J Lipid Atheroscler.
2012 Dec;1(2):87-94. 10.12997/jla.2012.1.2.87.
Cost-effectiveness of the Use of Statins in the Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. steadyhan@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2198366
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12997/jla.2012.1.2.87
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Statins reduce risk of cardiovascular disease through lowering of LDL-C (Low Density Lipoprotein cholesterol). We analyzed cost-effectiveness of statins in the reduction of serum LDL-C level among Korean population at high cardiovascular risk.
METHODS
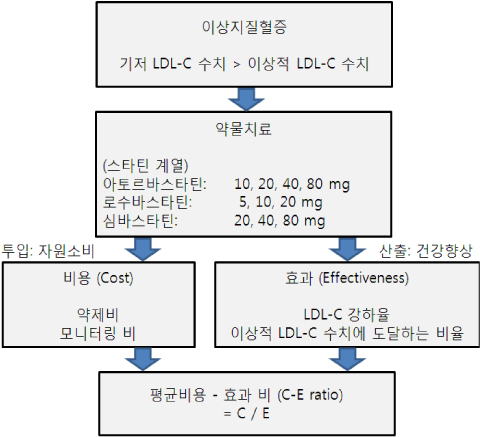
Rosuvastatin (5, 10, and 20 mg), atorvastatin (10, 20, 40, and 80 mg) and simvastatin (20, 40, and 80 mg) were included for the analysis, because those statins and doses were mostly prescribed in Korea. We determined effectiveness as % reduction of LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) levels per mg dose and % population reached to the ideal LDL-C level (<100 mg/dL), which is the target goal of LDL-C level for the high cardiovascular risk group as recommended by NCEP-ATP III guideline. The annual cost, which included overall cost for the drug price and management during follow up, was calculated. Average cost-effectiveness ratio (ACER) was calculated and used as the parameter representing cost-effectiveness of each statins.
RESULTS
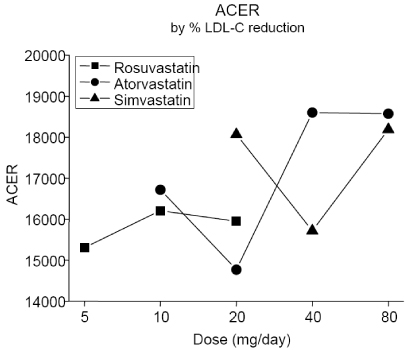
The lowest dose of each statins showed that achieving LDL-C target level was not high even in subjects showing relatively low basal LDL-C levels (<160 mg/dL). Also in case basal LDL-C level was over 160 mg/dL, the majority of statins were not sufficient to control LDL-C levels except atorvastatin 80 mg. In case of basal LDL-C level was lower than 160 mg/dl, atorvastatin 20 mg was the most cost-effective statin for LDL-C reduction regardless of considering basal LDL-C level. Simvastatin 40 mg was also cost-effective if basal LDL-C levels were between 100-129 mg/dL.
CONCLUSIONS
For the reduction of LDL-C level in high risk subjects showing moderately elevated basal LDL-C level, atorvastatin 20 mg is the most cost-effective statin treatment strategy and then simvastatin 40 mg or rosuvastatin 10 mg was the second best option.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cardiovascular Diseases
Cholesterol, LDL
Fluorobenzenes
Follow-Up Studies
Heptanoic Acids
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Korea
Lipoproteins
Pyrimidines
Pyrroles
Simvastatin
Sulfonamides
Atorvastatin Calcium
Rosuvastatin Calcium
Cholesterol, LDL
Fluorobenzenes
Heptanoic Acids
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Lipoproteins
Pyrimidines
Pyrroles
Simvastatin
Sulfonamides
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Economic Evaluation of Rosuvastatin and Atorvastatin for the Treatment of Dyslipidemia from a Korean Health System Perspective
Sunghwan Suh, Chang Hee Jung, Soon-Jun Hong, Jung-Sun Kim, Byung Ju Song, Hyun Soon Sohn, Sung Hee Choi
J Lipid Atheroscler. 2016;5(1):61-77. doi: 10.12997/jla.2016.5.1.61.
Reference
-
1. Fedder DO, Koro CE, L'Italien GJ. New National Cholesterol Education Program III guidelines for primary prevention lipid-lowering drug therapy: projected impact on the size, sex, and age distribution of the treatmenteligible population. Circulation. 2002; 105:152–156.
Article2. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CMB, Brewer HB, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, Pasternak RC, Smith SC, Stone NJ. for the Coordinating Committee of the National Cholesterol Education Program. Implications of Recent Clinical Trials for theNational Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Guidelines. Circulation. 2004; 110:227–239.
Article3. Shepherd J, Kastelein JJ, Bittner V, Deedwania P, Breazna A, Dobson S, Wilson DJ, Zuckerman A, Wenger NK. TNT (Treating to New Targets) Investigators. Intensive lipid lowering with atorvastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and chronic kidney disease: the TNT (Treating to New Targets) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 51:1448–1454.
Article4. Pedersen TR, Faergeman O, Kastelein JJ, Olsson AG, Tikkanen MJ, Holme I, Larsen ML, Bendiksen FS, Lindahl C, Szarek M, Tsai J. Incremental Decrease in End Points Through Aggressive Lipid Lowering (IDEAL) Study Group. High-dose atorvastatin vs usual-dose simvastatin for secondary prevention after myocardial infarction: the IDEAL study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2005; 294:2437–2445.
Article5. Colhoun HM, Betteridge DJ, Durrington PN, Hitman GA, Neil HA, Livingstone SJ, Thomason MJ, Mackness MI, Charlton-Menys V, Fuller JH. CARDS investigators. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with atorvastatin in type 2 diabetes in the Collaborative Atorvastatin Diabetes Study (CARDS): multicentre randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2004; 364:685–696.
Article6. Sever PS, Dahlöf B, Poulter NR, Wedel H, Beevers G, Caulfield M, Collins R, Kjeldsen SE, Kristinsson A, McInnes GT, Mehlsen J, Nieminen M, O'Brien E, Ostergren J. ASCOT investigators. Prevention of coronary and stroke events with atorvastatin in hypertensive patients who have average or lower-than-average cholesterol concentrations, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial--Lipid Lowering Arm (ASCOT-LLA): a multicentre randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2003; 361:1149–1158.
Article7. Gold MR, Siegel JE, Russell LB, Weinstein MC. Cost-effectiveness in Health and Medicine. 1st ed. New York (NY): Oxford University Press;1996.8. Nicholls SJ, Brandrup-Wognsen G, Palmer M, Barter PJ. Meta-analysis of Comparative Efficacy of Increasing Dose of Atorvastatin Versus Rosuvastatin Versus Simvastatin on Lowering Levels of Atherogenic Lipids (from VOYAGER). Am J Cardiol. 2010; 105:69–76.
Article9. Catapano AL. Statin-induced myotoxicity: pharmacokinetic differences among statins and the risk of rhabdomyolysis, with particular reference to pitavastatin. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2012; 10:257–267.
Article10. Preiss D, Sattar N. Statins and the risk of new-onset diabetes: a review of recent evidence. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011; 22:460–466.11. da Silva PM. Are all statins the same? Focus on the efficacy and tolerability of pitavastatin. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2011; 11:93–107.12. Koh KK, Quon MJ, Waclawiw MA. Are statins effective for simultaneously treating dyslipidemias and hypertension? Atherosclerosis. 2008; 196:1–8.
Article13. Teramoto T. The clinical impact of pitavastatin: comparative studies with other statins on LDL-C and HDL-C. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2012; 13:859–865.
Article14. Gotto A, Pownall H. Manual of lipid disorders. 3rd ed. New York: Lippincott and Williams;2003. p. 305–308.15. Kang HY, Ko SK, Liew D. Results of a Markov Model Analysis to Assess the Cost-Effectiveness of Statin Therapy for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: The Korean Individual-Microsimulation Model for Cardiovascular Health Interventions. Clin Ther. 2009; 31:2919–2930.
Article16. Conly J, Clement F, Tonelli M, Hemmelgarn B, Klarenbach S, Lloyd A, McAlister FA, Husereau D, Wiebe N, Au F, Manns B. for the Alberta Kidney Disease Network. Cost-effectiveness of the use of low- and high-potency statins in people at low cardiovascular risk. CMAJ. 2011.17. Jee SH, Suh I, Kim IS, Appel LJ. Smoking and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in men with low levels of serum cholesterol: the Korea Medical Insurance Corporation Study. JAMA. 1999; 282:2149–2155.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- HCV self-testing: Bridging screening gaps and ensuring cost-effectiveness for both high-risk and universal populations: Correspondence to editorial on “Self-testing strategy to eliminate hepatitis C as per World Health Organization’s goal: Analysis of disease burden and cost-effectiveness”
- Economic Evaluation of Rosuvastatin and Atorvastatin for the Treatment of Dyslipidemia from a Korean Health System Perspective
- Statins: a tale of two pathways—cardiovascular savior, renal ineffectual
- Cost-effectiveness of atezolizumab plus chemotherapy for advanced/ recurrent endometrial cancer
- Immunotherapy plus chemotherapy in patients with advanced endometrial cancer: a cost-effectiveness analysis