J Korean Soc Endocrinol.
2005 Oct;20(5):434-440. 10.3803/jkes.2005.20.5.434.
Regulation of Insulin Signaling through Protein Degradation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cell and Gene Therapy Research Institute, Pochon CHA University, Korea.
- KMID: 2200589
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.5.434
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
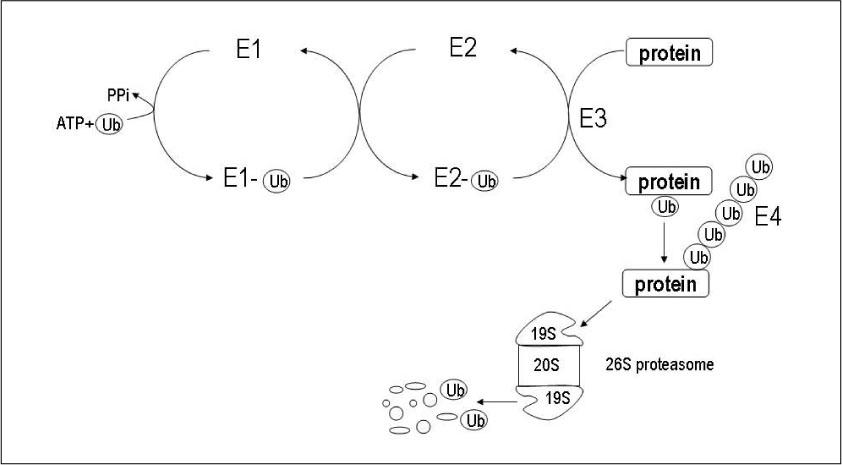
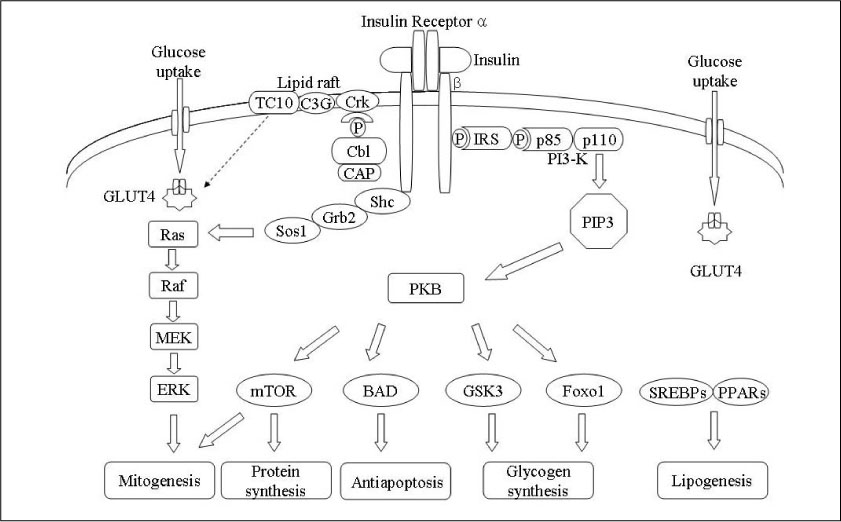
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hershko A, Ciechanover A, Heller H, Haas AL, Rose IA. Proposed role of ATP in protein breakdown: conjugation of proteins with multiple chains of the polypeptide of ATP-dependent proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1980. 77:1783–1786.2. Ciechanover A, Heller H, Elias S, Haas AL, Hershko A. ATP-dependent conjugation of reticulocyte proteins with the polypeptide required for protein degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1980. 77:1365–1368.3. Koegl M, Hoppe T, Schlenker S, Ulrich HD, Mayer TU, Jentsch S. A novel ubiquitination factor, E4, is involved in multiubiquitin chain assembly. Cell. 1999. 96:635–644.4. Grossman SR, Deato ME, Brignone C, Chan HM, Kung AL, Tagami H, Nakatani Y, Livingston DM. Polyubiquitination of p53 by a ubiquitin ligase activity of p300. Science. 2003. 300:342–344.5. Hershko A. Lessons from the discovery of the ubiquitin system. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996. 21:445–449.6. Leggett DS, Hanna J, Borodovsky An, Crosas B, Schmidt M, Baker RT, Walz T, Ploegh H, Finley D. Multiple associated proteins regulate proteasome structure and fuction. Mol Cell. 2002. 10:495–507.7. Kim MS, Kim YK, Kim YS, Seong M, Choi JK, Baek KH. Deubiquitinating enzyme USP36 contains the PEST motif and is polyubiquitinated. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. 330:797–804.8. Amerik AY, Hochstrasser M. Mechanism and function of deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004. 1695:189–207.9. Balakirev MY, Tcherniuk SO, Jaquinod M, Chroboczek J, Otubains . a new family of cysteine proteases in the ubiquitin pathway. EMBO Rep. 2003. 4:517–522.10. Brazil DP, Hemmings BA. Ten years of protein kinase B signaling: a hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001. 26:657–664.11. Frame S, Cohen P. GSK3 takes center stage more than 20 years after its discovery. Biochem J. 2001. 359:1–16.12. Satiel AR, Kahn CR. Insulin signaling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature. 2001. 414:799–806.13. Wilden PA, Kahn CR, Siddle K, White MF. Insulin receptor kinase domain autophosphorylation regulates receptor enzymatic function. J Biol Chem. 1992. 267:16660–16668.14. Ahmed Z, Smith BJ, Kotani K, Wilden P, Pillay TS. APS, an adapter protein with a PH and SH2 domain, is a substrate for the insulin receptor kinase. Biochem J. 1999. 341:665–668.15. Yokouchi M, Suzuki R, Masuhara M, Komiya S, Inoue A, Yoshimura A. Cloning and characterization of APS, an adaptor molecule containing PH and SH2 domains that is tyrosine phosphorylated upon B-cell receptor stimulation. Oncogene. 1997. 15:7–15.16. Joazeiro CA, Wing SS, Huang H, Leverson DJ, Hunter T, Liu YC. The tyrosine kinase negative regulator c-Cbl as a RING-Type, E2-dependent ubiquitin-protein ligase. Science. 1999. 286:309–312.17. Ribon V, Printen JA, Hoffman NG, Kay BK, Saltiel AR. A novel, multifunctional c-Cbl binding protein in insulin receptor signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. 18:872–879.18. White MF. The insulin signalling system and the IRS proteins. Diabetologia. 1997. 40:Suppl. 2. S2–S17.19. White MF. The IRS-signaling system: a network of docking proteins that mediate insulin and cytokine action. Recent Prog hormone Res. 1998. 53:119–138.20. Perderson TM, Kramer DL, Rondinone CM. Serine/threonine phosphorylation of IRS-1 triggers its degradation: possible regulation by tyrosine phosphorylation. Diabetes. 2001. 50:24–31.21. Sun XJ, Goldberg JL, Qiao LY, Mitchell JJ. Insulin induced insulin receptor substrate-1 degradation is mediated by the proteasome degradation pathway. Diabetes. 1999. 48:1359–1364.22. Zhande R, Mitchell JJ, Wu J, Sun XJ. Molecular mechanism of Insulin Induced degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. 22:1016–1026.23. Rui L, Fisher TL, Thomas J, White MF. Regulation of insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 by proteasome-mediated degradation of insulin receptor substrate 2. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:40362–40367.24. Rodnick KJ, Slot SW, Studelska DR, Hanpeter DE, Robinson LJ, Geuze HJ, James DE. Immunocytochemical and biochemical studies of GLUT4 in rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992. 267:6278–6285.25. Giorgino F, Robertis OD, Laviola L, Montrone C, Perrini S, McCowen KC, Smith RJ. The sentrin-conjugating enzyme mUbc9 interacts with GLUT4 and GLUT1 glucose transporters and regulates transporter levels in skeletal muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:1125–1130.26. Kamitani K, Nguyen HP, Yeh ETH. Preferential modification of nuclear proteins by a novel ubiquitin-like molecule. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:14001–14004.27. Mahajan R, Delphin C, Guan T, Gerace L, Melchior F. A small ubiquitin-related polypeptide Involved in targeting RanGAP1 to nuclear pore complex protein RanBP2. Cell. 1997. 88:97–107.28. Rui L, Yuan M, Frantz D, Shoelson S, White MF. SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 block insulin signaling by ubiquitin-mediated degradation of IRS1 and IRS2. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:42394–42398.29. Krebs DL, Hilton DJ. SOCS: physiological suppressors of cytokine signaling. J Cell Sci. 2000. 113:2813–2819.30. Kamura T, Sato S, Haque D, Liu L Jr, Kaelin WG, Conaway RC, Conaway WC. The Elongin BC complex interacts with the conserved SOCS-box motif present in members of the SOCS, ras, WD-40 repeat, and ankyrin repeat families. Genes Dev. 1998. 12:3872–3881.31. Kamura T, Sato S, Haque D, Liu L Jr, Kaelin WG, Conaway RC, Conaway JW. The Elongin BC complex interacts with the conserved SOCS-box motif present in members of the SOCS, ras, WD-40 repeat, and ankyrin repeat families. Genes Dev. 1998. 12:3872–3881.32. Burgering BM, Kops GJ. Cell cycle and death control: long live Forkheads. Trends Biochem Sci. 2002. 27:352–360.33. Birkenkamp KU, Coffer PJ. Regulation of cell survival and proliferation by the FOXO (Forkhead box, class O) subfamily of Forkhead transcription factors. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001. 31:292–297.34. Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 1999. 96:857–868.35. Rena G, Guo S, Cichy SC, Unterman TG, Cohen P. Phosphorylation of the Transcription Factor Forkhead Family Member FKHR by Protein Kinase B. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:17179–17183.36. Matsuzaki H, Daitoku H, Hatta M, Tanaka K, Fukamizu A. Insulin-induced phosphorylation of FKHR (Foxo1) targets to proteasomal degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003. 100:11285–11290.37. Blanquart C, Barbier O, Fruchart JC, Staels B, Glineur C. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) turnover by the ubiquitin-proteasome system controls the ligand-induced expression level of its target genes. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:37254–37259.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent Insights into Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 Transcriptional Regulation
- Regulation of Protein Degradation by Proteasomes in Cancer
- Negative Regulation of Intracellular Cytokine Signal Transduction
- Pja2 Inhibits Wnt/β-catenin Signaling by Reducing the Level of TCF/LEF1
- Charged MVB protein 5 is involved in T-cell receptor signaling