J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Sep;58(3):192-196. 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.192.
Angiographic and Clinical Factors Related with Good Functional Outcome after Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Cerebral Artery Occlusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. skparkns@gmail.com
- KMID: 2191358
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.192
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The aim of this study is to investigate good prognostic factors for an acute occlusion of a major cerebral artery using mechanical thrombectomy.
METHODS
Between January 2013 to December 2014, 37 consecutive patients with acute occlusion of a major cerebral artery treated by mechanical thrombectomy with stent retrievers were conducted. We analyzed clinical and angiographic factors retrospectively. The collateral flow and the result of recanalization were sorted by grading systems. Outcome was assessed by National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) and modified Rankin Scale (mRS) at 90 days. We compared the various parameters between good and poor angiographic and clinical results.
RESULTS
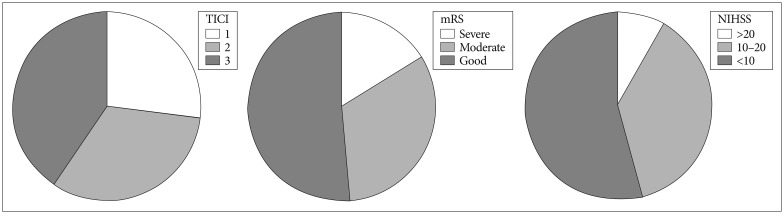
Twenty seven patients demonstrated good recanalization [Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction (TICI) 2b or 3] after thrombectomy. At the 90-day follow up, 19 patients had good (mRS, 0-2), 14 had moderate (3-4) and four had poor outcomes (5-6). The mRS of older patients (> or =75 years) were poor than younger patients. Early recanalization, high Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction risk score, and low baseline NIHSS were closely related to 90-day mRS, whereas high TICI was related to both mRS and the decrease in the NIHSS.
CONCLUSION
NIHSS decreased markedly only when recanalization was successful. A good mRS was related to low initial NIHSS, good collateral, and early successful recanalization.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Akins PT, Amar AP, Pakbaz RS, Fields JD. SWIFT Investigators. Complications of endovascular treatment for acute stroke in the SWIFT trial with solitaire and Merci devices. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014; 35:524–528. PMID: 24029392.
Article2. Alajbegovic A, Djelilovic-Vranic J, Nakicevic A, Todorovic L, Tiric-Campara M. Post stroke depression. Med Arch. 2014; 68:47–50. PMID: 24783913.
Article3. Bae GS, Kwon HJ, Kang CW, Choi SW, Kim SH, Koh HS. Mechanical thrombectomy using a solitaire stent in acute ischemic stroke; initial experience in 40 patients. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2012; 14:164–169. PMID: 23210042.
Article4. Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:11–20. PMID: 25517348.5. Broderick JP, Palesch YY, Demchuk AM, Yeatts SD, Khatri P, Hill MD, et al. Endovascular therapy after intravenous t-PA versus t-PA alone for stroke. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:893–903. PMID: 23390923.
Article6. Castonguay AC, Zaidat OO, Novakovic R, Nguyen TN, Taqi MA, Gupta R, et al. Influence of age on clinical and revascularization outcomes in the North American Solitaire Stent-Retriever Acute Stroke Registry. Stroke. 2014; 45:3631–3636. PMID: 25358699.
Article7. Ciccone A, Valvassori L, Nichelatti M, Sgoifo A, Ponzio M, Sterzi R, et al. Endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:904–913. PMID: 23387822.
Article8. Danière F, Lobotesis K, Machi P, Eker O, Mourand I, Riquelme C, et al. Patient selection for stroke endovascular therapy--DWI-ASPECTS thresholds should vary among age groups : insights from the RECOST study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015; 36:32–39. PMID: 25273535.9. de Weerd L, Luijckx GJ, Groenier KH, van der Meer K. Quality of life of elderly ischaemic stroke patients one year after thrombolytic therapy. A comparison between patients with and without thrombolytic therapy. BMC Neurol. 2012; 12:61. PMID: 22835054.
Article10. Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:1019–1030. PMID: 25671798.
Article11. Guo RY, Su L, Liu LA, Wang CX. [Effects of Linggui Bafa on the therapeutic effect and quality of life in patients of post-stroke depression]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2009; 29:785–790. PMID: 19873912.12. Higashida RT, Furlan AJ, Roberts H, Tomsick T, Connors B, Barr J, et al. Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2003; 34:e109–e137. PMID: 12869717.
Article13. Kidwell CS, Jahan R, Gornbein J, Alger JR, Nenov V, Ajani Z, et al. A trial of imaging selection and endovascular treatment for ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:914–923. PMID: 23394476.
Article14. Kim TK, Rhim JK, Lee CJ, Oh SH, Chung BS. The Limitations of thrombectomy with Solitaire™ AB as first-line treatment in acute ischemic stroke : a single center experience. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2012; 14:203–209. PMID: 23210048.
Article15. Kurre W, Aguilar-Pérez M, Niehaus L, Fischer S, Schmid E, Bäzner H, et al. Predictors of outcome after mechanical thrombectomy for anterior circulation large vessel occlusion in patients aged ≥80 years. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013; 36:430–436. PMID: 24281266.
Article16. Lansberg MG, Bluhmki E, Thijs VN. Efficacy and safety of tissue plasminogen activator 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke : a metaanalysis. Stroke. 2009; 40:2438–2441. PMID: 19478213.
Article17. Molina CA, Chamorro A, Rovira À, de Miquel A, Serena J, Roman LS, et al. REVASCAT : a randomized trial of revascularization with SOLITAIRE FR device vs. best medical therapy in the treatment of acute stroke due to anterior circulation large vessel occlusion presenting within eight-hours of symptom onset. Int J Stroke. 2015; 10:619–626. PMID: 24206399.
Article18. Raoult H, Eugène F, Ferré JC, Gentric JC, Ronzière T, Stamm A, et al. Prognostic factors for outcomes after mechanical thrombectomy with solitaire stent. J Neuroradiol. 2013; 40:252–259. PMID: 23684343.
Article19. Röther J, Ford GA, Thijs VN. Thrombolytics in acute ischaemic stroke : historical perspective and future opportunities. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013; 35:313–319. PMID: 23615379.
Article20. Saake M, Breuer L, Gölitz P, Köhrmann M, Schwab S, Dörfler A, et al. Clinical/perfusion CT CBV mismatch as prognostic factor in intraarterial thrombectomy in acute anterior circulation stroke. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2014; 121:39–45. PMID: 24793473.
Article21. Seifert M, Ahlbrecht A, Dohmen C, Spuentrup E, Moeller-Hartmann W. Combined interventional stroke therapy using intracranial stent and local intraarterial thrombolysis (LIT). Neuroradiology. 2011; 53:273–282. PMID: 20556600.
Article22. Shindo A, Kawanishi M, Kawakita K, Okauchi M, Kawai N, Hayashi N, et al. Treatment of acute cerebral artery occlusion using the penumbra system : our early experience. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014; 54:441–449. PMID: 24759097.
Article23. Sugg RM, Noser EA, Shaltoni HM, Gonzales NR, Campbell MS, Weir R, et al. Intra-arterial reteplase compared to urokinase for thrombolytic recanalization in acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:769–773. PMID: 16611762.24. Taussky P, Tawk RG, Daugherty WP, Hanel RA. Medical therapy for ischemic stroke : review of intravenous and intra-arterial treatment options. World Neurosurg. 2011; 76(6 Suppl):S9–S15. PMID: 22182278.25. von Sarnowski B, Kleist-Welch Guerra W, Kohlmann T, Moock J, Khaw AV, Kessler C, et al. Long-term health-related quality of life after decompressive hemicraniectomy in stroke patients with life-threatening space-occupying brain edema. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012; 114:627–633. PMID: 22236827.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical and radiological outcomes of mechanical thrombectomy in simultaneous anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery occlusion
- Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke with occlusion of the M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery: A literature review
- Critical Use of Balloon Angioplasty after Recanalization Failure with Retrievable Stent in Acute Cerebral Artery Occlusion
- Delayed Development of Symptomatic Arterial Stenosis after a Mechanical Thrombectomy for an Acute Embolic Occlusion of the Middle Cerebral Artery
- The Limitations of Thrombectomy with Solitaire(TM) AB as First-line Treatment in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Single Center Experience