J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2016 May;59(3):322-324. 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.3.322.
Device for Catheter Placement of External Ventricular Drain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University School of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. hgbaeb@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2192116
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.3.322
Abstract
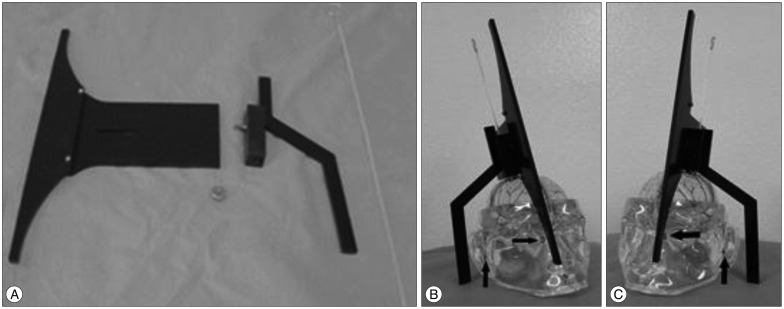
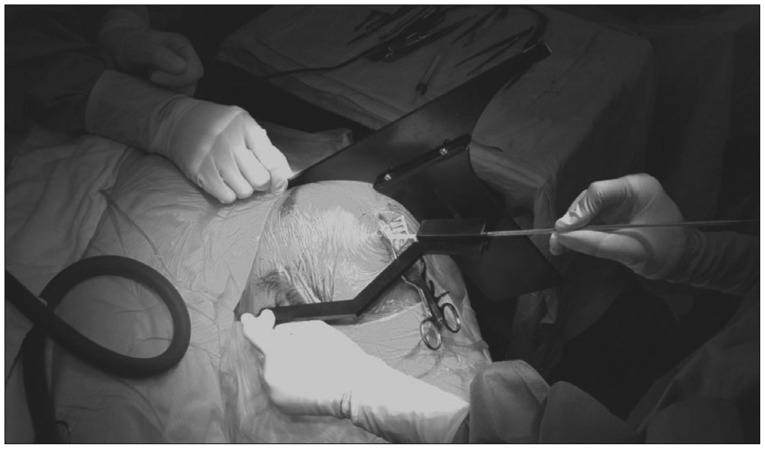
- To introduce a new device for catheter placement of an external ventricular drain (EVD) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This device was composed of three portions, T-shaped main body, rectangular pillar having a central hole to insert a catheter and an arm pointing the tragus. The main body has a role to direct a ventricular catheter toward the right or left inner canthus and has a shallow longitudinal opening to connect the rectangular pillar. The arm pointing the tragus is controlled by back and forth movement and turn of the pillar attached to the main body. Between April 2012 and December 2014, 57 emergency EVDs were performed in 52 patients using this device in the operating room. Catheter tip located in the frontal horn in 52 (91.2%), 3rd ventricle in 2 (3.5%) and in the wall of the frontal horn of the lateral ventricle in 3 EVDs (5.2%). Small hemorrhage along to catheter tract occurred in 1 EVD. CSF was well drained through the all EVD catheters. The accuracy of the catheter position and direction using this device were 91% and 100%, respectively. This device for EVD guides to provide an accurate position of catheter tip safely and easily.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Adjustable Ghajar Guide Technique for Accurate Placement of Ventricular Catheters: A Pilot Study
Sang-Youl Yoon, Youngseok Kwak, Jaechan Park
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017;60(5):604-609. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2016.1011.004.
Reference
-
1. Becker DP, Nulsen FE. Control of hydrocephalus by valve-regulated venous shunt : avoidance of complications in prolonged shunt maintenance. J Neurosurg. 1968; 28:215–226. PMID: 5300461.
Article2. Ghajar JB. A guide for ventricular catheter placement. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 1985; 63:985–986. PMID: 4056916.3. Hsieh CT, Chen GJ, Ma HI, Chang CF, Cheng CM, Su YH, et al. The misplacement of external ventricular drain by freehand method in emergent neurosurgery. Acta Neurol Belg. 2011; 111:22–28. PMID: 21510229.4. Huyette DR, Turnbow BJ, Kaufman C, Vaslow DF, Whiting BB, Oh MY. Accuracy of the freehand pass technique for ventriculostomy catheter placement : retrospective assessment using computed tomography scans. J Neurosurg. 2008; 108:88–91. PMID: 18173315.
Article5. Lee JH, Park CW, Lee U, Kim YB, Yoo CJ, Kim EY, et al. Accuracy of the free hand placement of an external ventricular drain (EVD). Korean J Cerebrovasc Surg. 2010; 12:82–86.6. O'Neill BR, Velez DA, Braxton EE, Whiting D, Oh MY. A survey of ventriculostomy and intracranial pressure monitor placement practices. Surg Neurol. 2008; 70:268–273. PMID: 18207539.7. Toma AK, Camp S, Watkins LD, Grieve J, Kitchen ND. External ventricular drain insertion accuracy : is there a need for change in practice? Neurosurgery. 2009; 65:1197–1200. PMID: 19934980.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple Intracranial Calcifications as a Complication of External Ventricular Drain Placement
- Treatment strategies of drain after complicated laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis
- Usefulness of an Additional Mattress Suture for the Extracranial Drainage Catheter
- Placement of an Implantable Port Catheter in the Biliary Stent: An Experimental Study in Dogs
- Ventriculostomy-Associated Infection : Analysis of Risk Factors and the Venue of External Ventricular Drainage