J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2016 May;59(3):319-321. 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.3.319.
Quadriplegia Following Epileptic Seizure : Things to Keep in Mind
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Meram Faculty of Medicine, Necmettin Erbakan University, Konya, Turkey. hhkozak@gmail.com
- 2Deparment of Neurology, Beyhekim State Hospital, Konya, Turkey.
- 3Deparment of Neurosurgery, Beyhekim State Hospital, Konya, Turkey.
- KMID: 2192115
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.3.319
Abstract
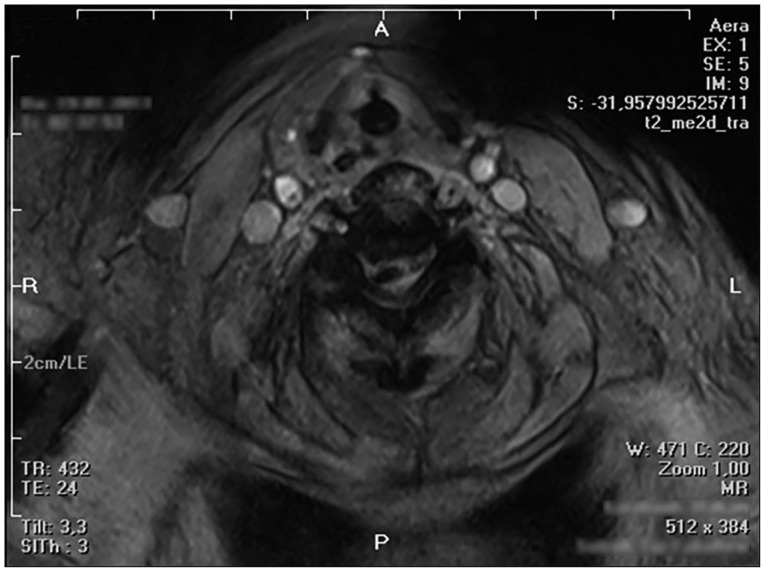
- People with epilepsy are believed to be at a higher risk of incurring accidental injury than people who do not have seizures. The incidence of injury, either due to seizure or accident as a consequent of seizure is also high and varies from 0.03% to 3%. The most common injuries are head contusions, lacerations, burns and fractures. In this article, we present a case of quadriplegia after a generalized epileptic seizure.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Davis DP, Hoyt DB, Ochs M, Fortlage D, Holbrook T, Marshall LK, et al. The effect of paramedic rapid sequence intubation on outcome in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. J Trauma. 2003; 54:444–453. PMID: 12634522.
Article2. Fitzpatrick LA. Pathophysiology of bone loss in patients receiving anticonvulsant therapy. Epilepsy Behav. 2004; 5(Suppl 2):S3–S15. PMID: 15123006.
Article3. Kirby S, Sadler RM. Injury and death as a result of seizures. Epilepsia. 1995; 36:25–28. PMID: 8001504.
Article4. Kumar SK, Freeman BJ. Quadriplegia following grand mal seizures. Injury. 1999; 30:626–629. PMID: 10707232.
Article5. Lhatoo SD, Johnson AL, Goodridge DM, MacDonald BK, Sander JW, Shorvon SD. Mortality in epilepsy in the first 11 to 14 years after diagnosis : multivariate analysis of a long-term, prospective, population-based cohort. Ann Neurol. 2001; 49:336–344. PMID: 11261508.
Article6. Mollaoğlu M, Bolayır E. Epilepsili hastalarda yaralanmalar ve ilişkili bazı faktörler. Nöropsikiyatri Arşivi. 2013; 50:269–273.7. Nakken KO, Lossius R. Seizure-related injuries in multihandicapped patients with therapy-resistant epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1993; 34:836–840. PMID: 8404734.
Article8. Nei M, Bagla R. Seizure-related injury and death. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2007; 7:335–341. PMID: 17618541.
Article9. Neufeld MY, Vishne T, Chistik V, Korczyn AD. Life-long history of injuries related to seizures. Epilepsy Res. 1999; 34:123–127. PMID: 10210026.
Article10. Parrish GA, Skiendzielewski JJ. Bilateral posterior fracture-dislocations of the shoulder after convulsive status epilepticus. Ann Emerg Med. 1985; 14:264–266. PMID: 3977152.
Article11. Pedersen KK, Christiansen C, Ahlgren P, Lund M. Incidence of fractures of the vertebral spine in epileptic patients. Acta Neurol Scand. 1976; 54:200–203. PMID: 821305.
Article12. Russell-Jones DL, Shorvon SD. The frequency and consequences of head injury in epileptic seizures. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989; 52:659–662. PMID: 2732739.
Article13. Souverein PC, Webb DJ, Weil JG, Van Staa TP, Egberts AC. Use of antiepileptic drugs and risk of fractures : case-control study among patients with epilepsy. Neurology. 2006; 66:1318–1324. PMID: 16682661.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Thoracocervicofacial Purpura Occurred After Epileptic Seizure
- Seizure Disorders Mimicking Epilepsy
- Epileptic Seizure Due to Disulfiram Treatment
- The Effect of Zonisamide in Epileptic Patients
- Relationship between Serum Levels of Homocysteine and Folate and Seizure Severity in Patients with Idiopathic Epilepsy