J Korean Med Assoc.
2015 Dec;58(12):1119-1124. 10.5124/jkma.2015.58.12.1119.
Current status of quality management of medical imaging in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ljs@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2195139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2015.58.12.1119
Abstract
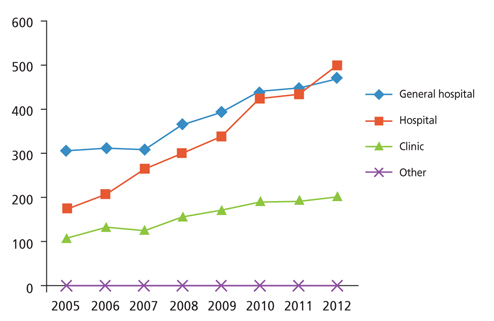
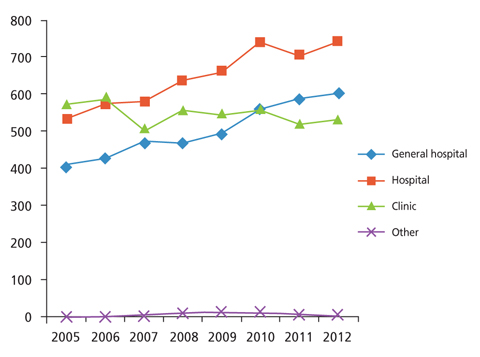
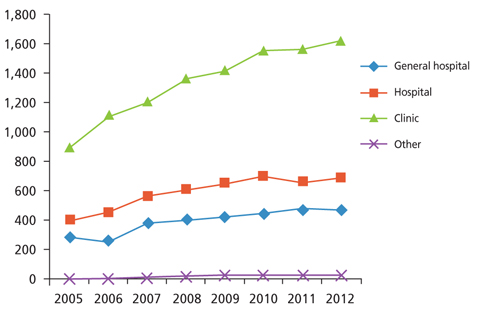
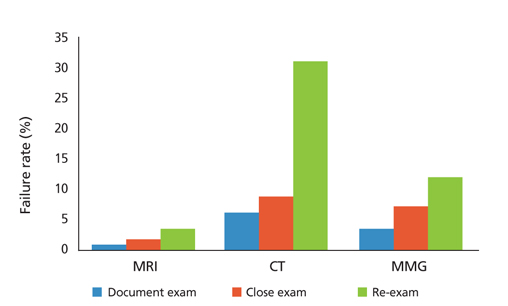
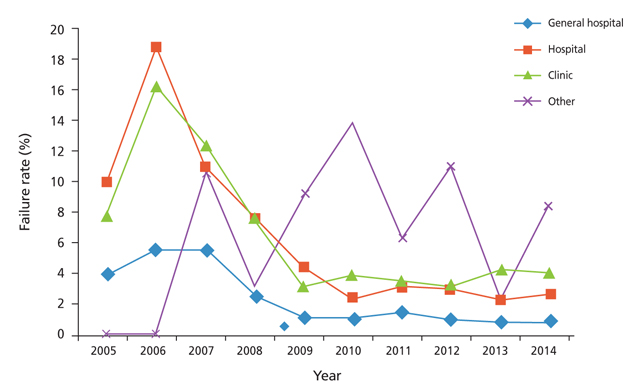
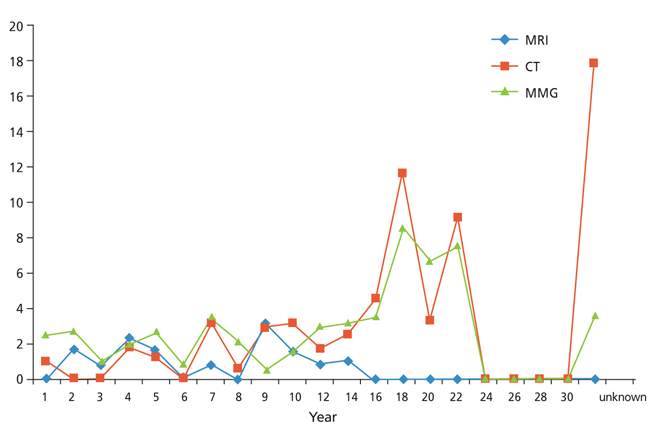
- Imaging modalities have developed in tandem with technical developments in recent years. It is common practice worldwide to establish a medical imaging quality control system in accordance with resources and need. In2003, the Korean governmentinstituted a medical imaging quality control system for high-priced and high-end medical imaging equipment. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), and mammography were included in this program. General image quality has continuously improved, but some problems remain. The medical imaging quality control program will be extended to other equipment such as positron emission tomography-CT, simulation CT for radiation treatment, and extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy. Education programs for equipment control personnel should be improved and the quality control system should be refined.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Quality management in medical imaging
Seung Eun Jung
J Korean Med Assoc. 2015;58(12):1109-1111. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2015.58.12.1109.Status of Interchange of Medical Imaging in Korea: A Questionnaire Survey of Physicians
Moon Hyung Choi, Seung Eun Jung, Sungjun Kim, Na-Young Shin, Hwan Seok Yong, Hyunsik Woo, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Kwang Nam Jin, SeonHyeong Choi
J Korean Soc Radiol. 2018;79(5):247-253. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2018.79.5.247.
Reference
-
1. Korean Institute for Accreditation of Medical Imaging. 10 Year history of Korean Institute for Accreditation of Medical Imaging. Seoul: Korean Institute for Accreditation of Medical Imaging;2015.2. Rule for Installation and Operation of Specialized Medical Equipment. Ministry of Health and Welfare L;2015. 01. 01. No. 283.3. Cha SH. Study for revision of safety testing standards and methods for CT and mammography. Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2011.4. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Plan for minor revision of Rules for Installation and Operation of Specialized Medical Equipment [Internet]. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare;cited 2015 Aug 18. Available from: http://www.mohw.go.kr/front_new/jb/sjb0403vw.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=03&MENU_ID=030403&BOARD_ID=200&BOARD_FLAG=00&CONT_SEQ=271091&page=1.5. Korean Society of Radiology. 2013 Policy task report. Seoul: Korean Society of Radiology;2013.6. Jung SE. Study for improvement of policy regarding specialized high end medical equipment. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2013.7. Kim JH. Study for reasonable management of high end medical imaging equipment. Seoul: Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service;2013.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Principles of quality management in medical imaging
- Future of quality management of medical imaging
- Current status and policy options for high-tech medical devices in Korea: vertical and horizontal synchronization of health policy
- Survey of Current Status of Quality Control of Gamma Cameras in Republic of Korea
- Medical Management for Radiation-induced Dysphagia