J Lung Cancer.
2008 Dec;7(2):98-100. 10.6058/jlc.2008.7.2.98.
Gemcitabine-Related Radiation Recall in a Patient with Metastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Asan Medical Center, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea. ekchoi@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Ulsan University Hospital, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2200035
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6058/jlc.2008.7.2.98
Abstract
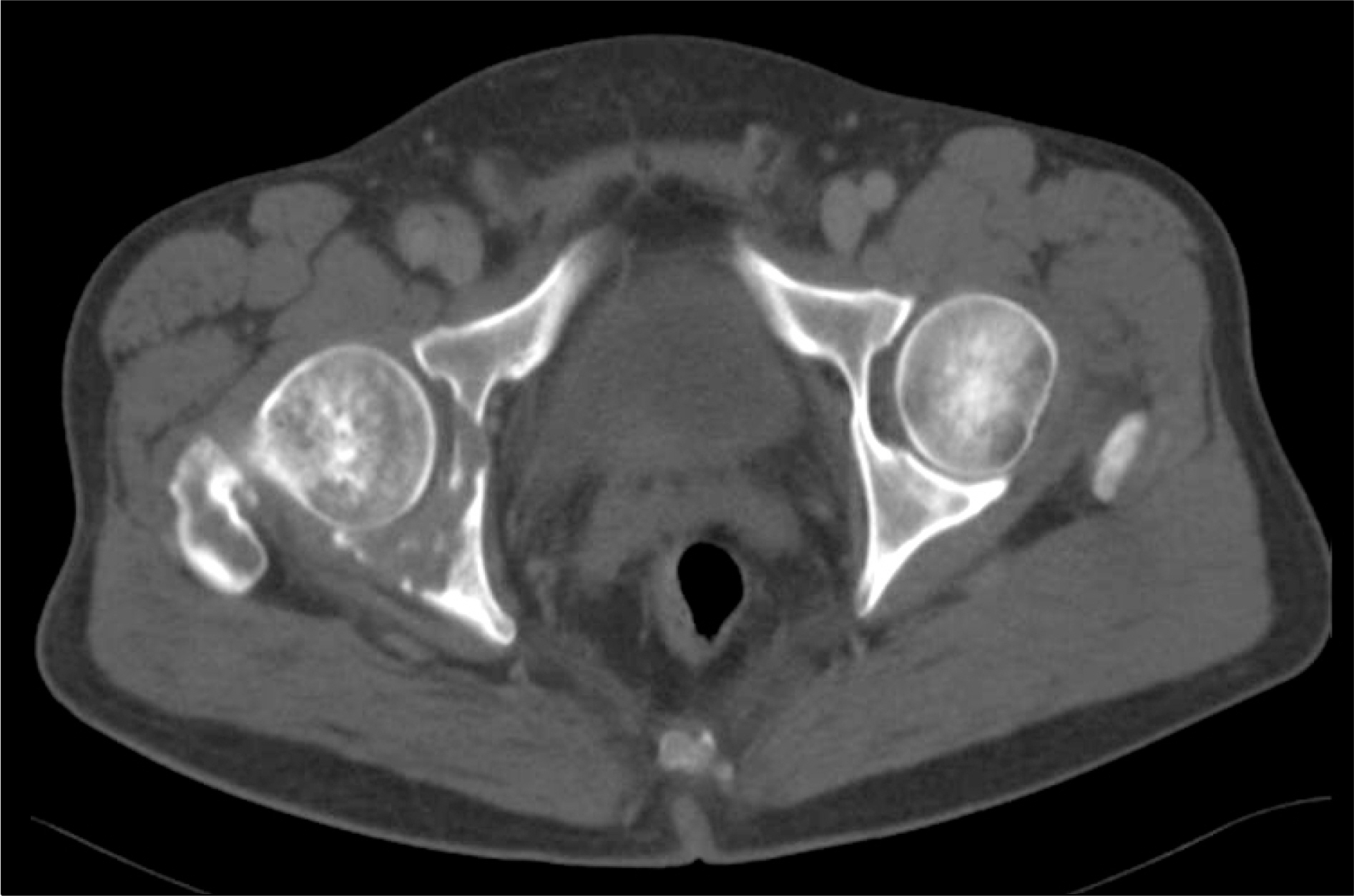
- A sixty-seven year old male was treated with palliative radiation therapy due to his right hip joint pain, and the pain was caused by osteolytic right acetabular metastasis. He underwent 30 Gy irradiation and then his painful symptoms disappeared at the 1 month follow-up after radiation therapy. He next received received systemic chemotherapy with 3 cycles of gemcitabine plus cisplatin and then 6 cycles of docetaxel. He visited the emergency room at the time of 4 months after the completion of radiation therapy with complaints of relapsed right hip joint pain. On MRI, localized muscular swelling with infiltration and without contrast-enhancement was seen within the previous radiation field, and the clinical impression was radiation-recall myositis. We provided symptomatic treatment and his right hip joint pain with disability disappeared 2 weeks after the treatment. No relapse of the right hip joint pain developed during the patient's survival period. We experienced a case of radiation-recall myositis that was related to gemcitabine use after radiation therapy
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Tan CT, Dargeon HW, Burchenal JH. The effect of actino-mycin D on cancer in childhood. Pediatrics. 1959; 24:544–561.2. Del Guidice SM, Gerstley JK. Sunlight-induced radiation recall. Int J Dermatol. 1988; 27:415–416.
Article3. Azria D, Magne N, Zouhair A, et al. Radiation recall: a well recognized but neglected phenomenon. Cancer Treat Rev. 2005; 31:555–570.
Article4. Donaldson SS, Glick JM, Wilbur JR. Letter: Adriamycin activating a recall phenomenon after radiation therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1974; 81:407–408.5. Kellie SJ, Plowman PN, Malpas JS. Radiation recall and radiosensitization with alkylating agents. Lancet. 1987; 1:1149–1150.6. Yeo W, Leung SF, Johnson PJ. Radiation-recall dermatitis with docetaxel: establishment of a requisite radiation threshold. Eur J Cancer. 1997; 33:698–699.
Article7. Welsh JS, Torre TG, DeWeese TL, O'Reilly S. Radiation myositis. Ann Oncol. 1999; 10:1105–1108.
Article8. Friedlander PA, Bansal R, Schwartz L, Wagman R, Posner J, Kemeny N. Gemcitabine-related radiation recall preferentially involves internal tissue and organs. Cancer. 2004; 100:1793–1799.
Article9. Ganem G, Solal-Celigny P, Joffroy A, Tassy D, Delpon A, Dupuis O. Radiation myositis: the possible role of gemcitabine. Ann Oncol. 2000; 11:1615–1616.
Article10. Fogarty G, Ball D, Rischin D. Radiation recall reaction following gemcitabine. Lung Cancer. 2001; 33:299–302.
Article11. Jeter MD, Janne PA, Brooks S, et al. Gemcitabine-induced radiation recall. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 53:394–400.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gemcitabine-Induced Radiation Recall Dermato-Myositis
- Radiation Recall Myositis during Gemcitabine Chemotherapy
- Radiation Recall Dermatitis Induced by Gefitinib
- Role of Radiation Therapy for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Focused on Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy in Stage I
- Erlotinib HCL (Tarceva(R)) Induced Radiation Recall Dermatitis