J Korean Soc Endocrinol.
2006 Aug;21(4):266-271. 10.3803/jkes.2006.21.4.266.
Type 2 Diabetes and Mitochondria
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Korea University, Korea.
- KMID: 2200840
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.4.266
Abstract
- Liver, muscle, and adipose tissue are resistant to insulin action in type 2 diabetes. In spite of intensive studies, few diabetic genes have been identified. Recently, mitochondrial impairment has been observed in the muscle and adipose tissues of type 2 diabetes patients, implying that mitochondrial dysfunction could be a pivotal factor in type 2 diabetes. Here, we discuss mitochondrial malfunction leading to type 2 diabetes.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Malecki MT. Genetics of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005. 68:Suppl 1. S10–S21.2. Saltiel AR, Kahn CR. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature. 2001. 414:799–806.3. Moller DE. New drug targets for type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Nature. 2001. 414:821–827.4. Marx J. Unraveling the causes of diabetes. Science. 2002. 296:686–689.5. Janson J, Laedtke T, Parisi JE, O'Brien P, Petersen RC, Butler PC. Increased risk of type 2 diabetes in Alzheimer disease. Diabetes. 2004. 53:474–481.6. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:Suppl 1. S5–S20.7. Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001. 414:782–787.8. Kadowaki H, Takahashi Y, Ando A, Momomura K, Kaburagi Y, Quin JD, MacCuish AC, Koda N, Fukushima Y, Taylor SI, Akanuma Y, Yazaki Y, Kadowaki T. Four mutant alleles of the insulin receptor gene associated with genetic syndromes of extreme insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997. 237:516–520.9. Barroso I, Gurnell M, Crowley VE, Agostini M, Schwabe JW, Soos MA, Maslen GL, Williams TD, Lewis H, Schafer AJ, Chatterjee VK, O'Rahilly S. Dominant negative mutations in human PPARgamma associated with severe insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Nature. 1999. 402:880–883.10. George S, Rochford JJ, Wolfrum C, Gray SL, Schinner S, Wilson JC, Soos MA, Murgatroyd PR, Williams RM, Acerini CL, Dunger DB, Barford D, Umpleby AM, Wareham NJ, Davies HA, Schafer AJ, Stoffel M, O'Rahilly S, Barroso I. A family with severe insulin resistance and diabetes due to a mutation in AKT2. Science. 2004. 304:1325–1328.11. Saltiel AR. New perspectives into the molecular pathogenesis and treatment of type 2 diabetes. Cell. 2001. 104:517–529.12. Petersen KF, Befroy D, Dufour S, Dziura J, Ariyan C, Rothman DL, DiPietro L, Cline GW, Shulman GI. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the elderly: possible role in insulin resistance. Science. 2003. 300:1140–1142.13. Schrauwen P, Hesselink MK. Oxidative capacity, lipotoxicity, and mitochondrial damage in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004. 53:1412–1417.14. Taylor R. Causation of type 2 diabetes-the Gordian knot unravels. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:639–641.15. Hojlund K, Wrzesinski K, Larsen PM, Fey SJ, Roepstorff P, Handberg A, Dela F, Vinten J, McCormack JG, Reynet C, Beck-Nielsen H. Proteome analysis reveals phosphorylation of ATP synthase beta-subunit in human skeletal muscle and proteins with potential roles in type 2 diabetes. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:10436–10442.16. Petersen KF, Dufour S, Befroy D, Garcia R, Shulman GI. Impaired mitochondrial activity in the insulin-resistant offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:664–671.17. Lowell BB, Shulman GI. Mitochondrial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Science. 2005. 307:384–387.18. Choo HJ, Kim JH, Kwon OB, Lee CS, Mun JY, Han SS, Yoon YS, Yoon G, Choi KM, Ko YG. Mitochondria are impaired in the adipocytes of type 2 diabetic mice. Diabetologia. 2006. 49:784–791.19. Wilson-Fritch L, Nicoloro S, Chouinard M, Lazar MA, Chui PC, Leszyk J, Straubhaar J, Czech MP, Corvera S. Mitochondrial remodeling in adipose tissue associated with obesity and treatment with rosiglitazone. J Clin Invest. 2004. 114:1281–1289.20. Bogacka I, Xie H, Bray GA, Smith SR. Pioglitazone induces mitochondrial biogenesis in human subcutaneous adipose tissue in vivo. Diabetes. 2005. 54:1392–1399.21. Hammarstedt A, Jansson PA, Wesslau C, Yang X, Smith U. Reduced expression of PGC-1 and insulin-signaling molecules in adipose tissue is associated with insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. 301:578–582.22. Semple RK, Crowley VC, Sewter CP, Laudes M, Christodoulides C, Considine RV, Vidal-Puig A, O'Rahilly S. Expression of the thermogenic nuclear hormone receptor coactivator PGC-1alpha is reduced in the adipose tissue of morbidly obese subjects. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004. 28:176–179.23. Stumvoll M. Thiazolidinediones-some recent developments. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2003. 12:1179–1187.24. Wilson-Fritch L, Burkart A, Bell G, Mendelson K, Leszyk J, Nicoloro S, Czech M, Corvera S. Mitochondrial biogenesis and remodeling during adipogenesis and in response to the insulin sensitizer rosiglitazone. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. 23:1085–1094.25. Abel ED, Peroni O, Kim JK, Kim YB, Boss O, Hadro E, Minnemann T, Shulman GI, Kahn BB. Adipose-selective targeting of the GLUT4 gene impairs insulin action in muscle and liver. Nature. 2001. 409:729–733.26. Hegele RA, Cao H, Frankowski C, Mathews ST, Leff T. PPARG F388L, a transactivation-deficient mutant, in familial partial lipodystrophy. Diabetes. 2002. 51:3586–3590.27. Trayhurn P, Wood IS. Adipokines: inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br J Nutr. 2004. 92:347–355.28. Masuzaki H, Paterson J, Shinyama H, Morton NM, Mullins JJ, Seckl JR, Flier JS. A transgenic model of visceral obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Science. 2001. 294:2166–2170.29. Evans RM, Barish GD, Wang YX. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat Med. 2004. 10:355–361.30. Ahima RS, Flier JS. Leptin. Annu Rev Physiol. 2000. 62:413–437.31. Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S, Yamashita S, Noda M, Kita S, Ueki K, Eto K, Akanuma Y, Froguel P, Foufelle F, Ferre P, Carling D, Kimura S, Nagai R, Kahn BB, Kadowaki T. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med. 2002. 8:1288–1295.32. Banerjee RR, Rangwala SM, Shapiro JS, Rich AS, Rhoades B, Qi Y, Wang J, Rajala MW, Pocai A, Scherer PE, Steppan CM, Ahima RS, Obici S, Rossetti L, Lazar MA. Regulation of fasted blood glucose by resistin. Science. 2004. 303:1195–1198.33. Hotamisligil GS, Peraldi P, Budavari A, Ellis R, White MF, Spiegelman BM. IRS-1-mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-alpha-and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Science. 1996. 271:665–668.34. Fasshauer M, Paschke R. Regulation of adipocytokines and insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 2003. 46:1594–1603.35. Kim BW, Choo HJ, Lee JW, Kim JH, Ko YG. Extracellular ATP is generated by ATP synthase complex in adipocyte lipid rafts. Exp Mol Med. 2004. 36:476–485.36. Ballinger SW, Shoffner JM, Hedaya EV, Trounce I, Polak MA, Koontz DA, Wallace DC. Maternally transmitted diabetes and deafness associated with a 10.4 kb mitochondrial DNA deletion. Nat Genet. 1992. 1:11–15.37. Lee HC, Wei YH. Mitochondrial role in life and death of the cell. J Biomed Sci. 2000. 7:2–15.38. Croteau DL, Bohr VA. Repair of oxidative damage to nuclear and mitochondrial DNA in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:25409–25412.39. Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y, Nakayama O, Makishima M, Matsuda M, Shimomura I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2004. 114:1752–1761.40. Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 2001. 414:813–820.41. Lazar MA. How obesity causes diabetes: not a tall tale. Science. 2005. 307:373–375.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mitochondria DNA Polymorphism and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Mitochondrial-Encoded Peptide MOTS-c, Diabetes, and Aging-Related Diseases
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
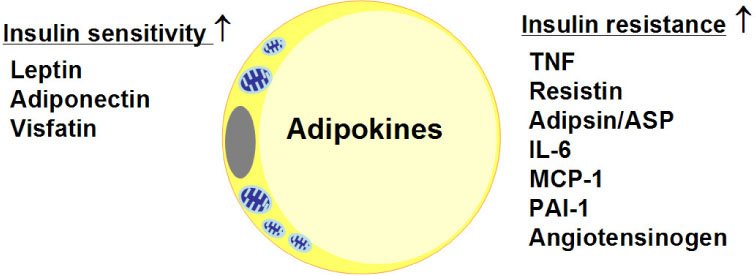
- Mitochondrial TFAM as a Signaling Regulator between Cellular Organelles: A Perspective on Metabolic Diseases
- Mitochondrial Gene Therapy