J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2016 May;59(3):287-291. 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.3.287.
The Prevalence of Undiagnosed Presurgical Cognitive Impairment and Its Postsurgical Clinical Impact in Older Patients Undergoing Lumbar Spine Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurological Surgery, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ybkim1218@gmail.com
- KMID: 2192108
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.3.287
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Because elderly patients are undergoing more surgeries, the importance of postoperative cognitive impairment (CI) evaluations is rising, especially for spine surgery, which is related to subjective pain. We investigated the prevalence of undiagnosed CI among elderly patients who underwent spine surgery and the impact of CI on postoperative outcomes.
METHODS
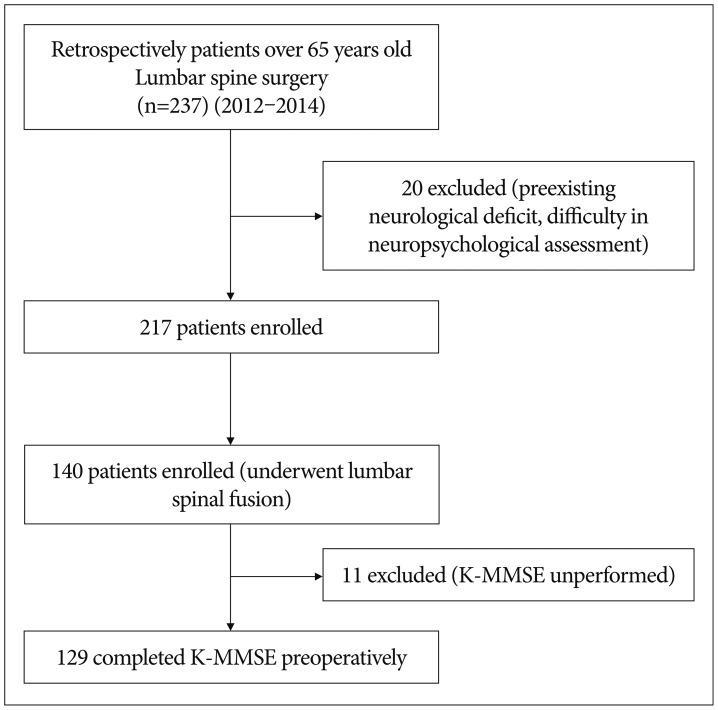
The preoperative cognitive statuses of 129 patients over 65 who underwent lumbar spine surgery from 2012 to 2014 were determined with the Mini-Mental State Examination, and patients with scores under 24 were diagnosed with CI. The patients were then divided into a CI group (n=49) and non-cognitive impairment (NCI) group (n=80).
RESULTS
Among the 129 patients, 49 (38.0%) were diagnosed with CI, and 9 (7.0%) had severe CI. The age of the CI group (72.88±6.20 years) was significantly greater than that of the NCI group (69.96±4.53 years). In contrast, the postoperative visual analog scale scores and performance statuses did not differ significantly. However, postoperative delirium was more frequent and the hospital stay length was longer in the CI group compared with the NCI group (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
A high prevalence of undiagnosed CI was discovered among elderly patients undergoing spine surgery. The existence of CI was associated with higher rates of postoperative delirium and prolonged hospital stays, which affected clinical outcomes. Thus, CI assessments should be included in preoperative evaluations of elderly patients prior to spine surgery.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Evered LA, Silbert BS, Scott DA, Maruff P, Ames D, Choong PF. Preexisting cognitive impairment and mild cognitive impairment in subjects presenting for total hip joint replacement. Anesthesiology. 2011; 114:1297–1304. PMID: 21502855.
Article2. Fick DM, Steis MR, Waller JL, Inouye SK. Delirium superimposed on dementia is associated with prolonged length of stay and poor outcomes in hospitalized older adults. J Hosp Med. 2013; 8:500–505. PMID: 23955965.
Article3. Fineberg SJ, Nandyala SV, Marquez-Lara A, Oglesby M, Patel AA, Singh K. Incidence and risk factors for postoperative delirium after lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:1790–1796. PMID: 23797502.
Article4. Han C, Jo SA, Jo I, Kim E, Park MH, Kang Y. An adaptation of the Korean mini-mental state examination (K-MMSE) in elderly Koreans : demographic influence and population-based norms (the AGE study). Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008; 47:302–310. PMID: 17936377.
Article5. Hogue CW Jr, Hershey T, Dixon D, Fucetola R, Nassief A, Freedland KE, et al. Preexisting cognitive impairment in women before cardiac surgery and its relationship with C-reactive protein concentrations. Anesth Analg. 2006; 102:1602–1608. PMID: 16717295.
Article6. Inouye SK. Predisposing and precipitating factors for delirium in hospitalized older patients. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 1999; 10:393–400. PMID: 10473946.
Article7. Inouye SK, Charpentier PA. Precipitating factors for delirium in hospitalized elderly persons. Predictive model and interrelationship with baseline vulnerability. JAMA. 1996; 275:852–857. PMID: 8596223.
Article8. Lee HB, Mears SC, Rosenberg PB, Leoutsakos JM, Gottschalk A, Sieber FE. Predisposing factors for postoperative delirium after hip fracture repair in individuals with and without dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011; 59:2306–2313. PMID: 22188077.
Article9. Moller JT, Cluitmans P, Rasmussen LS, Houx P, Rasmussen H, Canet J, et al. Long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly ISPOCD1 study. ISPOCD investigators. International Study of Post-Operative Cognitive Dysfunction. Lancet. 1998; 351:857–861. PMID: 9525362.
Article10. Monk TG, Weldon BC, Garvan CW, Dede DE, van der Aa MT, Heilman KM, et al. Predictors of cognitive dysfunction after major noncardiac surgery. Anesthesiology. 2008; 108:18–30. PMID: 18156878.
Article11. Partridge JS, Dhesi JK, Cross JD, Lo JW, Taylor PR, Bell R, et al. The prevalence and impact of undiagnosed cognitive impairment in older vascular surgical patients. J Vasc Surg. 2014; 60:1002–1011.e3. PMID: 25017513.
Article12. Seo JS, Park SW, Lee YS, Chung C, Kim YB. Risk factors for delirium after spine surgery in elderly patients. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014; 56:28–33. PMID: 25289122.
Article13. Shi Q, Warren L, Saposnik G, Macdermid JC. Confusion assessment method : a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2013; 9:1359–1370. PMID: 24092976.14. Silbert BS, Scott DA, Evered LA, Lewis MS, Maruff PT. Preexisting cognitive impairment in patients scheduled for elective coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Anesth Analg. 2007; 104:1023–1028. PMID: 17456647.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Visual and Hearing Impairment on Depression and Cognitive Function in Community-dwelling Elderly: The Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging 2008
- Depression and Cognitive Impairment in the Elderly
- Factors affecting postsurgical stability in skeletal Class III malocclusion patients
- Effects of Cognitive-based Interventions of Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Patterns of mental disorders among the elderly in a Korean rural community