J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Feb;57(2):94-99. 10.3340/jkns.2015.57.2.94.
Association of Carotid Intraplaque Hemorrhage and Territorial Acute Infarction in Patients with Acute Neurological Symptoms Using Carotid Magnetization-Prepared Rapid Acquisition with Gradient-Echo
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chonbuk National University Medical School and Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Chonbuk National University Medical School and Hospital, Jeonju, Korea. kwak8140@jbnu.ac.kr
- 3Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2191189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.57.2.94
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
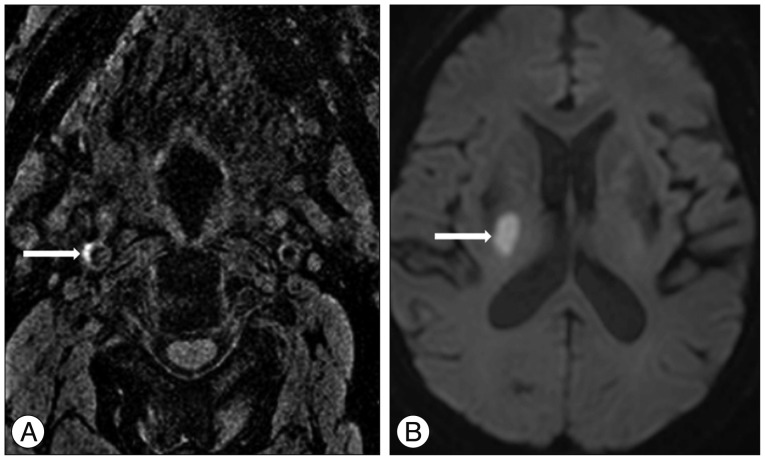
The purpose of our study was to assess prevalence of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage (IPH) and associations between territorial acute infarction and IPH on magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition with gradient-echo (MPRAGE) in patients with acute neurologic symptoms.
METHODS
83 patients with suspected acute neurologic symptoms were evaluated with both brain diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and carotid MPRAGE sequences. Carotid plaque with high signal intensity on MPRAGE of >200% that of adjacent muscle was categorized as IPH. We analyzed the prevalence of IPH and its correlation with territorial acute infarction.
RESULTS
Of 166 arteries, 39 had a carotid artery plaque. Of these arteries, 26 had carotid artery stenosis less than 50%. In all carotid arteries, MR-depicted IPH was found in 7.2% (12/166). High-signal intensity on DWI was found in 17.5% (29/166). Combined lesion with ipsilateral high-signal intensity on DWI and IPH on carotid MPRAGE sequence was found in 6 lesions (6/166, 3.6%). Of patients with carotid artery plaque, MR-predicted IPH was found in 30.8% (12/39) and match lesions with high-signal intensity on DWI and MPRAGE was found in 15.4% (6/39). MR-predicted IPH was significantly higher prevalence in high-grade stenosis group (p=0.010). Relative risk between carotid MPRAGE-positive signal and ipsilateral high-signal intensity on DWI in arteries with carotid artery plaques was 6.8 (p=0.010).
CONCLUSION
Carotid MPRAGE-positive signal in patients was associated with an increased risk of territorial acute infarction as detected objectively by brain DWI. The relative risk of stroke was increased in high-grade stenosis categories.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Carotid Intraplaque Hemorrhage Imaging: Diagnostic Value of High Signal Intensity Time-of-Flight MR Angiography Compared with Magnetization-Prepared Rapid Acquisition with Gradient-Echo Sequencing
Ji-eun Ahn, Hyo Sung Kwak, Gyung Ho Chung, Seung Bae Hwang
Investig Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;22(2):94-101. doi: 10.13104/imri.2018.22.2.94.
Reference
-
1. Bitar R, Moody AR, Leung G, Symons S, Crisp S, Butany J, et al. In vivo 3D high-spatial-resolution MR imaging of intraplaque hemorrhage. Radiology. 2008; 249:259–267. PMID: 18796681.
Article2. de Sauvage Nolting PR, de Groot E, Zwinderman AH, Buirma RJ, Trip MD, Kastelein JJ. Regression of carotid and femoral artery intima-media thickness in familial hypercholesterolemia : treatment with simvastatin. Arch Intern Med. 2003; 163:1837–1841. PMID: 12912721.
Article3. Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, Bruno A, Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke : a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2013; 44:870–947. PMID: 23370205.
Article4. Kolodgie FD, Gold HK, Burke AP, Fowler DR, Kruth HS, Weber DK, et al. Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary atheroma. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:2316–2325. PMID: 14668457.
Article5. Lindsay AC, Biasiolli L, Lee JM, Kylintireas I, MacIntosh BJ, Watt H, et al. Plaque features associated with increased cerebral infarction after minor stroke and TIA : a prospective, case-control, 3-T carotid artery MR imaging study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012; 5:388–396. PMID: 22498328.
Article6. Lovett JK, Coull AJ, Rothwell PM. Early risk of recurrence by subtype of ischemic stroke in population-based incidence studies. Neurology. 2004; 62:569–573. PMID: 14981172.
Article7. McNally JS, Kim SE, Yoon HC, Findeiss LK, Roberts JA, Nightingale DR, et al. Carotid magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition with gradient-echo signal is associated with acute territorial cerebral ischemic events detected by diffusion-weighted MRI. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012; 5:376–382. PMID: 22495769.
Article8. Mercuri M, Bond MG, Sirtori CR, Veglia F, Crepaldi G, Feruglio FS, et al. Pravastatin reduces carotid intima-media thickness progression in an asymptomatic hypercholesterolemic mediterranean population : the Carotid Atherosclerosis Italian Ultrasound Study. Am J Med. 1996; 101:627–634. PMID: 9003110.
Article9. Ota H, Yarnykh VL, Ferguson MS, Underhill HR, Demarco JK, Zhu DC, et al. Carotid intraplaque hemorrhage imaging at 3.0-T MR imaging : comparison of the diagnostic performance of three T1-weighted sequences. Radiology. 2010; 254:551–563. PMID: 20093526.
Article10. Parmar JP, Rogers WJ, Mugler JP 3rd, Baskurt E, Altes TA, Nandalur KR, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of carotid atherosclerotic plaque in clinically suspected acute transient ischemic attack and acute ischemic stroke. Circulation. 2010; 122:2031–2038. PMID: 21041694.
Article11. The Long-Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischaemic Disease (LIPID) Study Group. Prevention of cardiovascular events and death with pravastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and a broad range of initial cholesterol levels. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:1349–1357. PMID: 9841303.12. Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease : the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet. 1994; 344:1383–1389. PMID: 7968073.13. Rosamond W, Flegal K, Friday G, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2007 update : a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007; 115:e69–e171. PMID: 17194875.14. Saam T, Cai J, Ma L, Cai YQ, Ferguson MS, Polissar NL, et al. Comparison of symptomatic and asymptomatic atherosclerotic carotid plaque features with in vivo MR imaging. Radiology. 2006; 240:464–472. PMID: 16864672.
Article15. Saam T, Hetterich H, Hoffmann V, Yuan C, Dichgans M, Poppert H, et al. Meta-analysis and systematic review of the predictive value of carotid plaque hemorrhage on cerebrovascular events by magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 62:1081–1091. PMID: 23850912.
Article16. Sitzer M, Müller W, Siebler M, Hort W, Kniemeyer HW, Jäncke L, et al. Plaque ulceration and lumen thrombus are the main sources of cerebral microemboli in high-grade internal carotid artery stenosis. Stroke. 1995; 26:1231–1233. PMID: 7604420.
Article17. Smilde TJ, van Wissen S, Wollersheim H, Trip MD, Kastelein JJ, Stalenhoef AF. Effect of aggressive versus conventional lipid lowering on atherosclerosis progression in familial hypercholesterolaemia (ASAP) : a prospective, randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet. 2001; 357:577–581. PMID: 11558482.
Article18. Spagnoli LG, Mauriello A, Sangiorgi G, Fratoni S, Bonanno E, Schwartz RS, et al. Extracranial thrombotically active carotid plaque as a risk factor for ischemic stroke. JAMA. 2004; 292:1845–1852. PMID: 15494582.
Article19. Sun J, Balu N, Hippe DS, Xue Y, Dong L, Zhao X, et al. Subclinical carotid atherosclerosis : short-term natural history of lipid-rich necrotic core--a multicenter study with MR imaging. Radiology. 2013; 268:61–68. PMID: 23513240.
Article20. Sun J, Underhill HR, Hippe DS, Xue Y, Yuan C, Hatsukami TS. Sustained acceleration in carotid atherosclerotic plaque progression with intraplaque hemorrhage : a long-term time course study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012; 5:798–804. PMID: 22897993.
Article21. Takaya N, Yuan C, Chu B, Saam T, Polissar NL, Jarvik GP, et al. Presence of intraplaque hemorrhage stimulates progression of carotid atherosclerotic plaques : a high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. Circulation. 2005; 111:2768–2775. PMID: 15911695.
Article22. Takaya N, Yuan C, Chu B, Saam T, Underhill H, Cai J, et al. Association between carotid plaque characteristics and subsequent ischemic cerebrovascular events : a prospective assessment with MRI--initial results. Stroke. 2006; 37:818–823. PMID: 16469957.
Article23. Turc G, Oppenheim C, Naggara O, Eker OF, Calvet D, Lacour JC, et al. Relationships between recent intraplaque hemorrhage and stroke risk factors in patients with carotid stenosis : the HIRISC study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012; 32:492–499. PMID: 22075251.
Article24. Yamada K, Song Y, Hippe DS, Sun J, Dong L, Xu D, et al. Quantitative evaluation of high intensity signal on MIP images of carotid atherosclerotic plaques from routine TOF-MRA reveals elevated volumes of intraplaque hemorrhage and lipid rich necrotic core. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2012; 14:81. PMID: 23194180.
Article25. Yim YJ, Choe YH, Ko Y, Kim ST, Kim KH, Jeon P, et al. High signal intensity halo around the carotid artery on maximum intensity projection images of time-of-flight MR angiography : a new sign for intraplaque hemorrhage. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008; 27:1341–1346. PMID: 18504753.
Article26. Yoshimura S, Yamada K, Kawasaki M, Asano T, Kanematsu M, Takamatsu M, et al. High-intensity signal on time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography indicates carotid plaques at high risk for cerebral embolism during stenting. Stroke. 2011; 42:3132–3137. PMID: 21868725.
Article27. Yuan C, Mitsumori LM, Ferguson MS, Polissar NL, Echelard D, Ortiz G, et al. In vivo accuracy of multispectral magnetic resonance imaging for identifying lipid-rich necrotic cores and intraplaque hemorrhage in advanced human carotid plaques. Circulation. 2001; 104:2051–2056. PMID: 11673345.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Carotid Intraplaque Hemorrhage Imaging: Diagnostic Value of High Signal Intensity Time-of-Flight MR Angiography Compared with Magnetization-Prepared Rapid Acquisition with Gradient-Echo Sequencing
- Carotid Intraplaque Hemorrhage is Associated with Acute Cerebral Ischemic Events and Progression of Stenosis on Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Lethal Outcome due to Misdiagnosis between Acute Cerebral Infarction and Epidural Hematoma Expansion after Blunt Trauma: A Case Report
- A Unique Ultrasonographic Finding of Carotid Thrombus in a Patient with Acute Cardiogenic Cerebral Infarction
- Spontaneous Cerebral Microbleeds on Gradient Echo MR Imaging in the Stroke Patients