J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Sep;58(3):294-297. 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.294.
Idiopathic Spinal Cord Herniation Presented as Brown-Sequard Syndrome: A Case Report and Surgical Outcome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. swchoi@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2191387
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.294
Abstract
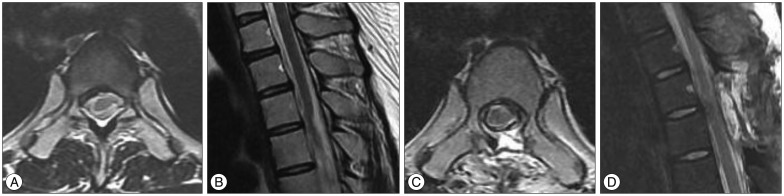
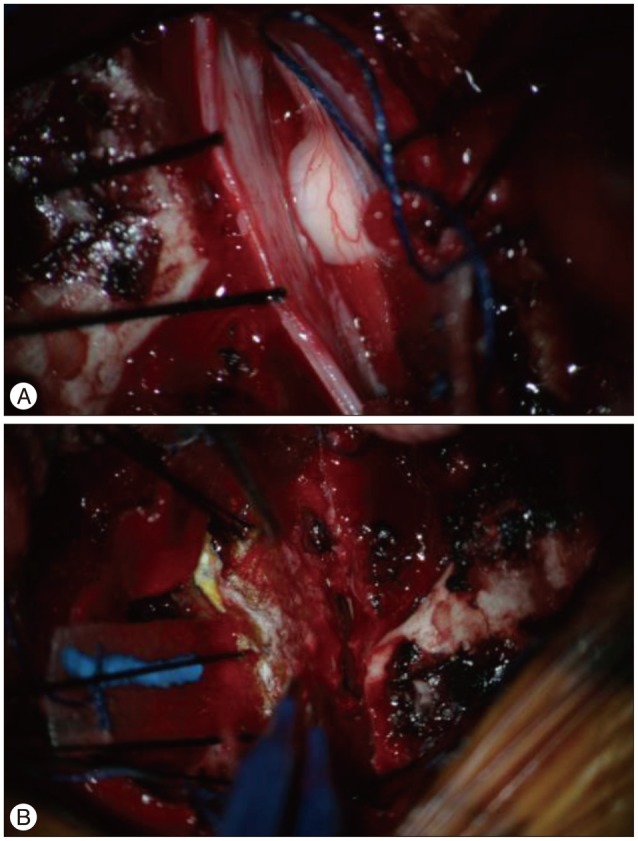
- Spinal cord herniation is a rare condition that has become increasingly recognised in the last few years. The authors report a case of idiopathic spinal cord herniation in a 33 year old woman performed with progressive Brown-Sequard syndrome. The diagnosis was made on MR imaging. After repairing the herniation, the patient made a gradual improvement. Potential causes are discussed, including a possible role of dural defect. In conclusion, idiopathic spinal cord herniation is a potentially treatable condition that should be more readily diagnosed that increasing awareness and improved imaging techniques.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abe M, Komori H, Yamaura I, Kayano T. Spinal cord herniation into an extensive extradural meningeal cyst : postoperative analysis of intracystic flow by phase-contrast cine MRI. J Orthop Sci. 1999; 4:450–456. PMID: 10664429.
Article2. Aizawa T, Sato T, Tanaka Y, Kotajima S, Sekiya M, Kokubun S. Idiopathic herniation of the thoracic spinal cord : report of three cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:E488–E491. PMID: 11598531.3. Barbagallo GM, Marshman LA, Hardwidge C, Gullan RW. Thoracic idiopathic spinal cord herniation at the vertebral body level : a subgroup with a poor prognosis? Case reports and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97(3 Suppl):369–374. PMID: 12408396.
Article4. Borges LF, Zervas NT, Lehrich JR. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : a treatable cause of the Brown-Sequard syndrome--case report. Neurosurgery. 1995; 36:1028–1032. discussion 1032-1033PMID: 7791969.5. Brugières P, Malapert D, Adle-Biassette H, Fuerxer F, Djindjian M, Gaston A. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation: value of MR phase-contrast imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:935–939. PMID: 10369369.6. Ellger T, Schul C, Heindel W, Evers S, Ringelstein EB. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation causing progressive Brown-Séquard syndrome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2006; 108:388–391. PMID: 16483712.
Article7. Ewald C, Kühne D, Hassler WE. Progressive spontaneous herniation of the thoracic spinal cord : case report. Neurosurgery. 2000; 46:493–495. discussion 495-496PMID: 10690741.8. Gandhi D, Goyal M, Bourque PR. Case 138 : Idiopathic spinal cord herniation. Radiology. 2008; 249:384–388. PMID: 18796690.9. Ghostine S, Baron EM, Perri B, Jacobson P, Morsette D, Hsu FP. Thoracic cord herniation through a dural defect : description of a case and review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 2009; 71:362–366. discussion 366-367PMID: 18207514.
Article10. Haber MD, Nguyen DD, Li S. Differentiation of idiopathic spinal cord herniation from CSF-isointense intraspinal extramedullary lesions displacing the cord. Radiographics. 2014; 34:313–329. PMID: 24617681.
Article11. Heo SH, Kim JH, Ahn TB, Kim EJ, Park KC, Yoon SS, et al. A case suggesting spontaneous spinal cord herniation presented as brown-sequard syndrome. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2007; 25:133–135.12. Isu T, Iizuka T, Iwasaki Y, Nagashima M, Akino M, Abe H. Spinal cord herniation associated with an intradural spinal arachnoid cyst diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery. 1991; 29:137–139. PMID: 1870677.
Article13. Iyer RV, Coutinho C, Lye RH. Spontaneous spinal cord herniation. Br J Neurosurg. 2002; 16:507–510. PMID: 12498498.
Article14. Jin SC, Lee SR, Park DW, Joo KB. Spontaneous herniation of the thoracic spinal cord : a case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2001; 45:353–355.
Article15. Joseph T, Adeosun A, Paes T, Bahal V. Randomised controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of TachoComb H patches in controlling PTFE suture-hole bleeding. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2004; 27:549–552. PMID: 15079782.
Article16. Kim JM, Oh SH, Kim KJ, Park SH, Park KS. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation as a treatable cause of progressive brown-sequard syndrome. J Clin Neurol. 2007; 3:204–207. PMID: 19513134.
Article17. Lang G, Csekeö A, Stamatis G, Lampl L, Hagman L, Marta GM, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical application of human fibrinogen/thrombin-coated collagen patch (TachoComb) for treatment of air leakage after standard lobectomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004; 25:160–166. PMID: 14747106.
Article18. Massicotte EM, Montanera W, Ross Fleming JF, Tucker WS, Willinsky R, TerBrugge K, et al. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : report of eight cases and review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:E233–E241. PMID: 11979181.19. Matsumura T, Takahashi MP, Nozaki S, Kang J. [A case of idiopathic spinal cord herniation]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1996; 36:566–570. PMID: 8810851.20. Miyaguchi M, Nakamura H, Shakudo M, Inoue Y, Yamano Y. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation associated with intervertebral disc extrusion : a case report and review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:1090–1094. PMID: 11337631.
Article21. Miyake S, Tamaki N, Nagashima T, Kurata H, Eguchi T, Kimura H. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation. Report of two cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1998; 88:331–335. PMID: 9452246.22. Mokri B. Spontaneous low cerebrospinal pressure/volume headaches. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2004; 4:117–124. PMID: 14984683.
Article23. Muto A, Nishibe T, Kondo Y, Sato M, Yamashita M, Ando M. Sutureless repair with TachoComb sheets for oozing type postinfarction cardiac rupture. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005; 79:2143–2145. PMID: 15919331.
Article24. Najjar MW, Baeesa SS, Lingawi SS. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : a new theory of pathogenesis. Surg Neurol. 2004; 62:161–170. discussion 170-171PMID: 15261515.25. Novak K, Widhalm G, de Camargo AB, Perin N, Jallo G, Knosp E, et al. The value of intraoperative motor evoked potential monitoring during surgical intervention for thoracic idiopathic spinal cord herniation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012; 16:114–126. PMID: 22117142.
Article26. Parmar H, Park P, Brahma B, Gandhi D. Imaging of idiopathic spinal cord herniation. Radiographics. 2008; 28:511–518. PMID: 18349454.
Article27. Sagiuchi T, Iida H, Tachibana S, Utsuki S, Tanaka R, Fujii K. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation associated with calcified thoracic disc extrusion--case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2003; 43:364–368. PMID: 12924599.
Article28. Salvador Álvarez E, Jiménez De La Peña M, Herraiz Hidalgo L, Pardo Moreno J. [Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : a rare condition]. Radiologia. 2010; 52:353–356. PMID: 20382404.29. Sasani M, Ozer AF, Vural M, Sarioglu AC. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : case report and review of the literature. J Spinal Cord Med. 2009; 32:86–94. PMID: 19264054.
Article30. Sioutos P, Arbit E, Tsairis P, Gargan R. Spontaneous thoracic spinal cord herniation. A case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:1710–1713. PMID: 8839477.31. Summers JC, Balasubramani YV, Chan PC, Rosenfeld JV. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : clinical review and report of three cases. Asian J Neurosurg. 2013; 8:97–105. PMID: 24049553.
Article32. Tekkök IH. Spontaneous spinal cord herniation : case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2000; 46:485–491. discussion 491-492PMID: 10690740.33. Urbach H, Kaden B, Pechstein U, Solymosi L. Herniation of the spinal cord 38 years after childhood trauma. Neuroradiology. 1996; 38:157–158. PMID: 8692429.
Article34. Wada E, Yonenobu K, Kang J. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation : report of three cases and review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:1984–1988. PMID: 10908944.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Idiopathic Spinal Cord Herniation as a Treatable Cause of Progressive Brown-Sequard Syndrome
- Idiopathic Spinal Cord Herniation at Thoracic Spine Level: A Case Report
- A Brown-Sequard Syndrome Resulting from a Ruptured Cervical Disc Herniation: A Case Report
- Brown Sequard Syndrome Resulting from Cervical Disc Herniation Treated by Anterior Foraminotomy
- Brown-Sequard Syndrome due to Herniated Cervical Disc