J Korean Soc Surg Hand.
2015 Jun;20(2):55-58. 10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.2.55.
Ulnar Artery Thrombosis in Guyon's Canal
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea. chkim@gnah.co.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
- KMID: 2194100
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.2.55
Abstract
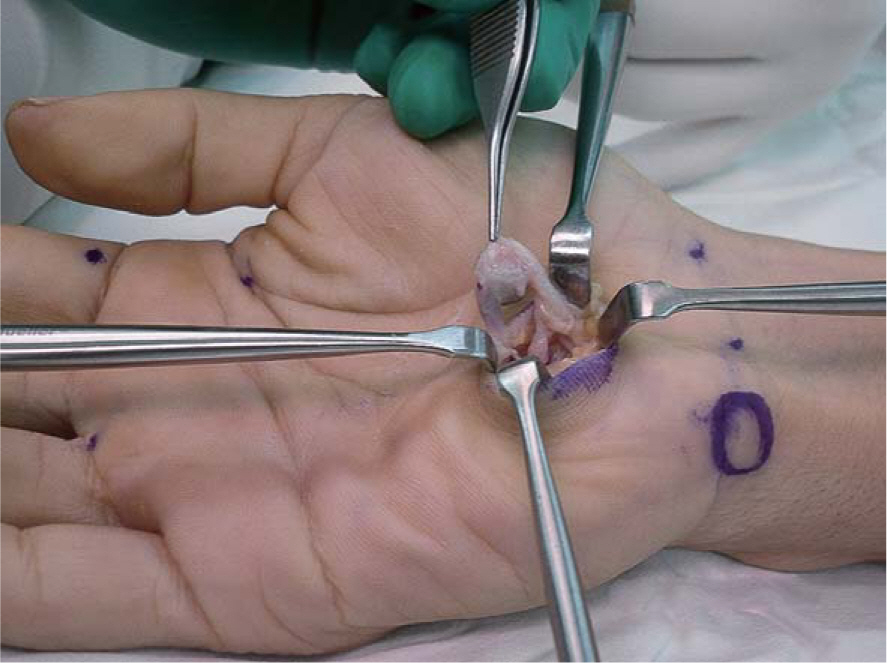
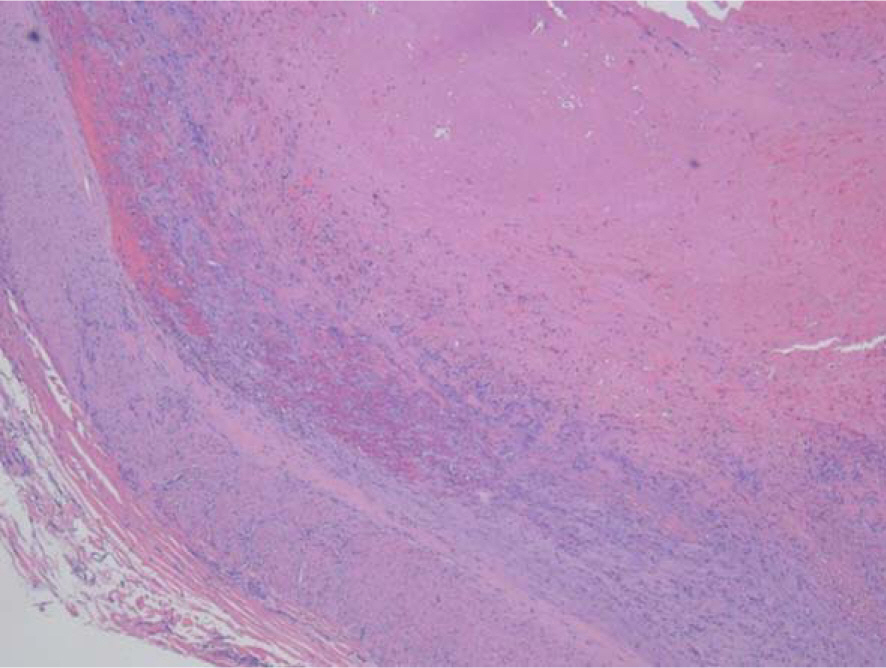
- Causes of ulnar nerve compression in Guyon's canal are various, but thrombosis of the ulnar artery due to a single trauma is rarely reported. We report a case of ulnar nerve compression caused by traumatic thrombosis of the ulnar artery in Guyon's canal. Surgical excision of the ulnar artery thrombus and end to end anastomosis resulted in complete relief of the patient's symptoms.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Compressive Neuropathy of the Deep Motor Branch of the Ulnar Nerve in Amateur Cyclist
Jae Jun Nam, In Cheul Choi, Ji Hun Park, Jong Woong Park
Korean J Sports Med. 2020;38(4):234-237. doi: 10.5763/kjsm.2020.38.4.234.
Reference
-
References
1. Bachoura A, Jacoby SM. Ulnar tunnel syndrome. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012; 43:467–74.
Article2. Aubeny E. RU486 combined with PG analogs in voluntary termination of pregnancy. Adv Contracept. 1991; 7:339–43.
Article3. Fong EP, Mahaffey PJ. Ulnar tunnel syndrome: an unusual cause. Hand Surg. 2000; 5:77–9.4. Park SR, Kim HS, Kang JS, Lee WH, Lee JH, Yeoum SH. Traumatic false aneurysm of ulnar artery: a case report. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 1998; 3:86–90.5. Karaarslan AA, Karakasli A, Mayda A, Karci T, Aycan H.6. Nitecki S, Anekstein Y, Karram T, Peer A, Bass A. Hypothenar hammer syndrome: apropos of six cases and review of the literature. Vascular. 2008; 16:279–82.
Article7. Lee YS, Song WS, Choi JC, et al. Ulna nerve compression caused by a tortuous ulnar artery. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2009; 14:250–4.8. Monacelli G, Rizzo MI, Spagnoli AM, Monarca C, Scuderi N. Ulnar artery thrombosis and nerve entrapment at Guyon’s canal: our diagnostic and therapeutic algorithm. In Vivo. 2010; 24:779–82.9. Chloros GD, Lucas RM, Li Z, Holden MB, Koman LA. Post-traumatic ulnar artery thrombosis: outcome of arterial reconstruction using reverse interpositional vein grafting at 2 years minimum follow-up. J Hand Surg Am. 2008; 33:932–40.
Article10. De Monaco D, Fritsche E, Rigoni G, Schlunke S, Von Wartburg U. Hypothenar hammer syndrome: retrospective study of nine cases. J Hand Surg Br. 1999; 24:731–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ulnar Nerve Compression in Guyon's Canal by Ganglion Cyst
- Ulnar Nerve Compression at Guyon's Canal by an Arteriovenous Malformation
- Ulnar Neuropathy Caused by a Schwannoma in the Guyon's Cannal
- Ulnar Artery Obstruction in Guyon Canal Compression Syndrome
- Compression Neuropathy of the Ulnar Nerve due to the Accessory Abductor Digiti Minimi at Guyon’s Canal: A Case Report