J Clin Neurol.
2007 Dec;3(4):204-207. 10.3988/jcn.2007.3.4.204.
Idiopathic Spinal Cord Herniation as a Treatable Cause of Progressive Brown-Sequard Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. pks1126@chol.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1808559
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2007.3.4.204
Abstract
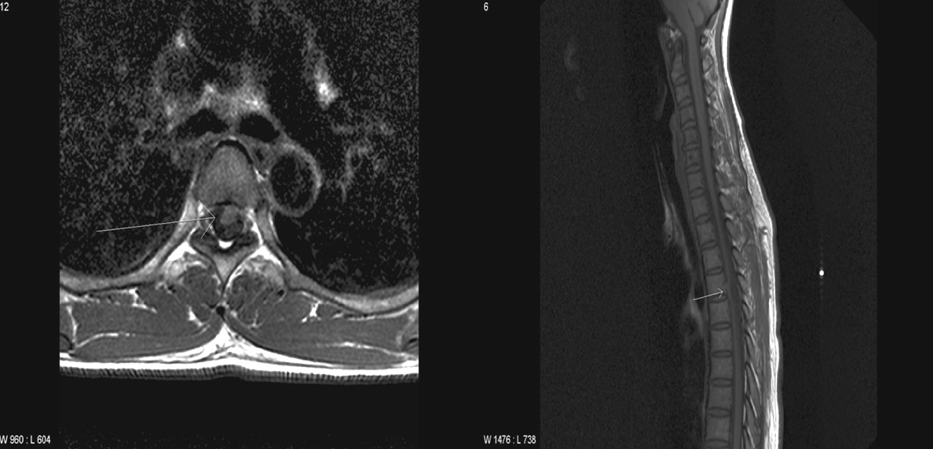
- Idiopathic spinal cord herniation is a rare spinal cord disorder caused by spinal cord prolapse through a adural defect. It is a curable disease, so early detection is of particular importance. We report a 38-year-old woman with Brown-Sequard syndrome which was caused by the thoracic spinal cord herniation. Her weakness was almost completely resolved after surgical management, which emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and surgical management in this rare disease entity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Idiopathic Spinal Cord Herniation Presented as Brown-Sequard Syndrome : A Case Report and Surgical Outcome
Min-Wook Ju, Seung-Won Choi, Jin-Young Youm, Hyon-Jo Kwon
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(3):294-297. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.294.
Reference
-
1. Massicotte EM, Montanera W, Ross Fleming JF, Tucker WS, Willinsky R, TerBrugge K, et al. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation: report of eight cases and review of the literature. Spine. 2002. 27:E233–E241.2. Wortzman G, Tasjer RR, Rewcastle NB, Richardson JC, Pearson FG. Spontaneous incarcerated herniation of the spinal cord into a vertebral body: a unique cause of paraplegia. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1974. 41:631–635.
Article3. Maira G, Denaro L, Doglietto F, Mangiola A, Colosimo C. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation: diagnostic, surgical, and follow-up data obtained in five cases. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006. 4:10–19.
Article4. Ellger T, Schul C, Heindel W, Evers S, Ringelstein EB. Idiopathic spinal cord herniation causing progressive Brown-Sequard syndrome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2006. 108:388–391.
Article5. Kim YJ, Kim YS, Kim JH, Joong HO, Ko YY, Oh SH, et al. Spontaneous thoracic spinal cord herniation. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2001. 30:1237–1240.6. Heo SH, Kim JH, Ahn TB, Kim EJ, Park KC, Yoon SS, et al. A case suggesting spontaneous spinal cord herniation presented as Brown-Sequard syndrome. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2007. 25:133–135.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Idiopathic Spinal Cord Herniation Presented as Brown-Sequard Syndrome: A Case Report and Surgical Outcome
- Idiopathic Spinal Cord Herniation at Thoracic Spine Level: A Case Report
- Brown Sequard Syndrome Resulting from Cervical Disc Herniation Treated by Anterior Foraminotomy
- A Brown-Sequard Syndrome Resulting from a Ruptured Cervical Disc Herniation: A Case Report
- Brown-Sequard Syndrome due to Herniated Cervical Disc