cortical Dysplasia in Patients with Recurrent Seizures: A Case Report
- Cortical Dysplasia of Brain: 2 Autopsy Cases
- Electrobehavioral and Pathological Characteristics in Cerebral Cortical Dysplasia Induced by External Irradiation in the Rat
- Cerebellar Glioblastoma Presenting as a Cerebellar Hemorrhage in a Child
- Septo-optic dysplasia plus diagnosed in a middle-aged woman