J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2011 Apr;49(2):145-151. 10.4047/jkap.2011.49.2.145.
Marginal fit of three-unit zirconia anterior fixed dental prostheses fabricated using CAD/CAM and MAD/MAM system
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. jhoyang@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2196121
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2011.49.2.145
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to compare the marginal fit of three-unit zirconia fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) fabricated using CAD/CAM and MAD/MAM system.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
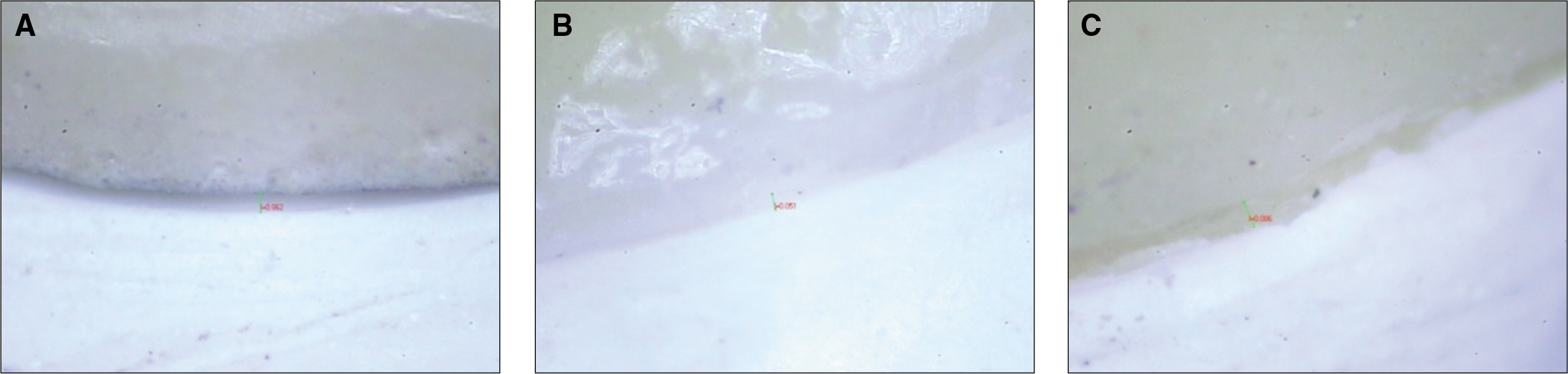
Dentiform maxillary central and lateral incisor were prepared for 3-unit FDP and fixed in yellow stone. This model was duplicated to epoxy resin die. On the resin die, fifteen 3-unit FDPs were fabricated. Metal-ceramic group was three-unit metal-ceramic FDPs, Everest(R) group was zirconia three-unit FDPs fabricated using the Everest(R) system (Kavo Dental GmbH, Biberach, Germany) and Rainbow(TM) group was zirconia three-unit FDPs fabricated using the Rainbow(TM) system (Dentium Co. Inc., Seoul, South Korea). They were cemented to resin dies with adhesive resin cement. After removing pontics, each retainers were separated and observed under measuring machine (Presize 440C) and analyzed through one-way ANOVA and Duncan test (alpha= .05).
RESULTS
Mean values and standard deviations of marginal gap dimensions in each group for three-unit FDPs were 78.5 +/- 11.05 microm for the metal-ceramic group, 59.30 +/- 11.63 microm for the Everest(R) group and 70.34 +/- 13.98 microm for the Rainbow(TM) group.
CONCLUSION
1. The Everest(R) group in comparison with metal-ceramic group showed better marginal fit, which had significant differences (P<.05). 2. The mean marginal gap values between Everest(R) and Rainbow(TM) group did not showed significant differences (P>.05). 3. The mean marginal gap values between Rainbow(TM) group and metal-ceramic group did not showed significant differences (P>.05). 4. The mean marginal gaps of each group were within clinically acceptable range (120 microm).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Sorensen JA. A rationale for comparison of plaque-retaining properties of crown systems. J Prosthet Dent. 1989. 62:264–9.
Article2.Sorensen SE., Larsen IB., Jo ¨rgensen KD. Gingival and alveolar bone reaction to marginal fit of subgingival crown margins. Scand J Dent Res. 1986. 94:109–14.
Article3.Tinschert J., Natt G., Mautsch W., Spiekermann H., Anusavice KJ. Marginal fit of alumina-and zirconia-based fixed partial dentures produced by a CAD/CAM system. Oper Dent. 2001. 26:367–74.4.Reich S., Wichmann M., Nkenke E., Proeschel P. Clinical fit of all-ceramic three-unit fixed partial dentures, generated with three different CAD/CAM systems. Eur J Oral Sci. 2005. 113:174–9.
Article5.Kang DR., Shim JS., Moon HS., Lee KW. Marginal fidelity of zirconia core using MAD/MAM system. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2010. 48:1–7.
Article6.McLean JW., von Fraunhofer JA. The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br Dent J. 1971. 131:107–11.
Article7.Belser UC., MacEntee MI., Richter WA. Fit of three porcelain-fused-to-metal marginal designs in vivo: a scanning electron microscope study. J Prosthet Dent. 1985. 53:24–9.
Article8.Coli P., Karlsson S. Precision of a CAD/CAM technique for the production of zirconium dioxide copings. Int J Prosthodont. 2004. 17:577–80.
Article9.Beuer F., Naumann M., Gernet W., Sorensen JA. Precision of fit: zirconia three-unit fixed dental prostheses. Clin Oral Investig. 2009. 13:343–9.
Article10.Sailer I., Fehe′r A., Filser F., Gauckler LJ., Lu ¨thy H., Ha¨mmerle CH. Five-year clinical results of zirconia frameworks for posterior fixed partial dentures. Int J Prosthodont. 2007. 20:383–8.11.Sailer I., Fehe′r A., Filser F., Lu¨thy H., Gauckler LJ., Scha¨rer P., Franz Ha¨mmerle CH. Prospective clinical study of zirconia posterior fixed partial dentures: 3-year follow-up. Quintessence Int. 2006. 37:685–93.12.Wettstein F., Sailer I., Roos M., Ha¨mmerle CH. Clinical study of the internal gaps of zirconia and metal frameworks for fixed partial dentures. Eur J Oral Sci. 2008. 116:272–9.
Article13.Sorensen JA. A standardized method for determination of crown margin fidelity. J Prosthet Dent. 1990. 64:18–24.
Article14.Moon BH., Yang JH., Lee SH., Chung HY. A study on the marginal fit of all-ceramic crown using CCD camera. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 1998. 36:273–92.15.Gassino G., Barone Monfrin S., Scanu M., Spina G., Preti G. Marginal adaptation of fixed prosthodontics: a new in vitro 360-degree external examination procedure. Int J Prosthodont. 2004. 17:218–23.16.Groten M., Axmann D., Pro ¨bster L., Weber H. Determination of the minimum number of marginal gap measurements required for practical in-vitro testing. J Prosthet Dent. 2000. 83:40–9.17.Yoon JW., Yang JH., Han JS., Lee JB. A study on the marginal fit of collarless metal ceramic fixed partial dentures. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2005. 43:707–16.18.Vigolo P., Fonzi F. An in vitro evaluation of fit of zirconium-oxide-based ceramic four-unit fixed partial dentures, generated with three different CAD/CAM systems, before and after porcelain firing cycles and after glaze cycles. J Prosthodont. 2008. 17:621–6.
Article19.Gonzalo E., Sua′rez MJ., Serrano B., Lozano JF. Comparative analysis of two measurement methods for marginal fit in metal-ceramic and zirconia posterior FPDs. Int J Prosthodont. 2009. 22:374–7.20.Rosentritt M., Behr M., Kolbeck C., Handel G. Marginal integrity of CAD/CAM fixed partial dentures. Eur J Dent. 2007. 1:25–30.21.Kohorst P., Brinkmann H., Dittmer MP., Borchers L., Stiesch M. Influence of the veneering process on the marginal fit of zirconia fixed dental prostheses. J Oral Rehabil. 2010. 37:283–91.
Article22.Shin HS., Kim SG. Comparison of marginal fit before and after porcelain build-up of two kinds of CAD/CAM zirconia all-ceramic restorations. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2008. 46:528–34.
Article23.Huh JB., Park CG., Kim HY., Park CK., Shin SW. Evaluation using Replica Technique on the marginal and internal fitness of zirconia cores by several CAD/CAM systems. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2010. 48:135–42.
Article24.Belles DM., Cronin RJ Jr., Duke ES. Effect of metal design and technique on the marginal characteristics of the collarless metal ceramic restoration. J Prosthet Dent. 1991. 65:611–9.
Article25.Bindl A., Mo¨rmann WH. Marginal and internal fit of all-ceramic CAD/CAM crown-copings on chamfer preparations. J Oral Rehabil. 2005. 32:441–7.
Article26.Witkowski S., Komine F., Gerds T. Marginal accuracy of titanium copings fabricated by casting and CAD/CAM techniques. J Prosthet Dent. 2006. 96:47–52.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of span length on the fit of zirconia framework fabricated using CAD/CAM system
- Comparison of occusal aspects in monolithic zirconia crown before and after occlusal adjustment during intraoral try-in: a case report
- Marginal fidelity of zirconia core using MAD/MAM system
- Marginal fit of anterior 3-unit fixed partial zirconia restorations using different CAD/CAM systems
- Comparative study in marginal adaptation of zirconia cores fabricated with 3 different CAD/CAM systems